Credit: ©Science China Press
Metal-based catalysts have shown considerable performances in heterogeneous catalysis for the production of various valuable products. With the development of modern chemical industry, enormous efforts have been devoted to the design and fabrication of highly efficient metal-based heterogeneous catalysts. Among the reported synthesis strategies, metal encapsulation, i.e., to uniformly disperse the nanoscale guest molecules within the pores/layers/vacancies of the porous supports, has been considered as one of the most effective protocols to enrich the amounts of active sites and enhance the interactions between the guest molecules and supports, thus promoting the activity and durability of the as-prepared catalysts through nanoconfinement and size effects. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), a class of emerging porous materials featuring large specific areas and tunable nanostructures, have been widely investigated as one of the ideal hosts for metal encapsulation.
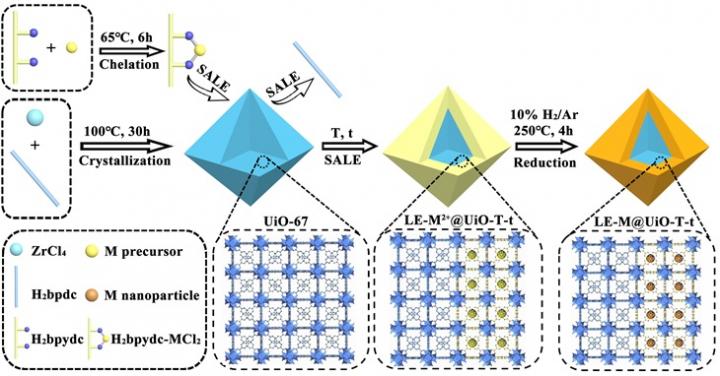
Recently, the research group of Professor Yingwei Li at South China University of Technology demonstrates a solvent assisted ligand exchange-hydrogen reduction (SALE-HR) strategy to selectively encapsulate ultrafine metal nanoparticles (Pd or Pt) within the shallow layers of MOF for highly efficient hydrogenation reactions.
Taking the synthesis of [email protected] as an example, UiO-67 was primarily synthesized under solvothermal condition. Subsequently, the H2bpydc-PdCl2 (H2bpydc represents 2,2′-bipyridine-5,5′-dicarboxylic acid) was utilized to substitute for the initial ligand (i.e., H2bpdc) at the shallow layers of UiO-67 through the solvent assisted ligand exchange (SALE) method, followed by hydrogen reduction (HR) of the Pd in 10% H2/Ar flow. Characterization results implied the selective encapsulation and homogeneous distribution of ultrafine Pd nanoparticles (ca. 1.85 nm) within the shallow layers of monodispersed octahedral UiO-67 crystalline. In addition, the composition of the obtained composites as well as the location and sizes of the encapsulated Pd nanoparticles could be easily modified by tuning the time and temperature of SALE. Besides, this strategy was also applicable for the encapsulation of Pt.
The selective encapsulation of Pd within the shallow layers of UiO-67 could efficiently reduce the influence of mass transfer resistance in liquid phase reactions, enhance the accessibility and metal dispersion of Pd active sites and therefore promote the metal utilizations. Besides, the nanoconfinement of UiO-67 can also suppress the Pd aggregation or leaching, hence enhancing the stability of the catalysts. As a result, the obtained [email protected] exhibited remarkable catalytic performances in the hydrogenation of nitroarenes, achieving a nearly quantitative conversion of nitrobenzene to aniline with a turnover frequency (TOF) value as high as 600 h?1. This work might open an avenue for the encapsulation of nanoparticles, nanoclusters or even single atoms of various metals within porous materials like MOFs for frontier applications including heterogeneous catalysis demonstrated here.
###
See the article:
Cui Z, Fan T, Chen L, Fang R, Li C, Li Y. Encapsulation of ultrafine Pd nanoparticles within the shallow layers of UiO-67 for highly efficient hydrogenation reactions. Sci. China Chem., 2020, DOI:10.1007/s11426-020-9881-7
Media Contact
Yingwei Li
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




