The veiny skeleton of a spinach leaf shows for the first time it can support the growth of artificial meat, a Boston College researcher reports
Credit: Food Bioscience
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (3/31/21) — Spinach, a cost-efficient and environmentally friendly scaffold, provided an edible platform upon which a team of researchers led by a Boston College engineer has grown meat cells, an advance that may accelerate the development of cultured meat, according to a new report in the advance online edition of the journal Food BioScience.
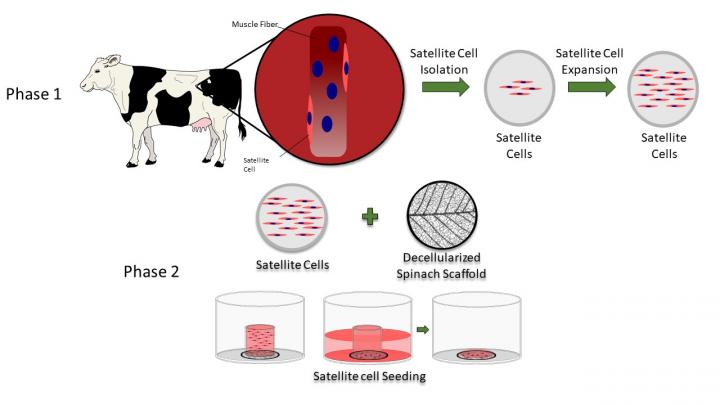
Stripped of all but its veiny skeleton, the circulatory network of a spinach leaf successfully served as an edible substrate upon which the researchers grew bovine animal protein, said Boston College Professor of Engineering Glenn Gaudette, the lead author of the new study. The results may help increase the production of cellular agriculture products to meet rising demand and reduce environmental costs.
“Cellular agriculture has the potential to produce meat that replicates the structure of traditionally grown meat while minimizing the land and water requirements,” said Gaudette, the inaugural chair of BC’s new Engineering Department. “We demonstrate that decellularizing spinach leaves can be used as an edible scaffold to grow bovine muscle cells as they develop into meat.”
Earlier advances by Gaudette in this area garnered worldwide attention. In 2017, Gaudette and a multi-university team showed that human heart tissue could be cultivated on a spinach leaf scaffold, which was chosen because it offered a natural circulatory system that is nearly impossible to replicate with available scientific tools and techniques.
“In our previous work, we demonstrated that spinach leaves could be used to create heart muscle patches,” said Gaudette. “Instead of using spinach to regrow replacement human parts, this latest project demonstrates that we can use spinach to grow meat.”
Gaudette said the team, which included Worcester Polytechnic Institute graduate students Jordan Jones and Alex Rebello, removed the plant cells from the spinach leaf and used the remaining vascular framework to grow isolated cow precursor meat cells. The cells remained viable for up to 14 days and differentiated into muscle mass.
“We need environmentally and ethically friendly ways to grow meat in order to feed the growing population,” said Gaudette, whose research is supported by New Harvest. “We set out to see if we can use an edible scaffold to accomplish this. Muscle cells are anchorage dependent, meaning they need to grab on to something in order to grow. In the lab, we can use plastic tissue culture plates, but plastic is not edible.”
The researchers point out that the successful results will lead to further characterization of the materials and scientific processes to better understand how to meet consumer demand and gauge how large-scale production could be accomplished in accordance with health and safety guidelines.
“We need to scale this up by growing more cells on the leaves to create a thicker steak,” said Guadette. “In addition, we are looking at other vegetables and other animal and fish cells.”
###
Media Contact
Ed Hayward
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




