We all know that if we don’t get enough sleep or don’t sleep well, we won’t be on top of our game the next day. And we know that many teens and preteens get too little or poor-quality sleep. Now, a large, first-of-its kind study from Boston Children’s Hospital spells out in detail how inadequate sleep can jeopardize brain organization in early adolescence. Findings appear in the journal Cerebral Cortex Communications.
Credit: Skylar Brooks and Caterina Stamoulis, Boston Children’s Hospital
We all know that if we don’t get enough sleep or don’t sleep well, we won’t be on top of our game the next day. And we know that many teens and preteens get too little or poor-quality sleep. Now, a large, first-of-its kind study from Boston Children’s Hospital spells out in detail how inadequate sleep can jeopardize brain organization in early adolescence. Findings appear in the journal Cerebral Cortex Communications.
“Early adolescence is a critical time in brain development,” says lead researcher Caterina Stamoulis, PhD, who directs the Computational Neuroscience Laboratory at Boston Children’s. “Preteens’ brain circuits are rapidly maturing, particularly those supporting higher-level thought processes like decision-making, problem-solving, and the ability to process and integrate information from the outside world. We show that inadequate sleep could have enormous implications for cognitive and mental health for individual children and at the population level.”
Stamoulis, with research assistant Skylar Brooks and Eliot Katz, MD, a physician in Boston Children’s Sleep Center, analyzed sleep and brain imaging data from more than 5,500 early adolescents (ages 9 to 11 years). The data are from the long-running, NIH-funded Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study.
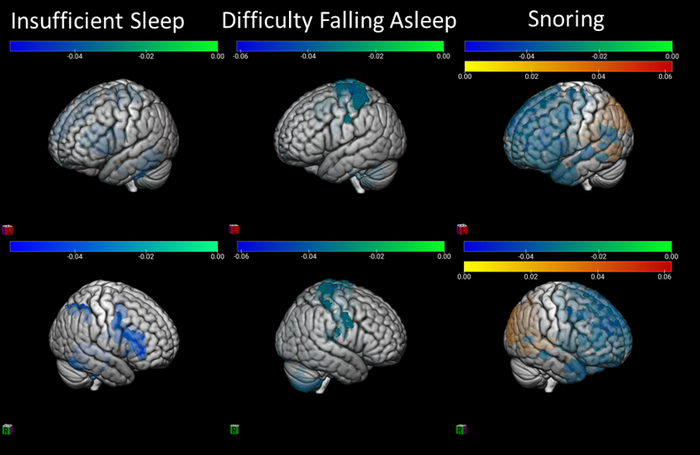
The sleep data were reported by parents on a 26-item survey with questions on sleep duration, sleep latency (time it typically takes the child to fall asleep), waking from sleep, difficulty falling back to sleep, difficulty breathing, snoring, nightmares, difficulty waking up, daytime sleepiness, and more.
The brain data came from functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) performed at rest, independent of any task. From these data, the researchers identified multiple brain networks that play fundamental roles in cognitive function. They then examined the networks’ properties — which reflect how efficiently the brain processes information and how resilient its circuitry is to stressors — as a function of sleep quantity and quality.
A rigorous computational analysis revealed that shorter sleep duration, longer sleep latency, frequent waking, and sleep-disordered breathing were associated with less efficient, flexible, and resilient brain networks. The researchers also observed abnormal network changes in specific parts of the brain: multiple cortical areas as well as the thalamus, basal ganglia, hippocampus, and cerebellum. The detrimental effects were widespread, from individual regions of the brain to large-scale circuits and the entire brain, and many appeared to be independent of unhealthy weight, which also negatively affected sleep quantity and quality.
“The network abnormalities we identified can potentially lead to deficits in multiple cognitive processes, including attention, reward, emotional regulation, memory, and the ability to plan, coordinate, and control actions and behaviors,” says Stamoulis.
The study also found racial disparities. Shorter sleep times and reduced sleep quality had disproportionate unhealthy effects on brain networks in non-white participants, who comprised about a third of the sample.
Additional findings on sleep:
- Girls slept less than boys, averaging 8 to 9 hours of sleep as compared with 9-11 hours for boys. They also took longer to fall asleep.
- Non-white children slept less than white children, averaging 8 to 9 hours versus 9 to 11 hours.
- Higher family income was significantly associated with longer sleep duration
- Longer screen time were significantly associated with shorter sleep duration
- Being overweight was associated with shorter sleep duration, more movement during the night, sweating, snoring, difficulty waking, and daytime sleepiness.
The study was funded by the National Science Foundation through its BRAIN and Harnessing the Data Revolution initiatives (grants 1940094, 1649865, 2116707) and the National Heart Lung Blood Institute (through R21HL135516 and R21HL156186).
About Boston Children’s Hospital
Boston Children’s Hospital is ranked the #1 children’s hospital in the nation by U.S. News & World Report and is the primary pediatric teaching affiliate of Harvard Medical School. Home to the world’s largest research enterprise based at a pediatric medical center, its discoveries have benefited both children and adults since 1869. Today, 3,000 researchers and scientific staff, including 10 members of the National Academy of Sciences, 25 members of the National Academy of Medicine and 10 Howard Hughes Medical Investigators comprise Boston Children’s research community. Founded as a 20-bed hospital for children, Boston Children’s is now a 415-bed comprehensive center for pediatric and adolescent health care. For more, visit our Answers blog and follow us on social media @BostonChildrens, @BCH_Innovation, Facebook and YouTube.
– ### –
Journal
Cerebral Cortex Communications
DOI
10.1093/texcom/tgab062
Article Title
Shorter Duration and Lower Quality Sleep Have Widespread Detrimental Effects on Developing Functional Brain Networks in Early Adolescence
Article Publication Date
26-Oct-2021




