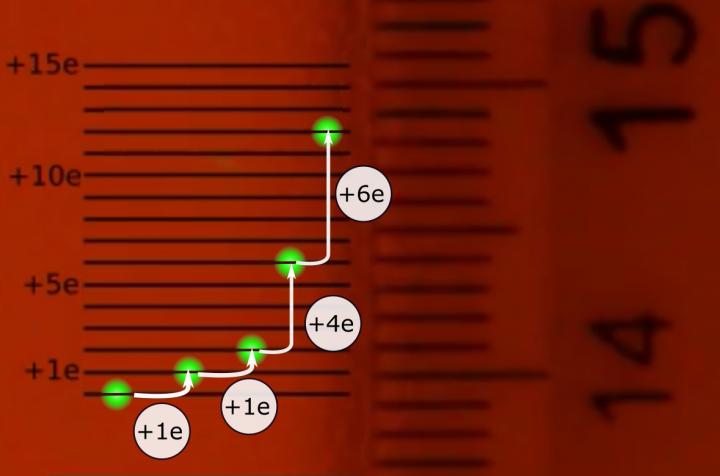
Researchers at the University of Gothenburg have observed the absorption of a single electron by a levitated droplet with such a magnification that it is visible with the naked eye and can even be measured with a normal millimeter scaled ruler.
Matter in the universe is composed of elementary particles like electrons, protons, and neutrons. They are everywhere, but they are so small that the human eye cannot discern them. In the last century, physicists have proven the existence of these particles through different experiments, but in most cases the observation of the particles have been indirect.
– Electrons are one of these fundamental particles. In 1909, Robert Millikan proved that the charge of the electron is quantized. In other words, there exists a minimum, indivisible amount of charge. He demonstrated that the electron´s charge is quantized by letting hundreds of charged droplets fall in an electric field and then perform a statistical analysis of their motion.
An experiment with a single levitated drop
-Now we have created a modern version of this classical experiment by levitating a single droplet in air using a laser, says Javier Marmolejo, Ph.D. at the Department of physics at the University of Gothenburg.
In this experiment, the quantization of the electric charge is directly visible for the first time without advanced equipment or a complex statistical analysis.
– We trapped a drop using a laser inside a strong electric field and added individual electrons by exposing it to alfa radiation. The drop performed quantized jumps every time it absorbed one or a few electrons. By magnifying the image of the droplet using a single lens, we were able to see the effect of a single electron absorption and to measure the jumps with a ruler. The bright spot moved about one millimeter for every absorbed electron (see video).
The drop had a diameter of 29 micrometers, which roughly corresponds to the thickness of a thin human hair. Despite this, it contains around 3.7 x1015 negatively charged electrons.
– The feat is incredible when one considers that the effect of adding single electron to a droplet that already has 3 700 000 000 000 000 is visible with the naked eye.
Now that it is possible to “see the effect of a single electron”, a new opportunity emerges to better communicate science regarding elementary particles to the general public, the researchers comment.
###
Contact:
Javier Tello Marmolejo, doctoral student, Department of Physics, University of Gothenburg, e-mail. [email protected], phone: 070 017 53 19
Dag Hanstorp, professor, Department of Physics, University of Gothenburg, phone: 0766-22 91 41, 031-786 91 41, e-mail: [email protected]
Link to article in Scientific Reports, “Visualizing the electron’s quantization with a ruler” : http://www.
Video: Javier Marmolejo
Illustration: Javier Marmolejo
Facts about the experiment
A laser trap was used to levitate a silicone oil droplet in air. The trap consisted of a green laser with a wavelength of 532 nanometers that was directed upwards and focused by a lens with a focal distance of 100 mm. The focal point was placed between two electrodes placed in the center of the experimental chamber. The electrodes were parallel and separated by 1 mm. A 29 micrometer droplet was dropped into the laser beam, where it was trapped. Between the plates, a 666 V potential difference was applied which created a strong electric field. Alfa radiation was directed towards the almost uncharged droplet, ionizing the air around it. When the droplet gained or lost charge, the force applied by the electric field changed which in turn changed its position. The effects were magnified 73 times by a lens and projected onto a wall. With this magnification, the micrometric movements of the drop were observable with the naked eye. A common millimeter ruler was placed on the wall where the researchers could directly observe the number of electrons the drop gained as it jumped about 1 mm per added electron.
Media Contact
Javier Tello Marmolejo
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/