Credit: CAO Peng et al.
Early-life inflammation, such as trauma and viral infections, strongly increases the risk of individual for depression in adulthood, however, the mechanisms are not clear yet.
A team led by Prof. ZHANG Zhi from Division of Life Sciences and Medicine of the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborating with Prof. XU Lin from CAS, revealed the mechanism by which early-life inflammation induces adolescent depression symptoms. This work has been published in Neuron on July 6th.
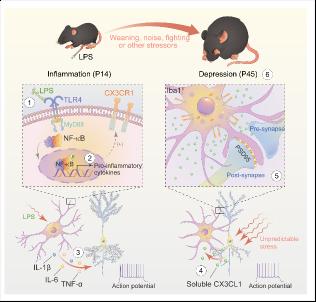
Clinically related studies have shown decreased anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) synaptic density and increased inflammation in the brain of depressed patients. Microglial cells are resident immune cells of the brain, and it transforms into reactive states in response to stress challenges. Under the pathological state, activated microglia are the commander of the inflammatory state of the brain tissue, which is closely related to the occurrence and development of depression.
In this work, researchers found that early-life inflammation would lead to the susceptibility of microglial in the ACC to random stress events during adolescent development, and microglia then overengulfed dendritic spines of neurons. This weakened the ability of ACC glutamatergic neuronal (ACCGlu) to fight stress, thus inducing adolescent depression.
To explore the responding and activating model of ACC microglia to stress during mouse development from childhood to adolescence (45 days after birth), researchers established inflammatory model by intraperitoneal administration of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) during the critical time window of mouse brain development (14 days after birth). 6 hours after LPS injection, multiple activation indexes of ACC microglia in mice significantly increased and recovered after 24 hours. Interestingly, during the later development, a series of unpredictable life stress events (such as weaning, caging, noise and fighting) could lead to the re-activation of ACC microglia in LPS mice, being more susceptible than normal mice.
Moreover, before stress, the sharply increase of ACCGlu activity helped mice resist the attack of stress and protect themselves. However, ACC microglia of mice with early-life inflammation were frequently activated by persistent stress in adolescence, and overengulfed the ACCGlu dendritic spines via CX3CR1 signals mediate, consequently reducing the activity of ACCGlu. As a result the body’s ability to cope with stress was impaired, which promoted depression in adolescent mice.
###
Media Contact
Jane FAN Qiong
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




