Credit: ©Science China Press
The diesel engine is the backbone of transportation due to its irreplaceability as the primary power source for the freight, navigation and marine engine industries and non-road engineering machinery for the foreseeable future. However, the control of contaminants from fuel combustion has become an urgent global concern. Nitrogen oxides are the primary pollutants from transportation and can contribute to the formation of haze, photochemical smog and acid rain. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ammonia (NH3-SCR) technology has been successfully and commercially applied for controlling pollution from diesel vehicle exhaust. The development of efficient and stable NH3-SCR catalysts has been pursued by scientists in the past decades to meet the complicated operating conditions in these vehicles.
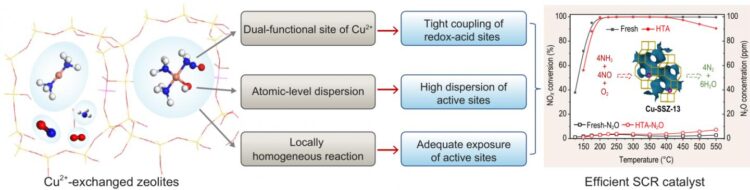
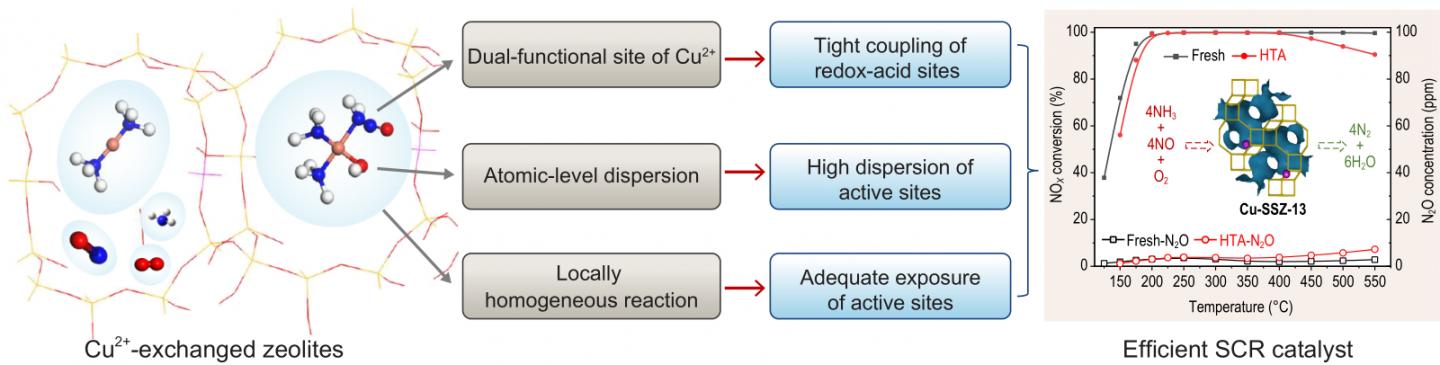
Cu-based small-pore zeolites have been demonstrated to be very promising candidates for efficient and stable NH3-SCR catalysts due to their unique structural features and physicochemical properties, e.g., small-pore structure, large cavity, large ion-exchange sites and ligand effect between Cu ions and reactant NH3. As a representative example, Cu-SSZ-13 small-pore zeolite has been commercially utilized to eliminate NOx from diesel vehicles.
In a new overview published in the Beijing-based National Science Review, scientists at Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing University of Chemical Technology and Zhejiang University present the latest advances in Cu-based small-pore zeolites applied to the NH3-SCR reaction. They summarize the major advances in Cu-SSZ-13 applied to the NH3-SCR reaction, including the state of copper species, the standard and fast SCR reaction mechanisms, the hydrothermal deactivation mechanism, poisoning resistance and synthetic methodology. They give a valuable summary of new insights on the matching between SCR catalyst design principles and the characteristics of Cu2+-exchanged zeolitic catalysts, highlighting the significant opportunity presented by zeolite-based catalysts. Moreover, more hydrothermally stable Cu-AEI and Cu-LTA zeolites are elaborated as well as other alternative zeolites applied to NH3-SCR. Principles for designing zeolites with excellent NH3-SCR performance and hydrothermal stability are proposed. These scientists likewise outlined the potential development directions of future Cu-based small-pore zeolites.
“In fact, zeolites with small-pore structures and adequate ion-exchange sites have great potential for utilization as NH3-SCR catalysts with high deNOx efficiency and hydrothermal stability,” they state from a broader perspective. Development of new types of small-pore zeolites with high SCR activity and hydrothermal stability is still worthwhile based on the design principles proposed in the review, since there is still considerable room in the small-pore zeolite family for researchers to explore.
###
See the article:
Yulong Shan, Jinpeng Du, Yan Zhang, Wenpo Shan, Xiaoyan Shi, Yunbo Yu, Runduo Zhang, Xiangju Meng, Feng-Shou Xiao, Hong He.
Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: opportunities and challenges of Cu-based small-pore zeolites.
Natl Sci Rev nwab010
https:/
The National Science Review is the first comprehensive scholarly journal released in English in China that is aimed at linking the country’s rapidly advancing community of scientists with the global frontiers of science and technology. The journal also aims to shine a worldwide spotlight on scientific research advances across China.
Media Contact
Hong He
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.