Over the last 100 years, many fossilized dinosaur eggs and nests have been found, but finding one with a well-preserved embryo inside is exceedingly rare. Now, researchers reporting in the journal iScience on December 21 have detailed one such specimen discovered in southern China.
Credit: Lida Xing
Over the last 100 years, many fossilized dinosaur eggs and nests have been found, but finding one with a well-preserved embryo inside is exceedingly rare. Now, researchers reporting in the journal iScience on December 21 have detailed one such specimen discovered in southern China.
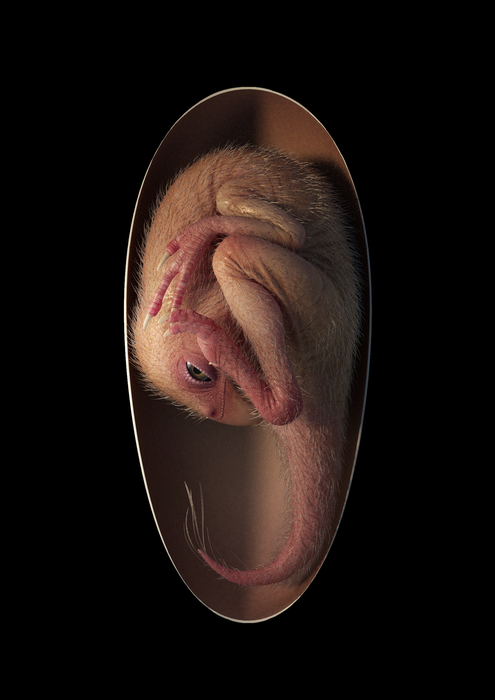
What’s more, their studies lead them to suggest that oviraptorosaurs (a group of therapods closely related to birds) took on a distinctive tucking posture before they hatched, a behavior that had been considered unique to birds. It raises the possibility that tucking behavior may have evolved first among non-avian theropods during the Cretaceous, the researchers say.
“Most known non-avian dinosaur embryos are incomplete with skeletons disarticulated,” said Waisum Ma (@FionMaWS) of the University of Birmingham, U.K. “We were surprised to see this embryo beautifully preserved inside a dinosaur egg, lying in a bird-like posture. This posture had not been recognized in non-avian dinosaurs before.”
The fossilized dinosaur embryo comes from Ganzhou, Jiangxi Province, southern China.
It had been acquired in 2000 by Liang Liu, director of a company called Yingliang Group, who suspected it might contain egg fossils. But it then ended up in storage, largely forgotten until about ten years later, when museum staff during the construction of Yingliang Stone Nature History Museum sorted through the boxes and unearthed the fossils.
“Museum staff identified them as dinosaur eggs and saw some bones on the broken cross section of one of the eggs,” Lida Xing of China University of Geosciences, Beijing, said. The fossils were then prepared, unveiling the embryo hidden within, which they named “Baby Yingliang.”
In the new study, Xing and colleagues report that the head lies ventral to the body, with the feet on either side, and the back curled along the blunt pole of the egg, in a posture previously unrecognized in a non-avian dinosaur. That’s especially notable because it’s reminiscent of a late-stage modern bird embryo.
Comparison of the specimen to other late-stage oviraptorosaur embryos suggests that before hatching, oviraptorosaurs developed avian-like postures late in their incubation. In modern birds, such coordinated embryonic movements are associated with tucking, a behavior that’s controlled by the central nervous system and is critical for hatching success.
The notion that such pre-hatching behavior may have originated among non-avian theropods can now be further investigated through more studies of other fossil embryos. But first, the researchers say they’ll continue studying this rare specimen in even more depth, using various imaging techniques to image its internal anatomy, such as skull bones, and other body parts that are still covered in rocks.
###
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, 111 Project, Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, and the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan.
iScience, Xing et al.: “An exquisitely preserved in-ovo theropod dinosaur embryo sheds light on avian-like prehatching postures” https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(21)01487-5
iScience (@iScience_CP) is an open-access journal from Cell Press that provides a platform for original research and interdisciplinary thinking in the life, physical, and earth sciences. The primary criterion for publication in iScience is a significant contribution to a relevant field combined with robust results and underlying methodology. Visit: http://www.cell.com/iscience. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact [email protected].
Journal
iScience
DOI
10.1016/j.isci.2021.103516
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
An exquisitely preserved in-ovo theropod dinosaur embryo sheds light on avian-like prehatching postures
Article Publication Date
21-Dec-2021




