Credit: by Aaron M. Kho, Tingwei Zhang, Jun Zhu, Conrad W. Merkle, Vivek J. Srinivasan
During the early 1800s, the first spectrometer was developed by spreading different colors of sunlight onto a screen. It was later noticed that certain dark bands in the solar spectrum, known as Fraunhofer lines, are associated with chemical elements in the solar atmosphere. Since then, scientists have applied spectroscopy to many different fields including astronomy, medicine, agriculture, chemistry, and security.
Typically composed of a diffractive element (such as a prism), a focusing element (such as a lens), and a detector, spectrometers measure emitted light intensity on a wavelength-by-wavelength basis to retrieve information about an object of interest. In a common design, the detector is a camera with pixels that measure different parts of the spectrum at the same time. Ideally, the ability to distinguish fine wavelength features, known as the spectral resolution, needs to be optimized. However, current approaches to characterize spectral resolution thoroughly require expensive additional components or intensive manual labor.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Aaron Kho from the Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of California Davis, United States, have developed a simple method to comprehensively assess spectrometer performance within seconds using only incoherent excess noise, i.e. fluctuations of light in excess of fundamental shot noise.
“This application of excess noise was originally inspired by speckle. Also initially viewed as a nuisance after the invention of the laser, speckle was later discovered to be useful for measuring blood flow, particle size, and the diffraction limit. Similarly, we found that excess noise can be useful too,” Mr. Kho said.
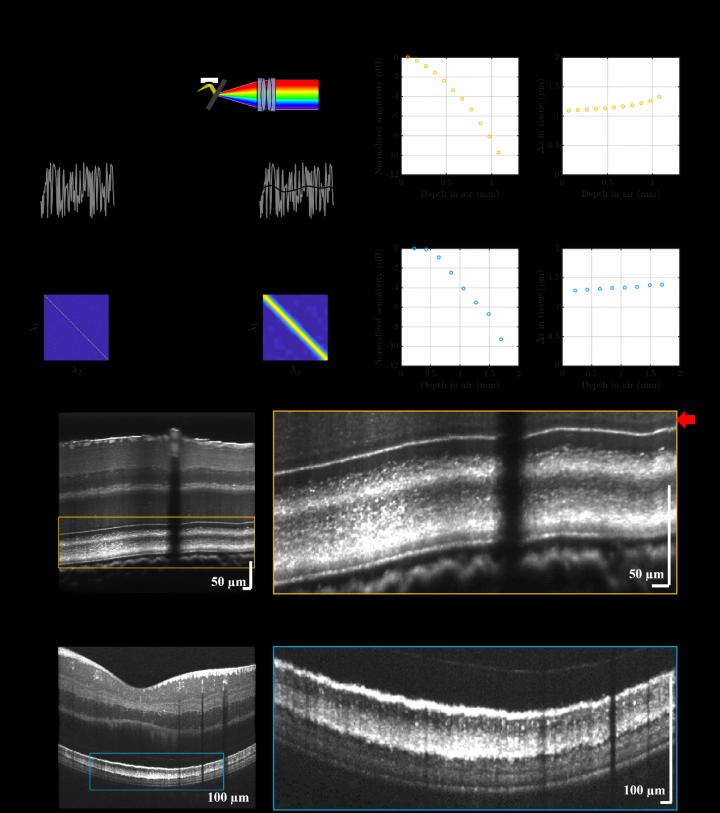
Here, Kho and colleagues propose that incoherent excess noise instills broadband light with high-resolution spectral encoding. With this insight, they devise and demonstrate an excess noise approach for rapidly characterizing the spectral resolution of broadband spectrometers. They also demonstrate a related, excess noise approach that is applied to two different spectrometers to create a precise one-to-one mapping between pixels that detect the same wavelength. The scientists call this procedure cross-calibration. Remarkably, both approaches are actually strengthened by incoherent excess noise, which degrades performance in most other photonics applications.
A major biomedical application of spectrometers is spectral domain Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), an imaging modality where the spectrometer measures an interference pattern to produce fine depth-resolved retinal images of living subjects. To date, spectrometer performance has limited the development of OCT at visible wavelengths. The authors demonstrate the utility of their excess noise characterization approach by employing it to provide feedback during visible light OCT spectrometer alignment. Achieving improved spectral resolution uniformity across a broad wavelength range, they demonstrate high quality visible light OCT imaging of the human and mouse retinas. The improved uniformity of depth resolution and sensitivity help to reveal a new band in the mouse photoreceptor layer.
“The proposed characterization and cross-calibration approaches will improve the rigor and reproducibility of data in the many fields that use spectrometers. The approaches seem to work with both superluminescent diodes and some supercontinuum light sources, which are widespread,” said Vivek J. Srinivasan, Associate Professor of Biomedical Engineering at University of California Davis and senior author on the study.
He continued to forecast: “The idea that the spectral encoding provided by excess noise can serve a useful purpose is also important. This insight could aid in the discovery of other applications where excess noise is similarly useful.”
###
Media Contact
Vivek J. Srinivasan
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




