Credit: SysBio
The Engine for Likelihood-Free Inference is open to everyone, and it can help significantly reduce the number of simulator runs.
Researchers have succeeded in building an engine for likelihood-free inference, which can be used to model reality as accurately as possible in a simulator. The engine may revolutionise the many fields in which computational simulation is utilised. This development work is resulting in the creation of ELFI, an engine for likelihood-free inference, which will significantly reduce the number of exhausting simulation runs necessary for the estimation of unknown parameters and to which it will be easy to add new inference methods.
'Computational research is based in large part on simulation, and fitting simulator parameters to data is of key importance, in order for the simulator to describe reality as accurately as possible. The ELFI inference software we have developed makes this previously extremely difficult task as easy as possible: software developers can spread their new inference methods to widespread use, with minimal effort, and researchers from other fields can utilise the newest and most effective methods. Open software advances replicability and open science,' says Samuel Kaski, professor at the Department of Computer Sciences and head of the Finnish Centre of Excellence in Computational Inference Research (COIN).
Software that is openly available to everyone is based on likelihood-free Bayesian inference, which is regarded as one of the most important innovations in statistics in the past decades. The simulator's output is compared to actual observations, and due to their random -nature simulation runs must be carried out multiple times. The inference software will improve estimation of unknown parameters with e.g. Bayesian optimisation, which will significantly reduce the number of necessary simulation runs.
Applications from medicine to environmental science
ELFI users will likely be researchers from fields in which traditionally used statistical methods cannot be applied.
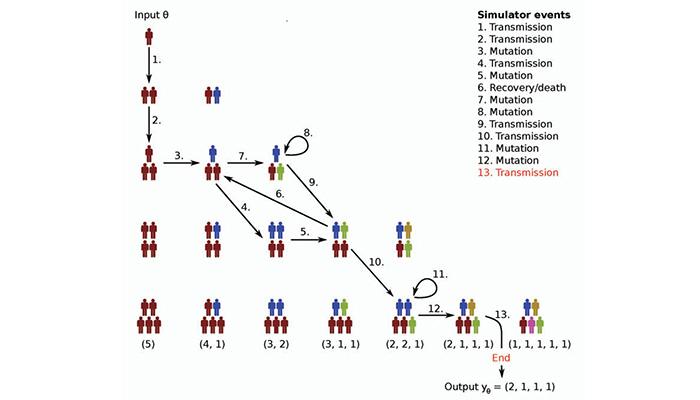
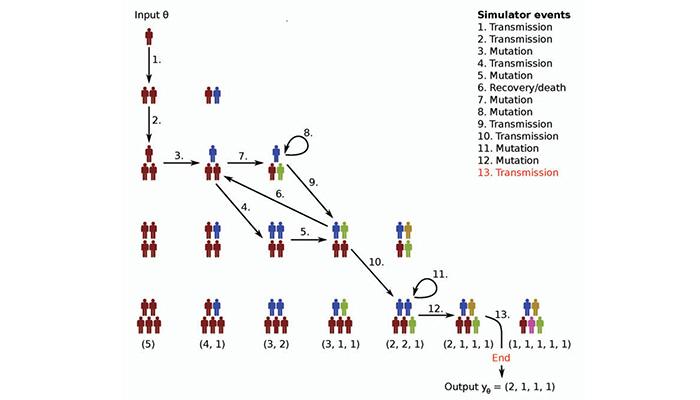
'Simulators can be applied in many fields. For example, a simulation of a disease can take into account how the disease is transmitted to another person, how long it will take for a person to recuperate or not recuperate, how a virus mutates or how many unique virus mutations exist. A number of simulation runs will therefore produce a realistic distribution describing the actual situation,' Professor Aki Vehtari explains.
The ELFI inference engine is easy to use and scalable, and the inference problem can be easily defined with a graphical model.
'Environmental sciences and applied ecology utilise simulators to study the impact of human activities on the environment. For example, the Finnish Environment Institute (SYKE) is developing an ecosystem model, which will be used for the research of nutrient cycles in the Archipelago Sea and e.g. the impacts of loading caused by agriculture and fisheries to algal blooming. The parametrisation of these models and the assessment of the uncertainties related to their predictions is challenging from a computational standpoint. We will test the ELFI inference engine in these analyses. We hope that parametrisation of the models can be sped up and improved with ELFI, meaning that conclusions are better reasoned,' says Assistant Professor Jarno Vanhatalo about environmental statistics research at the University of Helsinki.
###
ELFI was developed by Antti Kangasrääsiö, Jarno Lintusaari, Kusti Skytén, Marko Järvenpää, Henri Vuollekoski, Aki Vehtari and Samuel Kaski of Aalto University, at the Helsinki Institute for Information Technology (HIIT) and the Finnish Centre of Excellence in Computational Inference Research (COIN), which are jointly run by Aalto University and the University of Helsinki; Michael Gutmann from the University of Edinburgh; and Jukka Corander, who represents both the Department of Mathematics and Statistics at the University of Helsinki and the University of Oslo. The Academy of Finland is funding the research project. ELFI can be found online at http://elfi.readthedocs.io
Media Contact
Aki Vehtari
[email protected]
358-405-333-747
@aaltouniversity
http://www.aalto.fi/en/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag