Researchers and clinicians have been working to use focused ultrasound combined with microbubbles to open the blood-brain barrier (BBB) for both noninvasive diagnostic use as well as to deliver treatments to the brain for tumors and neurodegenerative diseases. However, the few existing devices for preclinical research are expensive, bulky and lack the precision needed for small animal research.
Credit: WashU/Chen Lab
Researchers and clinicians have been working to use focused ultrasound combined with microbubbles to open the blood-brain barrier (BBB) for both noninvasive diagnostic use as well as to deliver treatments to the brain for tumors and neurodegenerative diseases. However, the few existing devices for preclinical research are expensive, bulky and lack the precision needed for small animal research.
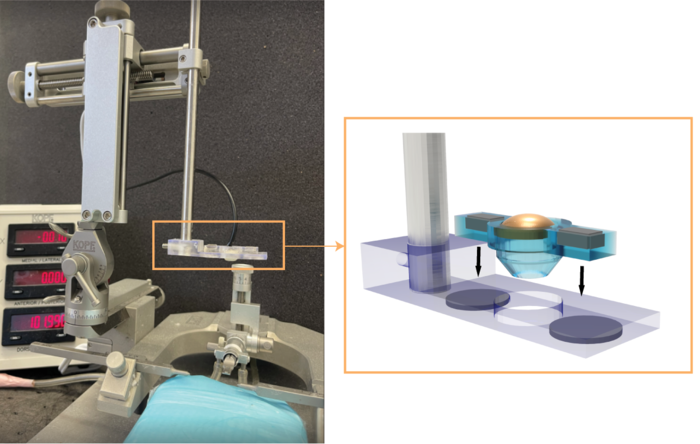
Hong Chen, associate professor of biomedical engineering at the McKelvey School of Engineering and of radiation oncology at the School of Medicine at Washington University in St. Louis, and her team have developed a low-cost, easy-to-use and highly precise focused ultrasound (FUS) device that can be used on small animal models in preclinical research.
The FUS transducer, created in-house using a 3D printer, costs about $80 to fabricate. It can be integrated with a commercially available stereotactic frame to precisely target a mouse brain. Results of the work were published online in IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering Feb. 15
The device had several benefits, Chen said, including achieving sub-millimeter targeting accuracy and having a tunable drug-delivery outcome. In addition, using higher frequency FUS transducers decreased the BBB opening volume and improved the precision of FUS-BBB opening in targeting individual structures in the mouse brain.
“We showed that under the same pressure level, a higher-frequency FUS transducer achieved a small drug delivery volume, improving the spatial precision of BBB opening compared with what has been achieved with lower-frequency transducers,” Chen said.
To create the transducer, the team only needed to connect wires to the electrodes on the elements. The rest of the parts were made on a 3D printer. With the use of a stereotactic frame, her team was able to target the exact location they wanted in the brain, which eliminated one of the barriers to more widespread use of the FUS technique. Chen’s team has made the design available on Github.
“We expect this device could be manufactured by research groups without ultrasound background and used in various applications in preclinical research with minimal training needed,” Chen said.
The team used contrast-enhanced MRI to measure the BBB opening volume at different acoustic pressures and evaluated the drug delivery outcome using a model drug. The device was shown to be very safe, with a microhemorrhage found in two mice at the highest tested acoustic pressures and no tissue damage found in other groups.
Focused ultrasound uses ultrasonic energy to target tumors or tissue in the brain. Once located, the researchers inject microbubbles into the blood that travel to the targeted tissue then pop, causing small tears of the blood-brain barrier. The ruptures allow drugs to be delivered or biomarkers from a tumor to pass through the blood-brain barrier and release into the blood. Chen and her lab have been perfecting the technique in preclinical models for the past several years.
Chen said she hopes this device can reduce the barriers to the adoption of the FUS technique by the broad research community.
Journal
IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering
DOI
10.1109/TBME.2022.3150781
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
An affordable and easy-to-use focused ultrasound device for noninvasive and high precision drug delivery to the mouse brain
Article Publication Date
15-Feb-2022




