Credit: University of Warwick
- In 2016 the Bank of England introduced plastic (polymer) banknotes, alongside 50 other countries that use polymer banknotes
- Counterfeit polymer banknotes on the streets have increased over the last few years, therefore the need to prevent and identify counterfeit banknotes has increased
- Using a technique called Polymer Substrate Fingerprinting, researchers from the University of Warwick are able to identify each banknote’s own fingerprint, which is unique and unclonable
Since the introduction of plastic (polymer) banknotes in 2016, the number of counterfeit notes on the streets has increased, however, researchers from Department of Computer Science at the University of Warwick have developed a novel technique called Polymer Substrate Fingerprinting, which identifies every banknote’s fingerprint which is unique and unclonable.
Polymer £5 notes were introduced to the UK in 2016, with the £10 note following in 2017 and the £20 note in 2020, however as polymer banknotes have been introduced to the UK, the number of counterfeit banknotes has also increased.
Researchers from the Department of Computer Science at the University of Warwick and their collaborator from Durham University, have had the paper ‘Anti-Counterfeiting for Polymer Banknotes Based on Polymer Substrate Fingerprinting’, published in the journal IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, in which they propose a novel technique called Polymer Substrate Fingerprinting, which can identify each banknote’s own unique, unclonable fingerprint.
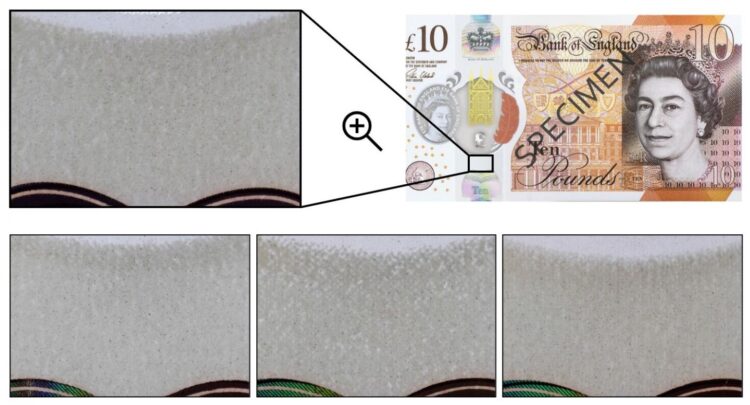
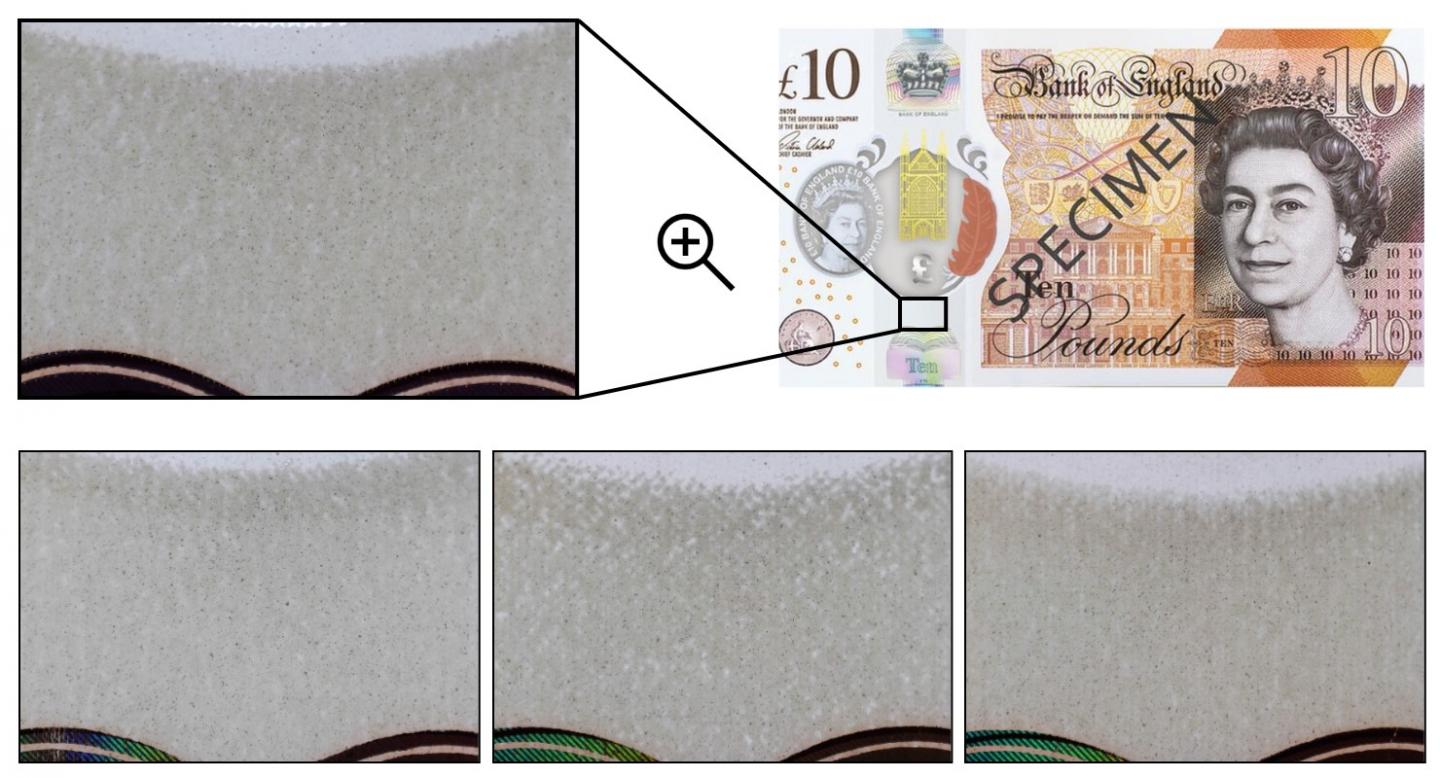
Researchers have found that every polymer banknote has a unique “fingerprint”, which is caused by the inevitable imperfection in the physical manufacturing process, whereby the opacity coating, a critical step during the production of polymer notes, leaves an uneven coating layer with a random dispersion of impurities in the ink. This imperfection results in random translucent patterns when a polymer banknote is back-lit by a light source.
Researchers have further presented a low-cost method to reliably capture these patterns, by using a commodity negative-film scanner, and processed them into a compact 2048-bit feature vector (fingerprint), to uniquely identify each individual banknote with extremely high accuracy.
The image analysis focuses on a small feature area, where the random translucent patterns from the opacity coating layer are directly exposed without being obstructed by security printing. For the example of the £10, the feature is chosen between the ‘ten’ hologram, and the see-through window. The random patterns extracted from the opacity coating layer form the unique ‘fingerprint’ is further protected by a veneer finish applied on both sides of the polymer note, and hence, is robust against rough handling in daily usage, similar to how the human iris is protected by the clear cornea in iris recognition.
Using 340 banknotes the researchers collected an extensive dataset of 6,200 sample images, and have proven that their method can identify each banknotes fingerprint successfully despite rough-daily handling.
Sheng Wang, a PhD student from the Department of Computer Science who has been designing, prototyping and testing this technique for that last two and half years comments:
“Although card and contactless payments tend to be more popular today banknotes still play a crucial role in society. In fact, there are 500 billion banknotes in circulation in the world, meaning counterfeit notes are a major threat to society and economy.
“Polymer banknotes have existing anti-counterfeit features, however we’ve found a new way to identify counterfeit notes without changing the manufacturing process, as the negative-film scanner can pick up each banknote’s unique fingerprint which cannot be cloned.
“We have also found the extracted fingerprints contain around 900 bits of entropy, which is dramatically higher than 249-bit entropy for iris-codes used in iris recognition. This high entropy makes our method extremely scalable to identify every polymer note globally.”
Professor Feng Hao, from the Department of Computer Science comments:
“Like every human has unique biometric features, we have found every polymer banknote has its own ‘bio-metric’, which is unique, naturally occurring, and can’t be physically cloned. This new finding gives us the basis to design a completely new anti-counterfeiting method for banknotes.
“It is universally believed that once counterfeiters have access to essentially the same printing equipment and ink as used by legitimate government to print fake banknotes the game is over, as there will be no way to distinguish genuine and fake banknotes. Contrary to this belief our research shows, perhaps surprisingly, that there is still hope to defeat counterfeiting even in that extreme scenario.”
###
Media Contact
Alice Scott
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.