Since the introduction on the market in 1995 of Doxil, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, liposomes have become one of the most clinically established drug delivery systems in nanomedicine. Among different liposomal formulations, cationic liposomes have attracted great attention because of their capacity to bind negatively charged nucleic acids to perform as non-viral gene delivery tools, and due to their potentials to fuse with cell membranes leading to a direct release of cargoes from liposomes into the cytoplasm and high drug delivery efficiency. However, in most cases, the drug/gene delivery and therapeutic efficacy by cationic liposomes are evaluated in vitro in serum-free conditions. It is known that once introduced in biological fluids, nanoscale objects (such as liposomes) absorb numerous proteins and biomolecules on their surface forming a layer called “protein corona”. This layer affects nanoparticle charge, size and surface properties and confers to nanoparticle new biological properties, which affect its following performance, such as distribution, toxicity, cellular internalization and final fate. Thus, it could be expected that the cationic liposome behaviour on cellular levels is different when exposed to a serum-free condition and a biological environment. Fully understand the behaviour of cationic liposomes in a biologically relevant environment, especially the effect of protein corona on the liposome interaction with cells, will help to guide the design of efficient liposomal formulations and narrow the gap between in vitro and in vivo studies.
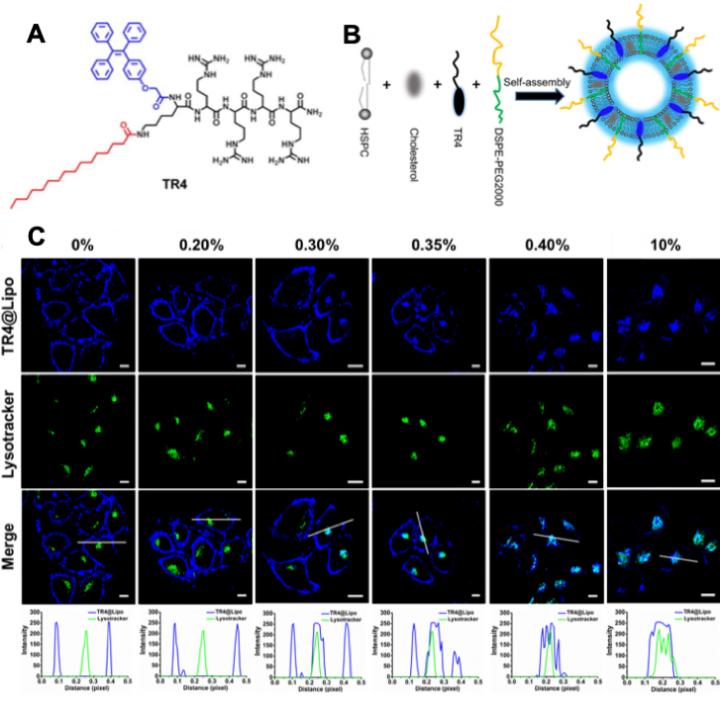
Within this context, Wang et al. have synthesized a cell membrane probe (called TR4) containing 4 arginine residues, a palmitic acid tail and tetraphenylethylene (TPE), and developed a cationic liposome (named TR4@Lipo) by inserting TR4 into hydrogenated phosphatidylcholine (HSPC)-cholesterol binary liposome membranes (Figure 1A-B). Benefiting from the aggregation-induced emission property of TPE, TR4 showed dramatically enhanced fluorescent intensity when restricted in the lipid bilayer, which endowed TR4@Lipo with a self-indicating capacity and made it visualized by confocal microscopy. Interestingly, when exposed to serum-free medium, TR4@Lipo interacted with cells through a cell membrane fusion behavior and this process did not consume energy. However, once introduced in a medium supplemented with fetal bovine serum or human serum and with protein corona forming on the liposome surface, TR4@Lipo was endocytosed by cells following an energy-dependent pathway (Figure 1C). Moreover, when doxorubicin (as a cargo model) was loaded in TR4@Lipo, it was observed that not only the internalization pathway of liposomes but also the intracellular distribution of cargoes were altered with protein corona formation.
Overall, by using a self-indicating liposome, the presented study highlights the effects of protein corona on the interactions of cationic liposomes, which switches the internalization of cationic liposomes from energy-independent membrane fusion to energy-dependent endocytosis, as well as modulating the intracellular distribution of encapsulated cargoes (Figure 2). This knowledge furthers our understanding of bio-nano interactions and is important for the efficient design and application of cationic liposomes in future studies.
###
See the article:
Yi-Feng Wang, Chunqiu Zhang, Keni Yang, Yufei Wang, Shaobo Shan, Yan Yan, Kenneth A Dawson, Chen Wang, Xing-Jie Liang.
Transportation of AIE-visualized nanoliposomes is dominated by the protein corona.
National Science Review, 2021;, nwab068,
https:/
Media Contact
Xing-Jie Liang
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.