Credit: Michigan State University
EAST LANSING, Mich. – The day of charging cellphones with finger swipes and powering Bluetooth headsets simply by walking is now much closer.
Michigan State University engineering researchers have created a new way to harvest energy from human motion, using a film-like device that actually can be folded to create more power. With the low-cost device, known as a nanogenerator, the scientists successfully operated an LCD touch screen, a bank of 20 LED lights and a flexible keyboard, all with a simple touching or pressing motion and without the aid of a battery.
The groundbreaking findings, published in the journal Nano Energy, suggest "we're on the path toward wearable devices powered by human motion," said Nelson Sepulveda, associate professor of electrical and computer engineering and lead investigator of the project.
"What I foresee, relatively soon, is the capability of not having to charge your cell phone for an entire week, for example, because that energy will be produced by your movement," said Sepulveda, whose research is funded by the National Science Foundation.
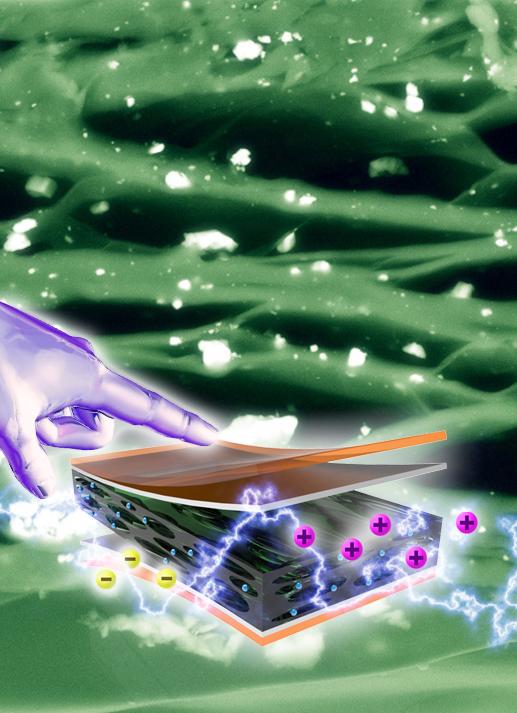
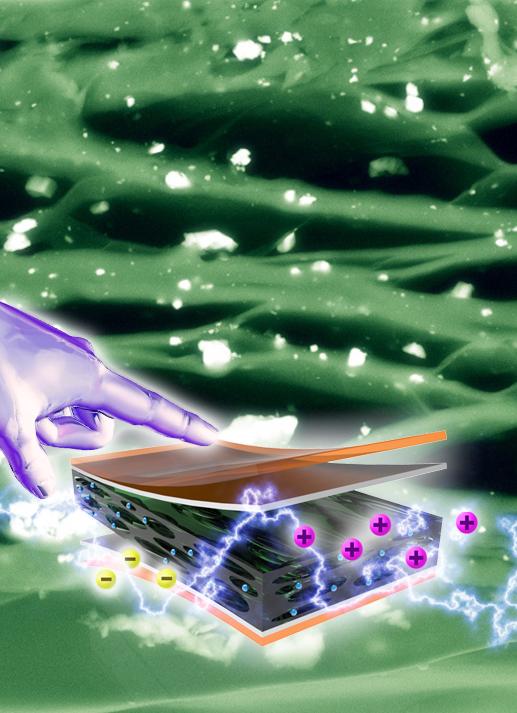
The innovative process starts with a silicone wafer, which is then fabricated with several layers, or thin sheets, of environmentally friendly substances including silver, polyimide and polypropylene ferroelectret. Ions are added so that each layer in the device contains charged particles. Electrical energy is created when the device is compressed by human motion, or mechanical energy.
The completed device is called a biocompatible ferroelectret nanogenerator, or FENG. The device is as thin as a sheet of paper and can be adapted to many applications and sizes. The device used to power the LED lights was palm-sized, for example, while the device used to power the touch screen was as small as a finger.
Advantages such as being lightweight, flexible, biocompatible, scalable, low-cost and robust could make FENG "a promising and alternative method in the field of mechanical-energy harvesting" for many autonomous electronics such as wireless headsets, cell phones and other touch-screen devices, the study says.
Remarkably, the device also becomes more powerful when folded.
"Each time you fold it you are increasing exponentially the amount of voltage you are creating," Sepulveda said. "You can start with a large device, but when you fold it once, and again, and again, it's now much smaller and has more energy. Now it may be small enough to put in a specially made heel of your shoe so it creates power each time your heel strikes the ground."
Sepulveda and his team are developing technology that would transmit the power generated from the heel strike to, say, a wireless headset.
###
Contributors to the study included MSU doctoral students Wei Li, David Torres and Tongyu Wang, as well as Chuan Wang, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering.
Media Contact
Andy Henion
[email protected]
517-355-3294
@MSUnews
http://msutoday.msu.edu/journalists/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag