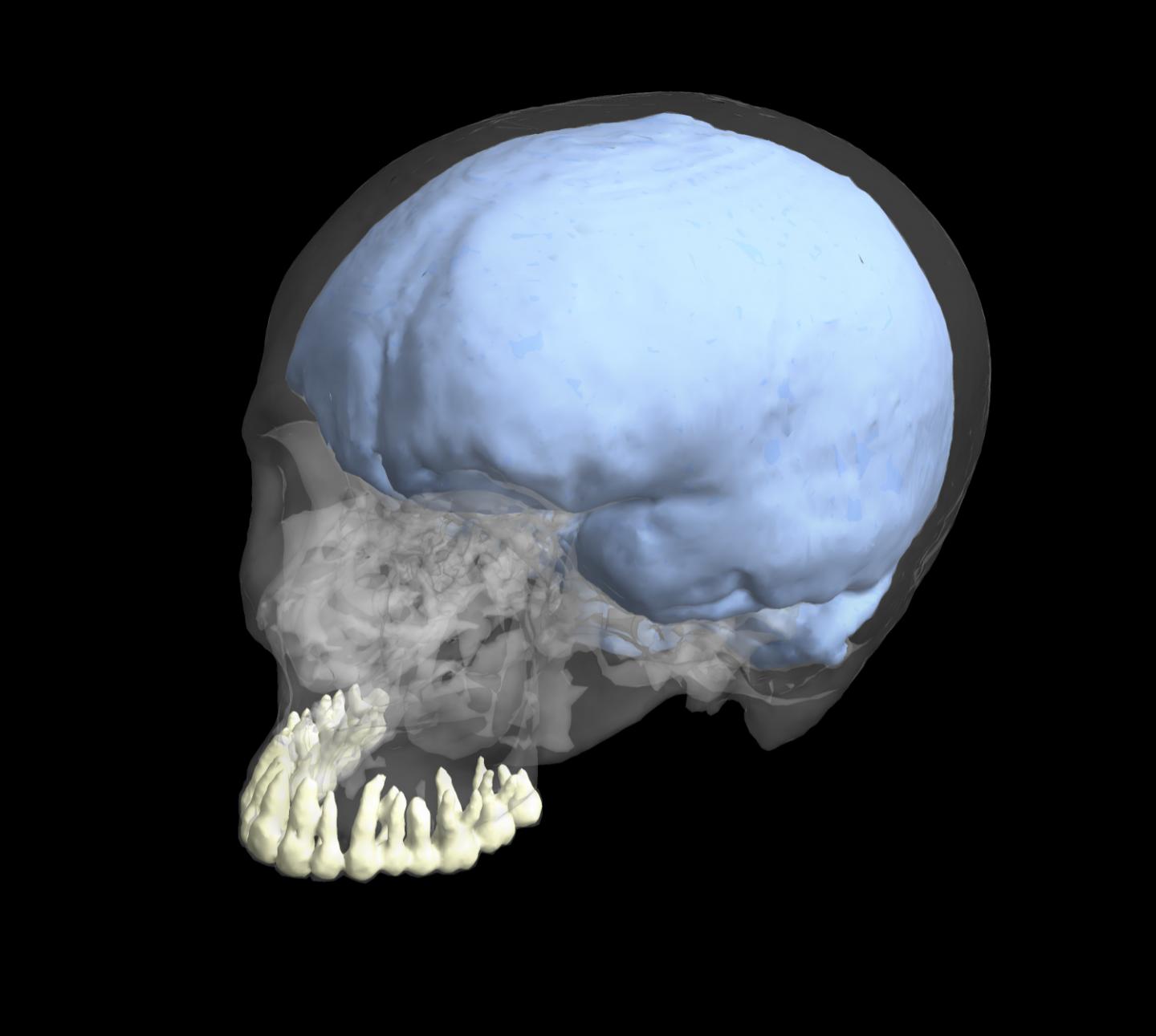
Credit: George Washington University
WASHINGTON (Jan. 2, 2017)–A new study from the George Washington University's Center for the Advanced Study of Human Paleobiology (CASHP) found that whereas brain size evolved at different rates for different species, especially during the evolution of Homo, the genus that includes humans, chewing teeth tended to evolve at more similar rates. The finding suggests that our brains and teeth did not evolve in lock step and were likely influenced by different ecological and behavioral factors.
This research challenges the classically accepted view that reduction of tooth size in hominins is linked with having a larger brain. The reasoning is that larger brains allowed hominins to start making stone tools and that the use of these tools reduced the need to have such large chewing teeth. But recent studies by other authors found that hominins had larger brains before chewing teeth became smaller, and they made and used stone tools when brains were still quite small, which challenges this relationship.
The new study evaluates this issue by measuring and comparing the rates at which teeth and brains have evolved along the different branches of the human evolutionary tree.
"The findings of the study indicate that simple causal relationships between the evolution of brain size, tool use and tooth size are unlikely to hold true when considering the complex scenarios of hominin evolution and the extended time periods during which evolutionary change has occurred," said Aida Gómez-Robles, lead author of the paper and a postdoctoral scientist at GW's CASHP.
To conduct the research, Dr. Gómez-Robles and her colleagues analyzed eight different hominin species. The researchers identified fast-evolving species by comparing differences between groups with those obtained when simulating evolution at a constant rate across all lineages, and they found clear differences between tooth evolution and brain evolution. If the classical view proposing co-evolution between brains and teeth is correct, they expected to see a close correspondence between species evolving at a fast rate for both traits. The differences they observed indicate that diverse and unrelated factors influenced the evolution of teeth and brains.
"Once something becomes conventional wisdom, in no time at all it becomes dogma," said Bernard Wood, university professor of human origins at GW and a co-author of the paper. "The co-evolution of brains and teeth was on a fast-track to dogma status, but we caught it in the nick of time."
The research published Jan. 2 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
###
Multimedia Resources
- Photos available upon request.
-GW-
Media Contact
Emily Grebenstein
[email protected]
202-994-6460
@GWtweets
http://www.gwu.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag