University of Rochester researchers combine freeform optics and a metasurface to avoid ‘bug eyes’
Credit: (University of Rochester illustration / Michael Osadciw)
“Image” is everything in the $20 billion market for AR/VR glasses. Consumers are looking for glasses that are compact and easy to wear, delivering high-quality imagery with socially acceptable optics that don’t look like “bug eyes.”
University of Rochester researchers at the Institute of Optics have come up with a novel technology to deliver those attributes with maximum effect. In a paper in Science Advances, they describe imprinting freeform optics with a nanophotonic optical element called “a metasurface.”
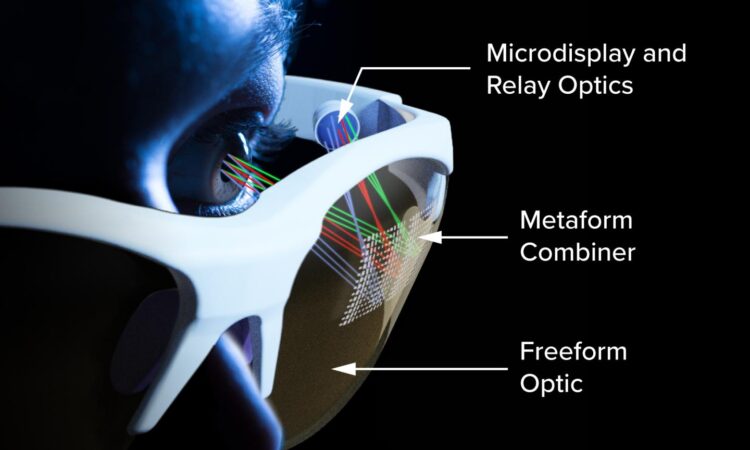
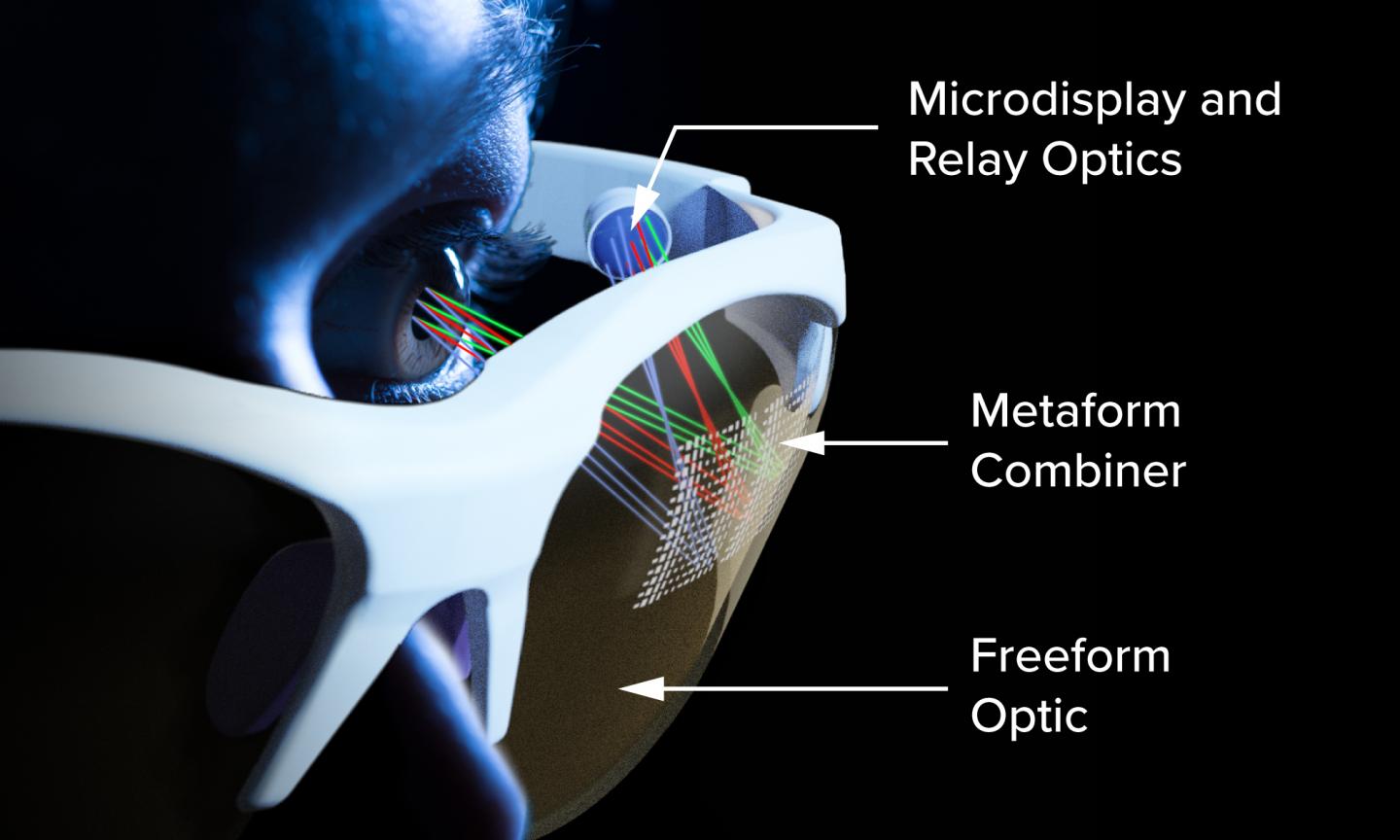
The metasurface is a veritable forest of tiny, silver, nanoscale structures on a thin metallic film that conforms, in this advance, to the freeform shape of the optics–realizing a new optical component the researchers call a metaform.
The metaform is able to defy the conventional laws of reflection, gathering the visible light rays entering an AR/VR eyepiece from all directions, and redirecting them directly into the human eye.
Nick Vamivakas, a professor of quantum optics and quantum physics, likened the nanoscale structures to small-scale radio antennas. “When we actuate the device and illuminate it with the right wavelength, all of these antennas start oscillating, radiating a new light that delivers the image we want downstream.”
“Metasurfaces are also called ‘flat optics’ so writing metasurfaces on freeform optics is creating an entirely new type of optical component,” says Jannick Rolland, the Brian J. Thompson Professor of Optical Engineering and director of the Center for Freeform Optics.
Adds Rolland, “This kind of optical component can be applied to any mirrors or lenses, so we are already finding applications in other types of components” such as sensors and mobile cameras.
WHY FREEFORM OPTICS WEREN’T ENOUGH
The first demonstration required many years to complete.
The goal is to direct the visible light entering the AR/VR glasses to the eye. The new device uses a freespace optical combiner to help do that. However, when the combiner is part of freeform optics that curve around the head to conform to an eyeglass format, not all of the light is directed to the eye. Freeform optics alone cannot solve this specific challenge.
That’s why the researchers had to leverage a metasurface to build a new optical component.
“Integrating these two technologies, freeform and metasurfaces, understanding how both of them interact with light, and leveraging that to get a good image was a major challenge,” says lead author Daniel Nikolov, an optical engineer in Rolland’s research group.
THE CHALLENGE OF FABRICATION
Another obstacle was bridging “from macroscale to nanoscale,” Rolland says. The actual focusing device measures about 2.5 millimeters across. But even that is 10,000 times larger than the smallest of the nanostructures imprinted on the freeform optic.
“From a design standpoint that meant changing the shape of the freeform lens and distributing the nanostructures on the lens in a way that the two of them work in synergy, so you get an optical device with a good optical performance,” Nikolov says.
This required Aaron Bauer, an optical engineer in Rolland’s group, to find a way to circumvent the inability to directly specify metasurfaces in optical design software. In fact, different software programs were used to achieve an integrated metaform device.
Fabrication was daunting, Nikolov says. It required using electron-beam lithography, in which beams of electrons were used to cut away sections of the thin-film metasurface where the silver nanostructures needed to be deposited. Writing with electron beams on curved freeform surfaces is atypical and required developing new fabrication processes.
The researchers used a JEOL electron-beam lithography (EBL) machine at the University of Michigan’s Lurie Nanofabrication Facility. To write the metasurfaces on a curved freeform optic they first created a 3D map of the freeform surface using a laser-probe measuring system. The 3D map was then programmed into the JEOL machine to specify at what height each of the nanostructures needed to be fabricated.
“We were pushing the capabilities of the machine,” Nikolov says. Fei Cheng, a postdoctoral associate in the Vamivakas group; Hitoshi Kato, a JEOL representative from Japan, and the Michigan staff of the nanofabrication lab, collaborated with Nikolov on achieving successful fabrication “after multiple iterations of the process.”
“This is a dream come true,” Rolland says. “This required integrated teamwork where every contribution was critical to the success of this project.”
###
Media Contact
Bob Marcotte
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.