LA JOLLA, CA—A team of scientists from Scripps Research has conducted promising early tests of a new strategy that might one day be used to prevent or treat type 2 diabetes.
Credit: Scripps Research
LA JOLLA, CA—A team of scientists from Scripps Research has conducted promising early tests of a new strategy that might one day be used to prevent or treat type 2 diabetes.
The scientists, whose results are reported in Nature Communications, tested an experimental compound called IXA4 in obese mice. They showed that the compound activates a natural signaling pathway that protects the animals from harmful, obesity-driven metabolic changes that would normally lead to diabetes.
“We were able to activate this pathway in both the liver and the pancreas with this one compound, and that added up to a significant overall improvement in metabolic health of obese animals,” says Scripps Research’s Luke Wiseman, PhD.
“This is the first time anyone has shown that a small molecule activating this pathway in this manner works to treat disease in a live animal,” adds Enrique Saez, PhD.
The study was a collaboration between the laboratories of Saez and Wiseman, who are both professors in the Department of Molecular Medicine at Scripps Research and co-senior authors on the new paper.
Type 2 diabetes remains a major public health problem: about 30 million people are estimated to have it in the U.S. alone. Driven largely by overweight and obesity, it features the loss of normal blood sugar regulation, and brings a multitude of health issues including higher risks of heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, retinal degeneration, and some cancers. There are many drugs for treating type 2 diabetes, but none that works well for every patient.
For several years, Wiseman’s lab has been studying a signaling pathway involving two proteins called IRE1 and XBP1s. When activated by a certain type of cellular stress, IRE1 activates XBP1s, which in turn alters the activity of a host of genes, including many metabolic genes, in an effort to reduce the cellular stress. Prior studies suggest that the activity of this pathway, at least in the short-term, can protect liver and fat cells from stresses caused by obesity—stresses that can harm these cells in ways that promote diabetes.
The IRE1/XBP1s pathway is not a straightforward diabetes drug target, however. Past research has shown that keeping IRE1/XBP1 switched on chronically ends up harming cells, triggering inflammation and worsening overall metabolic dysfunction.
“IRE1/XBP1s signaling is a response to cellular stress, and keeping it on all the time essentially tells the cell that the stress can’t be resolved—so the cell in effect kills itself,” Wiseman says.
In the new study, the researchers showed that a compound they identified a few years ago, IXA4, activates IRE1/XBP1s for just a few hours at a time. Because it otherwise allows IRE1 to turn off, it can in principle be given daily without triggering the deleterious signaling seen with constant IRE1 activation, making it a promising candidate to explore for human treatments.
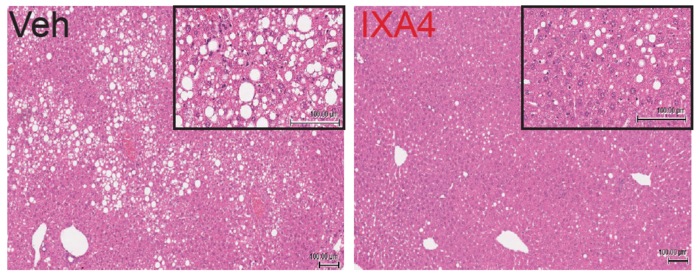
The team used IXA4 to treat mice that were obese from a high-fat, high-calorie diet. After just eight weeks, the treated mice had improved glucose metabolism and insulin activity, less fat buildup and inflammation in the liver, and no loss of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, compared to untreated obese mice.
IXA4 can reach only a limited set of tissues including the liver and pancreas, and so the team is now developing other compounds that can get into a broader set of cells including fat cells.
“We’re also continuing to work with IXA4 as a potential treatment for other metabolic disorders such as fatty liver disease,” Saez says.
The study’s first authors were Aparajita Madhavan, PhD, then a graduate student in the Wiseman lab, and Bernard Kok, PhD, a postdoctoral research associate in the Saez lab.
IXA4 was developed in collaboration with the laboratory of Jeffery Kelly, PhD, Lita Annenberg Hazen Professor of Chemistry at Scripps Research.
“Pharmacologic IRE1/XBP1s Activation Promotes Systemic Adaptive Remodeling in Obesity” was co-authored by Aparajita Madhavan, Bernard Kok, Bibiana Rius, Julia Grandjean, Adekunle Alabi, Verena Albert, Ara Sukiasyan, Evan Powers, Andrea Galmozzi, Enrique Saez, and Luke Wiseman, all of Scripps Research at the time of the study.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health (AG046495, DK123038, DK114785).
About Scripps Research
Scripps Research is an independent, nonprofit biomedical institute ranked the most influential in the world for its impact on innovation by Nature Index. We are advancing human health through profound discoveries that address pressing medical concerns around the globe. Our drug discovery and development division, Calibr, works hand-in-hand with scientists across disciplines to bring new medicines to patients as quickly and efficiently as possible, while teams at Scripps Research Translational Institute harness genomics, digital medicine and cutting-edge informatics to understand individual health and render more effective healthcare. Scripps Research also trains the next generation of leading scientists at our Skaggs Graduate School, consistently named among the top 10 US programs for chemistry and biological sciences. Learn more at www.scripps.edu.
Journal
Nature Communications




