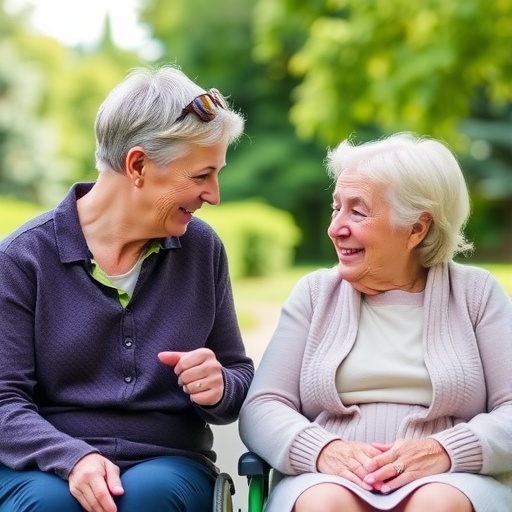
Researchers reveal the diversity of our neurons
Credit: MPI for Metabolism Research/ Nasim Biglari
The nerve cells, also called neurons, in our brain control all the basic processes of our body. For this reason, there are different types of neurons distributed over specific regions of the brain. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Metabolic Research and the CECAD Cluster of Excellence in Aging Research of the University of Cologne have developed an approach that allows them to show that neurons that are supposedly the same are actually very different: they not only sense different hormones for the body’s energy state, but also have a different influence on food intake. This can have a direct effect on our metabolism, for example by differentially restraining our appetite.
The brain processes our sensory perceptions, controls our behaviour and stores our memories. Because of these many functions, different types of nerve cells with specific tasks exist in different regions of our brain. One such type of nerve cells are the so-called POMC neurons, which play an important role in the metabolism of our body. “POMC neurons are critically involved in the control of appetite, energy expenditure and metabolism,” explains Nasim Biglari, a recently graduated PhD and first author of the study. “In recent years, it has been increasingly confirmed that POMC neurons are more diverse than previously thought.” Such differences result, for example, from a different response to hormones secreted by the body and are only noticeable when individual POMC neurons are compared with each other. In such a case, scientists refer to different subtypes of neurons. “Whether the different subtypes also play a different role in metabolism has not been clarified so far,” says Nasim Biglari.
Same nerve cell – different influence on food intake
“We have now succeeded in making different subtypes of neurons visible in mice at the genetic level and thus were able to subject them to more detailed investigation”, says Nasim Biglari. “Using this new, genetic approach, we were able to describe two different subtypes of POMC neurons in detail for the first time. For example, our results show a different distribution of the two subtypes within the same specific brain region. Moreover, they sense different hormones for the body’s energy state. The two subtypes even act differently on food intake, with one part of the POMC neurons suppressing appetite more potently than the other.” Because of the influence of POMC neurons on metabolism and food intake, these observations could also be relevant to diseases such as obesity and diabetes.
“We were able to show for the first time that the diversity of POMC neurons is important for their function in the control of metabolism. In further experiments, we would like to increasingly address the questions of how the two subtypes of POMC neurons influence metabolism in detail and which neuronal circuits in the brain they engage to carry out their effects”, Nasim Biglari is looking forward to future experiments. “More generally, however, the approach we have developed can also be used to identify cell subtypes in other organs and for other types of cells. This could lead to many more insights into the diversity of our body’s cells.”
###
Original publication
N. Biglari, I. Gaziano, J. Schumacher, J. Radermacher, L. Paeger, P. Klemm, W. Chen, S. Corneliussen, C. M. Wunderlich, M. Sue, S. Vollmar, T. Klo?ckener, T. Sotelo-Hitschfeld, A. Abbasloo, F. Edenhofer, F. Reimann, F. M. Gribble, H. Fenselau, P. Kloppenburg, F. T. Wunderlich und J. C. Bru?ning
Intersectional Targeting Reveals a Refined Microcircuit Architecture of Heterogenous, Glp1r- and Lepr-expressing POMC-Neurons.
Nature Neuroscience, 2021.
Published: 17 May 2021
Media Contact
Dr. Nasim Biglari
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




