Research featured on cover of American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology
Credit: American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology
LOUISVILLE, Ky. – When a new drug is being developed, the first question is, “Does it work?” The second question is, “Does it do harm?” No matter how effective a therapy is, if it harms the patient in the process, it has little value.
Doctoral student Robert Skolik and Associate Professor Michael Menze, Ph.D., in the Department of Biology at the University of Louisville, have found a way to make cell cultures respond more closely to normal cells, allowing drugs to be screened for toxicity earlier in the research timeline.
The vast majority of cells used for biomedical research are derived from cancer tissues stored in biorepositories. They are cheap to maintain, easy to grow and multiply quickly. Specifically, liver cancer cells are desirable for testing the toxicity of drugs for any number of diseases.
“You like to use liver cells because this is the organ that would detoxify whatever drug for whatever treatment you are testing,” Menze said. “When new drugs are being developed for diabetes or another disease, one of the concerns is whether they are toxic to the liver.”
The cells do come with limitations, however. Since they are cancer cells, they may not be as sensitive to toxins as normal cells, so they may not reveal issues with toxicity that can appear much later in the drug testing process.
Skolik and Menze have discovered that by changing two components of the media used to culture the cells, they can make liver cancer cells behave more like normal liver cells. Rather than using standard serum containing glucose, they used serum from which the glucose had been removed using dialysis and added galactose – a different form of sugar – to the media. The tumor cells metabolize galactose at a much slower rate than glucose. This changes the metabolism of the cells making them behave more like normal liver cells.
By using cells cultured with this modified serum, drugs may effectively be screened for toxicity earlier in the research process, possibly saving millions of dollars.
“It started just as a way to sensitize cells to mitochondrial activity, the cellular powerhouse, but then we realized we had a way to investigate how we are shifting cancer metabolism,” Skolik said. “In short, we have found a way to reprogram cancer cells to look – and act – more like a normal cell.”
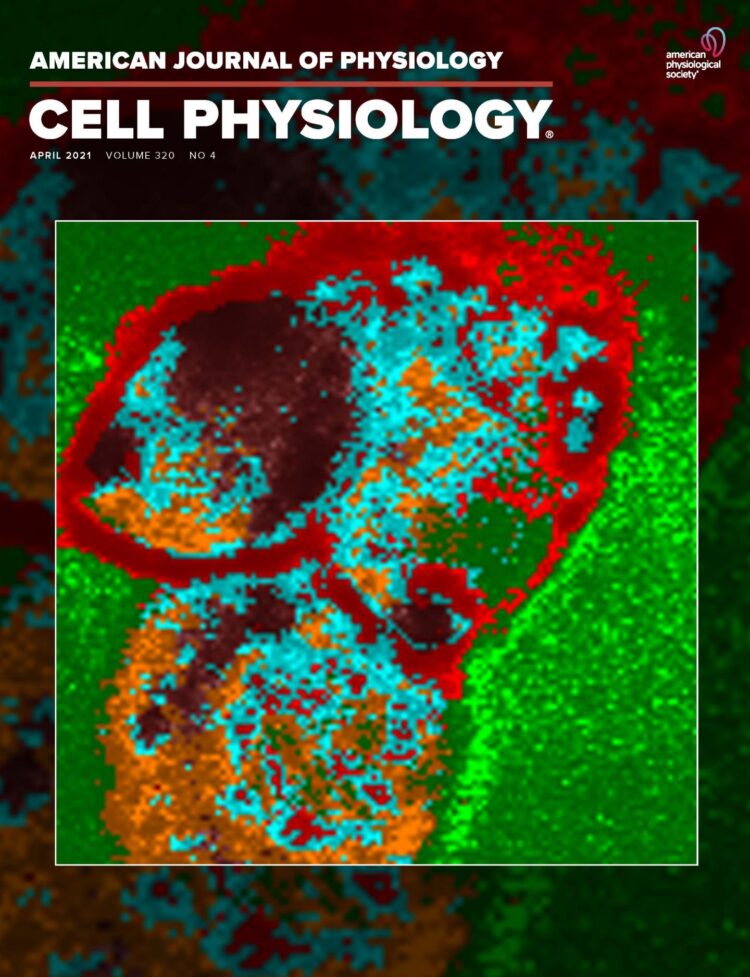
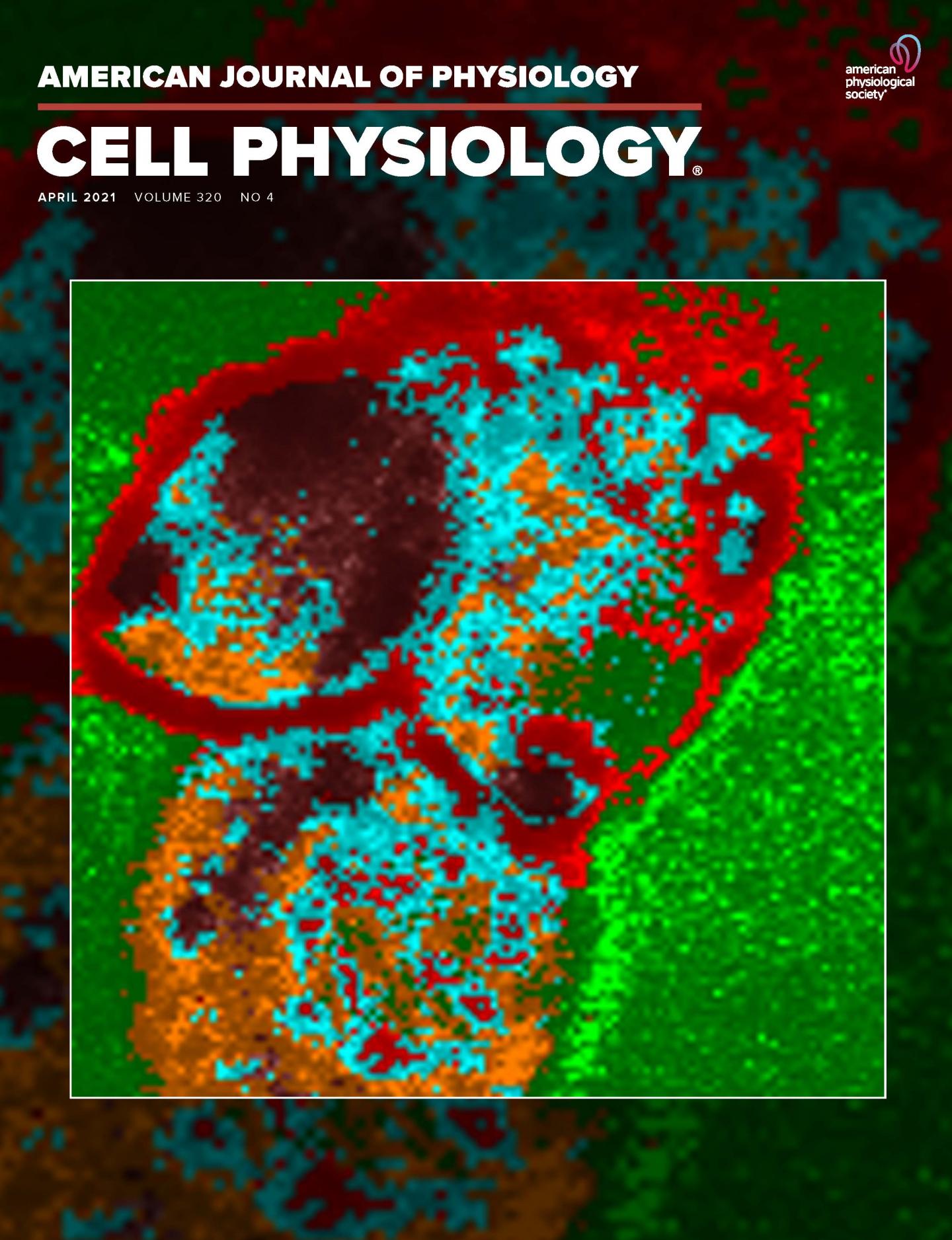
The research is featured on the cover of the April issue of American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology. The cover image was the work of Nilay Chakraborty, Ph.D., and Jason Solocinski at the University of Michigan-Dearborn, who developed a new process to obtain live images of the distribution of energy molecules in cells, showing how cells respond to changes in the cell culture conditions.
To fully realize the effect he reported, Skolik also cultured the cells for a longer period of time than usual.
“In the past, people would do a 12-hour adaptation to this new media. But what we showed is if you culture them for 4 to 5 weeks, you have a much more robust shift,” Skolik said.
“When it comes to gene expression, you get much more bang for the buck when you adapt them for a longer period.”
Although the modified serum for the cultures requires the additional step of dialysis and longer culture time, it can yield benefits at later testing stages.
“You would reserve this process for key experiments or toxicity screening,” Menze said. “However, if you go into a Phase 1 clinical trial and find toxicity there, it is way more expensive than using this method.”
###
Media Contact
Betty Coffman
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.