Spanish scientists conduct the most complete study to date of the feeding patterns of the tiger mosquito in Europe
Credit: university of granada
This study, published recently in the international journal Insects, was conducted by researchers from the University of Granada, the Doñana Biological Station, and the Biomedical Research Networking Centre for Epidemiology and Public Health (CIBERESP)
Researchers from the University of Granada (UGR), the Doñana Biological Station (EBD-CSIC), and the Biomedical Research Networking Centre for Epidemiology and Public Health (CIBERESP) have carried out the most comprehensive study to date of the eating patterns of the tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) and other invasive species of the same genus in Europe. The results of the study were recently published in the international journal Insects.
This research, which reviews all previously published studies on this topic, shows that these species of mosquitoes feed off different groups of vertebrates, especially mammals, and humans are also common hosts. Not surprisingly, human blood represents 93% of the blood meals of Aedes aegypti, the mosquito responsible for yellow fever.
Mosquitoes are one of the main groups of vector insects–that is, insects involved in the transmission of major pathogens that adversely affect people, livestock, and wildlife. As with other groups of animals, different species of invasive mosquitoes have become established in areas outside their original range. This is the case with different species of mosquitoes of the Aedes genus, which are of particular importance from the public health perspective, due to their capacity to transmit pathogens that cause serious diseases.
“Thus, the appearance of these species can modify the local epidemiology of many pathogens in invaded areas, including pathogens that circulate naturally in the environment, or imported pathogens,” explains one of the authors of the work, Josué Martínez de la Puente, a researcher at the UGR’s Department of Parasitology.
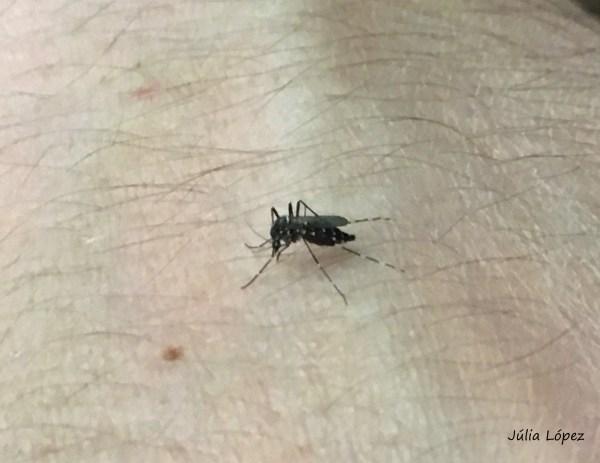
So far, four invasive species of the Aedes genus have established populations in Europe, which include such relevant vector species as the tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus.
Blood meals
To complete their life cycle and the development of their eggs, female mosquitoes require blood meals taken from different vertebrate hosts. In addition to causing discomfort, the bites they cause can transmit different pathogens. “Therefore, this blood-feeding behaviour represents a fundamental factor, the relevance of which needs to be studied to understand the epidemiology of different diseases. In this review article, we study the feeding patterns of those four invasive mosquitoes of the Aedes genus in Europe,” explains Martínez de la Puente.
The results show that these species of mosquitoes feed off different groups of vertebrates, especially mammals. Humans are common hosts for these mosquitoes, representing 93% of the blood meals of the Aedes aegypti species. In addition, mosquitoes are capable of feeding on the blood of other groups of vertebrates, including birds and even ectothermic animals (those whose body temperature changes in line with the temperature of the environment).
Given their capacity to transmit different pathogens and their feeding rates among humans, invasive mosquito species of the Aedes genus may have a significant impact on the transmission of these pathogens in urban and periurban areas, the authors conclude.
###
Media Contact
Josué Martínez de la Puente
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




