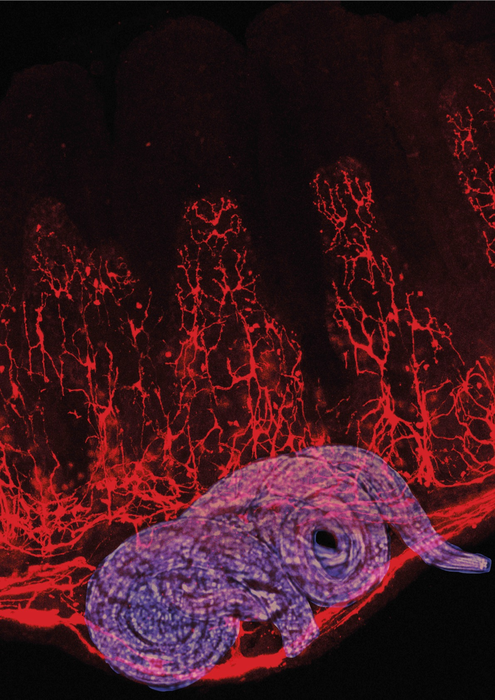
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have uncovered a fundamental role of glial cells in the nervous system of the gut in maintaining a healthy intestine. These cells have been found to coordinate the immune responses of the gut following pathogen invasion and could be key targets when exploring new treatments for inflammatory bowel conditions.
Credit: The Francis Crick Institute
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have uncovered a fundamental role of glial cells in the nervous system of the gut in maintaining a healthy intestine. These cells have been found to coordinate the immune responses of the gut following pathogen invasion and could be key targets when exploring new treatments for inflammatory bowel conditions.
Maintaining a healthy intestine and repairing tissue after infection or other types of injury is a complex process, and if this goes wrong, it can lead to inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and colitis. While much previous research in this area has focused on the activity of different immune cells, a lot of mysteries about the mechanisms behind these diseases still remain unanswered, which suggests that other cells may play a critical role.
In their study, published in Nature today (20 October), researchers studied the role of enteric glial cells in response to tissue damage. These cells lie within the gut wall and form part of the enteric nervous system which governs the contractions of intestinal muscles and other aspects of digestive function.
They infected mice with a common roundworm parasite, Heligmosomoides polygyrus, and found that when the parasite invades the gut wall, a protein, called interferon gamma, is quickly released by immune cells. Although this protein so far was thought to target cells of the immune system, this new study found that one of its first targets are the nearby glial cells. The protein activates these cells which then release signals that attract other immune cells to the site of damage to fight the infection.
To identify if similar mechanisms occur in humans, the researchers analysed data previously collected by others of colon samples from people with ulcerative colitis, a long-term condition where the colon and rectum become inflamed, and which causes severe diarrhoea and stomach cramps. Similar to the mouse cells, genes associated with interferon gamma were also activated in the human glial cells. This suggests that glial cells in the human gut are also implicated in inflammatory conditions of this organ.
Fränze Progatzky, author and postdoctoral scientist in the Crick’s Development and Homeostasis of the Nervous System Lab, says: “Sadly, currently treatments for inflammatory bowel disease are often limited to alleviating the symptoms, rather than tackling the cause. Our insights into the importance of enteric glial cells in maintaining a healthy intestine open the door to further studies into how these cells work and interact with the immune system and in the future could help us develop potential new treatments for these conditions.”
The team also studied the role of glial cells in maintaining healthy intestinal gut tissues, in the absence of infection. To do this, they blocked the ability of enteric glial cells to be activated by interferon gamma and found that this led to tissue inflammation even in normal mice. This shows the cells are also important outside of disease or injury, in maintaining healthy intestinal tissue.
Vassilis Pachnis, author and group leader of the Development and Homeostasis of the Nervous System Lab at the Crick, says: “Glial cells are present in many organs, and so it’s possible they also play similar roles in maintaining healthy tissue and mounting appropriate responses to pathogens or toxins in other parts of the body. It will be exciting to explore this possibility further.”
This research was carried out in collaboration with the AhRimmunity Laboratory at the Crick, led by Gitta Stockinger, and is part of an ongoing collaboration between the labs to study the processes which influence health and disease in the gut.
###
Journal
Nature
DOI
10.1038/s41586-021-04006-z
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
egulation of intestinal immunity and tissue repair by enteric glia
Article Publication Date
20-Oct-2021




