Credit: Masashi Yukawa & Takashi Toda, Hiroshima University
Cells replicate their genetic material and divide into two identical clones, perpetuating life — until they don’t. Some cells pause — or are intentionally made to pause — in the process. When the cell resumes division after such a pause, a displaced nucleus — an essential part of cell survival — can become caught in the fissure, splitting violently and killing both cells. But that is not always the case; some mutant cells can recover by pushing their nucleus to safety. Researchers from Hiroshima University in Japan are starting to understand how in the first step toward potential cell death rescue applications.
The results were published on Jan. 22 in iScience, a Cell Press journal.
The researchers examined fission yeast, a common model organism used for studying the molecular mechanisms underpinning the cell cycle. These rod-shaped cells provide an ideal view of each phase of mitosis, the process by which the cell duplicates and divides. In this process, the genetic-containing nucleus migrates to the center of the cell, dissolves its protective envelope, replicates and reassembles as two on each side of the cell. The center of the cell then pinches apart.
“Proper nuclear positioning is essential for the execution of a wide range of cellular processes in eukaryotic cells, which contain a nucleus bound in a membrane,” said first author Masashi Yukawa, assistant professor in the Hiroshima Research Center for Healthy Aging and the Graduate School of Integrated Sciences for Life, Hiroshima University. “Yet how the nucleus is retained in the center of the cell during mitosis remains elusive.”
Researchers can use drugs to pause this process and study it further or to help halt unhealthy cell division in various diseases. The nucleus, not yet divided, remains in the center of the cell.
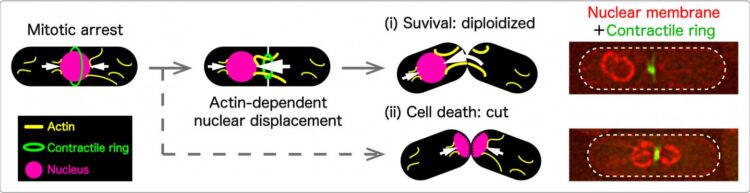
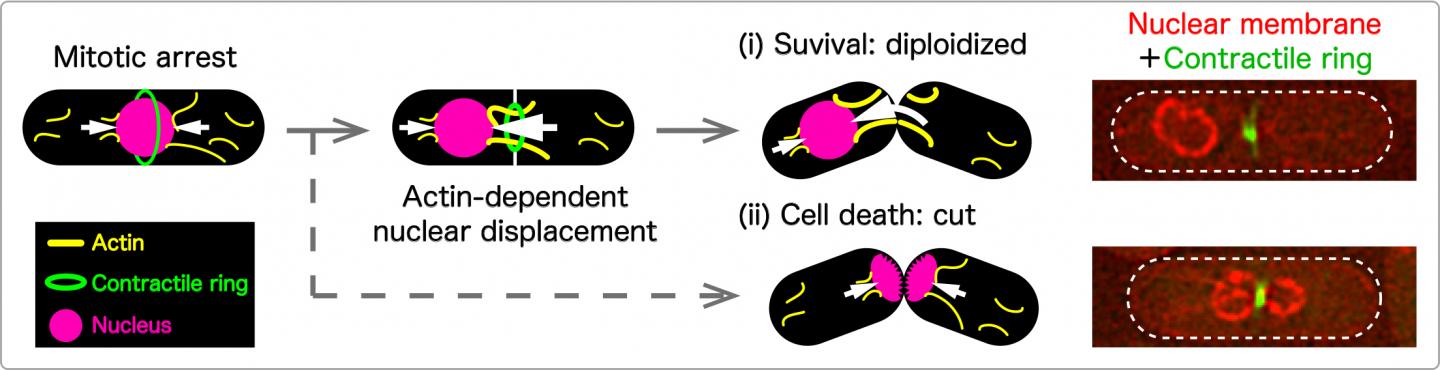
“We found several fission yeast mutants that arrest in mitosis all displace the nucleus towards one end of the cell,” Yukawa said. “Our questions are how and why these mutant cells translocate their nucleus from the cell center during mitosis.”
They found that microfilaments made of a protein called actin appear to play a role. These cable-like filaments act as arms, pushing the nucleus to the center of the cell.
“During prolonged mitotic arrest, the forces of the actin cables become unbalanced, pushing the nucleus to one side,” Yukawa said.
The researchers also found that the mitosis-induced ring that constricts the original cell into two helps push an off-balanced nucleus further to one side. When the cell splits, the nucleus remains intact.
“Eukaryotic cells may have a novel mitotic surveillance mechanism that involves an actin-mediated nuclear movement to escape from disastrous mitotic catastrophe,” Yukawa said. “We will continue to elucidate the mechanism by which cells keep the correct position of their nucleus during mitosis.
###
Yasuhiro Teratani and Takashi Toda, both with the Laboratory of Molecular and Chemical Cell Biology in the Graduate School of Integrated Sciences for Life at Hiroshima University, also authored this work. Toda is also affiliated with the Hiroshima Research Center for Healthy Aging at Hiroshima University.
The Japan Society for the Promotion of Science supported this work.
About Hiroshima University
Since its foundation in 1949, Hiroshima University has striven to become one of the most prominent and comprehensive universities in Japan for the promotion and development of scholarship and education. Consisting of 12 schools for undergraduate level and 4 graduate schools, ranging from natural sciences to humanities and social sciences, the university has grown into one of the most distinguished comprehensive research universities in Japan.
English website: https:/
Media Contact
Norifumi Miyokawa
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.