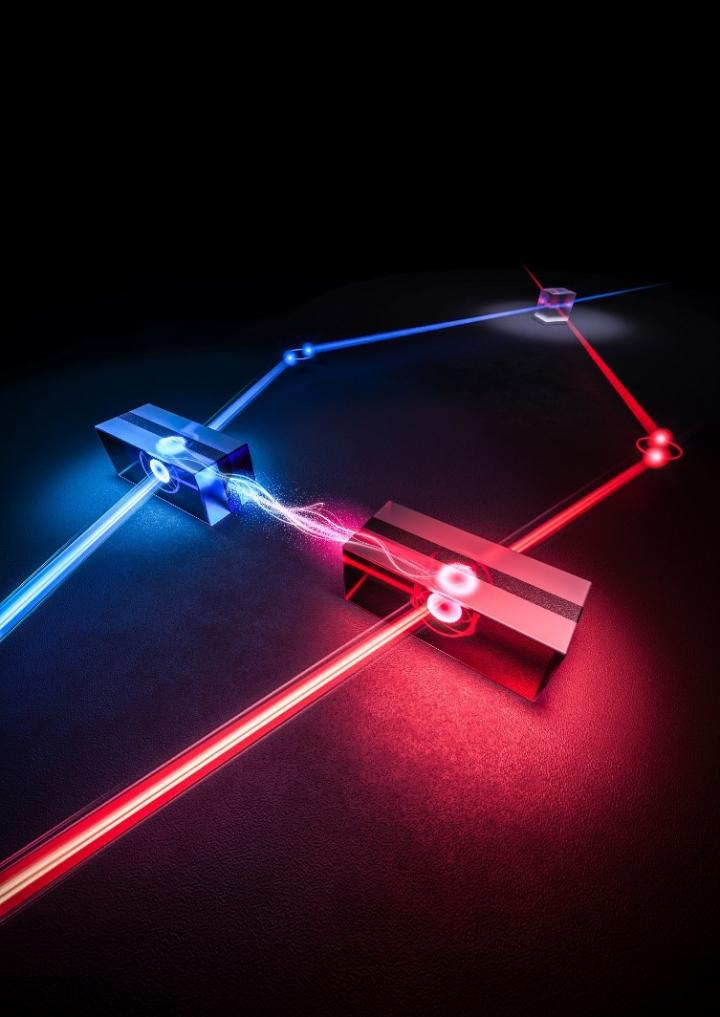
Chinese researchers realized an elementary link of a quantum repeater based on absorptive quantum memories (QMs) and demonstrated the multiplexed quantum repeater for the first time. On June 2nd?the work is published in Nature.
The fundamental task of a quantum network is to distribute quantum entanglement between two remote locations. However, the transmission loss of optical fiber has limited the distance of entanglement distribution to approximately 100 km on the ground. Quantum repeaters can overcome this difficulty by dividing long-distance transmission into several short-distance elementary links. The entanglement of two end nodes of each link is created firstly. Then the entanglement distance is gradually expanded through entanglement swapping between each link.
Previously, an elementary link of a quantum repeater has been realized in cold atomic ensembles and single quantum systems. These demonstrations are all based on emissive QMs, in which the entangled photons are emitted from QMs. Quantum repeaters constructed by emissive QMs have simple structures, but poor compatibilities. It is of great challenge to support deterministic entanglement sources and multiplexed operations simultaneously, which are two key technologies to enhance the entanglement distribution rate. Quantum repeaters based on absorptive QMs can overcome such limitation because they separate the quantum memories and the entangled photon sources.
The research team, led by Prof. LI Chuanfeng and Prof. ZHOU Zongquan from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), focuses on the research of absorptive QMs based on rare-earth-ion-doped crystals. For this kind of QMs, the entanglement source can be flexibly selected, including deterministic entanglement sources, while remaining the capability of multiplexed operations, and therefore should be more efficient for quantum repeater applications. In this work, they used external entangled photon-pair sources (EPPSs) based on spontaneous parametric down-conversion and achieved heralded entanglement distribution between two absorptive QMs for the first time.
They built an elementary link with an intermediate station and two nodes at the ends. Each node contains an absorptive QM with a bandwidth of 1GHz and a bandwidth-matched EPPS. In each node, one entangled photon of each photon pair was stored in the “Sandwich-like” QM while the other was transmitted to the middle station for joint Bell-state measurement (BSM). A successful entanglement swapping operation was heralded by the successful click of BSM. The entanglement between two QMs 3.5 meters apart was established with a fidelity of approximately 80.4%, although there weren’t any direct interactions between two remote QMs. Four temporal modes were employed in this demonstration of an elementary link of a quantum repeater, accelerating the entanglement distribution rate by four times.
Prof. ZHOU Zongquan said: “The use of absorptive quantum memory is expected to achieve high efficiency quantum repeater and quantum network in the future, and further promote the communication between ‘Cowherd and Weaver Girl’ in the quantum world.”
This work provides a feasible roadmap for the development of practical quantum repeaters and lays the foundation for the construction of high-speed quantum networks. Reviewers pointed out”The present work focuses on the ensemble approach, which has a number of advantages in the context of quantum repeater applications, multiplexing for instance”. They highly recommend this work as”a significant accomplishment that will form the basis for further research” and “a major step forward in the development of a practical quantum repeater”.
Prof. LI Chuanfeng said that the team will continue to improve the indicators of absorptive QM, ” we will use deterministic entanglement source to greatly improve the entanglement distribution rate, and to achieve practical quantum repeaters beyond direct transmission of optical fiber.”
LIU Xiao and HU Jun from CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information and CAS Center for Excellence in Quantum Information and Quantum Physics are the co-first authors. The corresponding authors are Prof. LI Chuanfeng and Prof. ZHOU Zongquan.
For future developments, the research team will continue to improve the performances of the absorptive QMs, and adopt deterministic entanglement sources, so as to greatly enhance the entanglement distribution rate, and to achieve a practical quantum repeater that outperform the direct transmission of photons.
###
Media Contact
Jane FAN Qiong
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.