Researchers from Kanazawa University find that gasdermin D, a protein known to be involved in cell death, is also crucial for activation and release of the key immune mediator interleukin-1α
Kanazawa, Japan – Interluekin-1α (IL-1α) is an important part of the immune response, but until now it has been unclear how this molecule is processed from its precursor, pro-IL-1α, and exits the cell during inflammasome activation. Now, researchers from Japan have found that gasdermin D, a protein that was already known to mediate pyroptosis, a form of regulated cell death, plays a crucial role in the maturation and release of IL-1α.
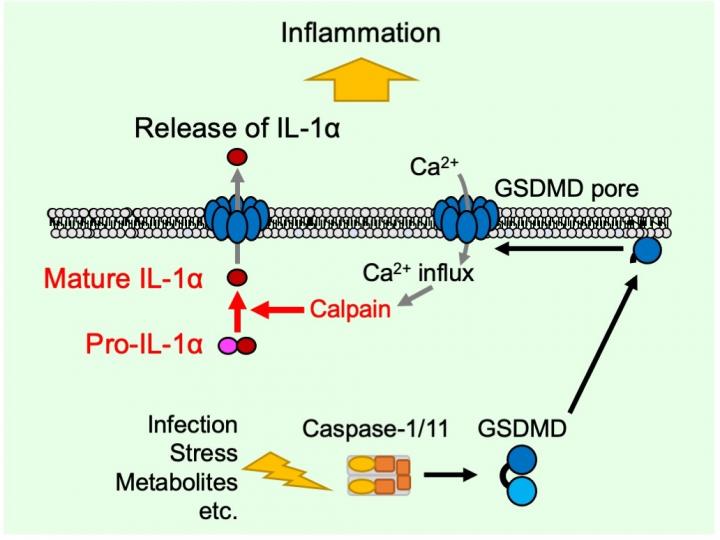
In a study published in March in Cell Reports, researchers from Kanazawa University report that, when the inflammasome (a part of the innate immune system) is activated, gasdermin D forms pores in the cell membrane that allow factors from outside of the cell to flow in, leading to the activation and release of mature IL-1α.
Previous work has shown that inflammasome activation leads to gasdermin D being cut in two by an enzyme, and that one half of the cut protein forms membrane pores. This leads to pyroptosis whereby the pores let water into the cells, causing them to swell and burst.
“We knew that caspase-1 cleaves gasdermin D, and that this enzyme is also important for IL-1α activation,” says lead author of the study Kohsuke Tsuchiya. “We therefore suspected that gasdermin D might be involved in the pathway leading to IL-1α release.”
To test this possibility, the researchers deleted the gene encoding gasdermin D, and found that this almost completely eliminated IL-1α exit from the cells. Unexpectedly, though, they also saw that virtually no mature IL-1α was present inside these cells.
“This made us think that gasdermin D is important not only for IL-1α release, but also IL-1α maturation,” explains Takashi Suda, lead author of the study. “When we looked into this in more detail, we found that gasdermin D did not need to cause cell lysis for these effects to take place. Instead, only its ability to form pores in the membrane was required for both IL-1α maturation and release.”
The researchers went on to show that pore formation by gasdermin D allows calcium influx and activation of calpains (a type of proteases), which promotes processing of the pro-IL-1α precursor into mature IL-1α maturation.
“Our findings provide the missing link between caspase-1 activity and IL-1α maturation,” says Tsuchiya.
Given that inflammasome activation is a key element of both inflammatory diseases and the response to infection, this study provides important insight into essential functions of the human immune system. Identifying gasdermin D as a regulator of immune function as well as cell death increases our understanding of how inflammasome activation ultimately leads to IL-1α release from immune cells.
###
Media Contact
Tomoya Sato
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.