Credit: by Haotian Wu, Xin Xin Gao, Lei Zhang, Guo Dong Bai, Qiang Cheng, Lianlin Li, and Tie Jun Cui
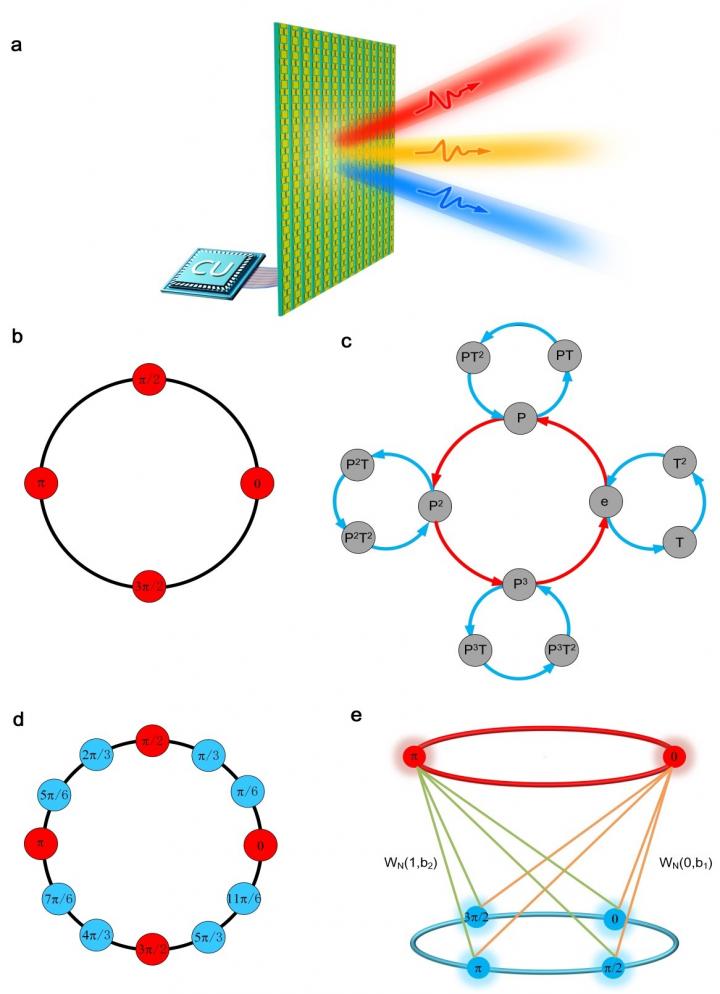
Spatiotemporal metasurfaces, driven by ultrafast dynamic modulations, opened up new possibilities for manipulating the harmonic modes of electromagnetic waves and generations of exotic physical phenomena, such as dispersion cancellation, Lorentz reciprocity broken, and Doppler illusions. In recent years, rapid development of information technologies have stimulated many information processing applications for metasurfaces, including computational imaging, wireless communications, and performing mathematical operations. With increasing amount of researches focused on the topic of information processing with metasurfaces, a general theory is urgently required to characterize the information processing abilities of the spatiotemporal metasurfaces. In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, Prof. Tie Jun Cui’s group at Southeast University (SEU) has reported a breakthrough on this topic. In this work, the information transition mechanisms of spatiotemporal metasurfaces are proposed and analyzed, in which the group extension and independent control of multiple harmonics are revealed and characterized as two major information transition mechanisms of the spatiotemporal metasurfaces.
Specifically, the group extension mechanism could be adopted to extend the output phase states of each meta-atom by a factor of q, where q is a function over the modulation periodicity, input phase states, and harmonic index. Accordingly, the output spectral response states of the spatiotemporal metasurface are extended greatly, such that more accurate manipulations of the electromagnetic information could be obtained without increasing the design complexity of the metasurfaces. Additionally, the researchers demonstrated that the independent control of the spectral responses of the spatiotemporal metasurface could be realized as well. The independent control of multiple harmonics could open up new possibilities for the metasurface-based multitasking, by which electromagnetic information could be independently processed with frequency-gapped channels. A proof-of-concept experiment is performed in the microwave regime to verify the mechanisms of the group extension and independent control of multiple harmonics with the spatiotemporal metasurface.
By incorporating the proposed model with the Shannon’s entropy theory, the authors further discovered the information transition efficiencies of the spatiotemporal metasurfaces with respect to the above two mechanisms. The obtained results could be applied to predict the channel capacity of the spatiotemporal metasurface, which would be helpful to guide the analysis and design of spatiotemporal metasurfaces for wireless communications. Moreover, they demonstrated that the output spectral responses of the spatiotemporal metasurface can help prove the Fermat’s little theorem, which in turn might provide more clues to understand the non-vanished spectra responses of the spatiotemporal metasurfaces.
“The proposed theory establishes a quantitative framework to characterize the information transition capabilities of the spatiotemporal metasurfaces, which provides deeper physical insights in understanding the spatiotemporal metasurfaces from the information perspective, and offers new approaches to facilitate the analysis and design. The presented framework and obtained results, with wide-ranged spectral applicability, would be helpful to lay the groundwork for future researches into the regime of information-based spatiotemporal metasurfaces, and expected to enable new information-oriented applications including cognitive harmonic wavefront engineering, intelligent computational imaging, and the 6th generation (6G) wireless communications.” the scientists forecast.
###
Media Contact
Tie Jun Cui
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




