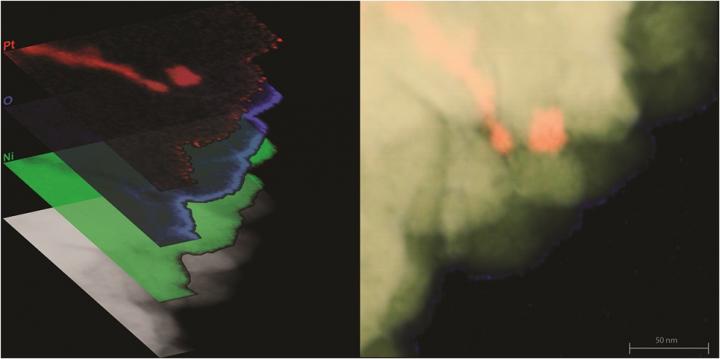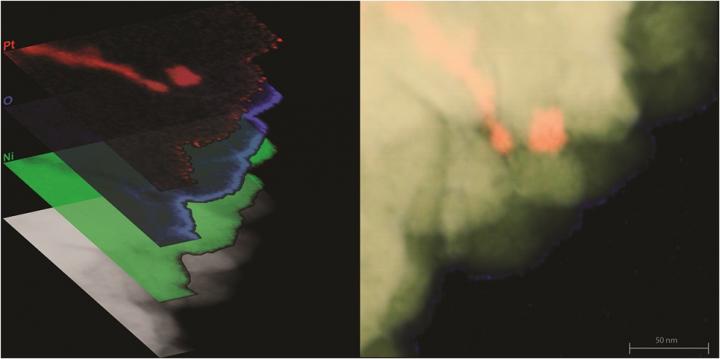
Credit: Imaging by Isabel Boona, OSU Center for Electron Microscopy and Analysis; Left image prepared by Renee Ripley. Courtesy of The Ohio State University.
COLUMBUS, Ohio–The same researchers who pioneered the use of a quantum mechanical effect to convert heat into electricity have figured out how to make their technique work in a form more suitable to industry.
In Nature Communications, engineers from The Ohio State University describe how they used magnetism on a composite of nickel and platinum to amplify the voltage output 10 times or more–not in a thin film, as they had done previously, but in a thicker piece of material that more closely resembles components for future electronic devices.
Many electrical and mechanical devices, such as car engines, produce heat as a byproduct of their normal operation. It's called "waste heat," and its existence is required by the fundamental laws of thermodynamics, explained study co-author Stephen Boona.
But a growing area of research called solid-state thermoelectrics aims to capture that waste heat inside specially designed materials to generate power and increase overall energy efficiency.
"Over half of the energy we use is wasted and enters the atmosphere as heat," said Boona, a postdoctoral researcher at Ohio State. "Solid-state thermoelectrics can help us recover some of that energy. These devices have no moving parts, don't wear out, are robust and require no maintenance. Unfortunately, to date, they are also too expensive and not quite efficient enough to warrant widespread use. We're working to change that."
In 2012, the same Ohio State research group, led by Joseph Heremans, demonstrated that magnetic fields could boost a quantum mechanical effect called the spin Seebeck effect, and in turn boost the voltage output of thin films made from exotic nano-structured materials from a few microvolts to a few millivolts.
In this latest advance, they've increased the output for a composite of two very common metals, nickel with a sprinkling of platinum, from a few nanovolts to tens or hundreds of nanovolts–a smaller voltage, but in a much simpler device that requires no nanofabrication and can be readily scaled up for industry.
Heremans, a professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering and the Ohio Eminent Scholar in Nanotechnology, said that, to some extent, using the same technique in thicker pieces of material required that he and his team rethink the equations that govern thermodynamics and thermoelectricity, which were developed before scientists knew about quantum mechanics. And while quantum mechanics often concerns photons–waves and particles of light–Heremans' research concerns magnons–waves and particles of magnetism.
"Basically, classical thermodynamics covers steam engines that use steam as a working fluid, or jet engines or car engines that use air as a working fluid. Thermoelectrics use electrons as the working fluid. And in this work, we're using quanta of magnetization, or 'magnons,' as a working fluid," Heremans said.
Research in magnon-based thermodynamics was up to now always done in thin films–perhaps only a few atoms thick–and even the best-performing films produce very small voltages.
In the 2012 paper, his team described hitting electrons with magnons to push them through thermoelectric materials. In the current Nature Communications paper, they've shown that the same technique can be used in bulk pieces of composite materials to further improve waste heat recovery.
Instead of applying a thin film of platinum on top of a magnetic material as they might have done before, the researchers distributed a very small amount of platinum nanoparticles randomly throughout a magnetic material–in this case, nickel. The resulting composite produced enhanced voltage output due to the spin Seebeck effect. This means that for a given amount of heat, the composite material generated more electrical power than either material could on its own. Since the entire piece of composite is electrically conducting, other electrical components can draw the voltage from it with increased efficiency compared to a film.
While the composite is not yet part of a real-world device, Heremans is confident the proof-of-principle established by this study will inspire further research that may lead to applications for common waste heat generators, including car and jet engines. The idea is very general, he added, and can be applied to a variety of material combinations, enabling entirely new approaches that don't require expensive metals like platinum or delicate processing procedures like thin-film growth.
###
The research was funded by the National Science Foundation's Materials Research Science and Engineering Program and the U.S. Army's Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative. The nanocomposite materials were synthesized with the help of the study's co-author Koen Vandaele, a visiting scholar from Ghent University in Belgium. Also involved in the study were co-authors and microscopy experts Isabel Boona and Professor David McComb from Ohio State's Center for Electron Microscopy and Analysis (CEMAS), who used CEMAS' state-of-the-art materials characterization equipment to validate the findings.
Media Contact
Matt Schutte
[email protected]
614-247-6445
@osuresearch
http://news.osu.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag