Credit: Phil Manlick. Photo credits (Left to Right): Flickr/Tambako the Jaguar/Renee Grayson and Wikimedia Commons/United States National Park Service/United States Fish and Wildlife Service.
MADISON – Ecologists at the University of Wisconsin-Madison have found that carnivores living near people can get more than half of their diets from human food sources, a major lifestyle disruption that could put North America’s carnivore-dominated ecosystems at risk.
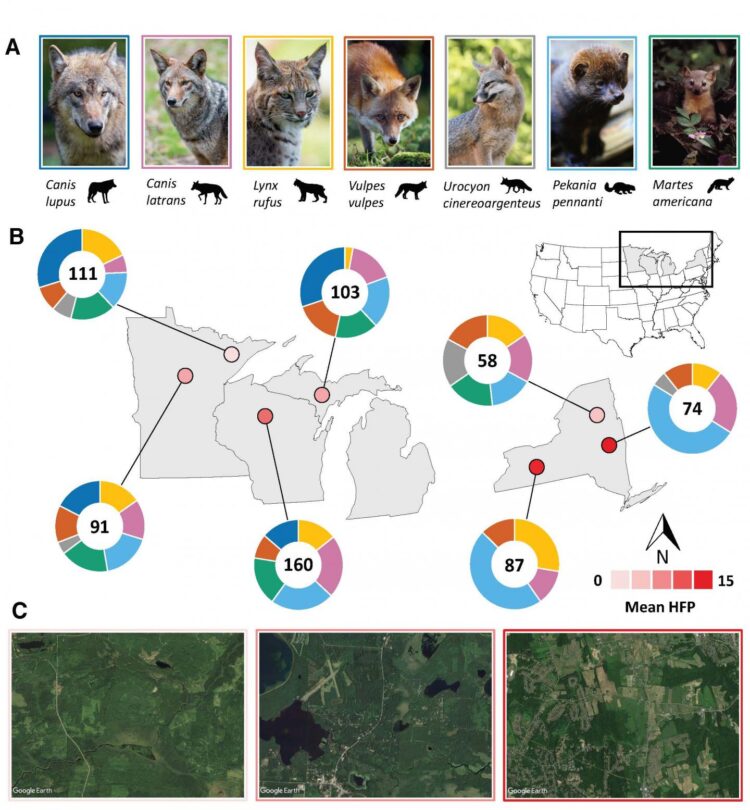
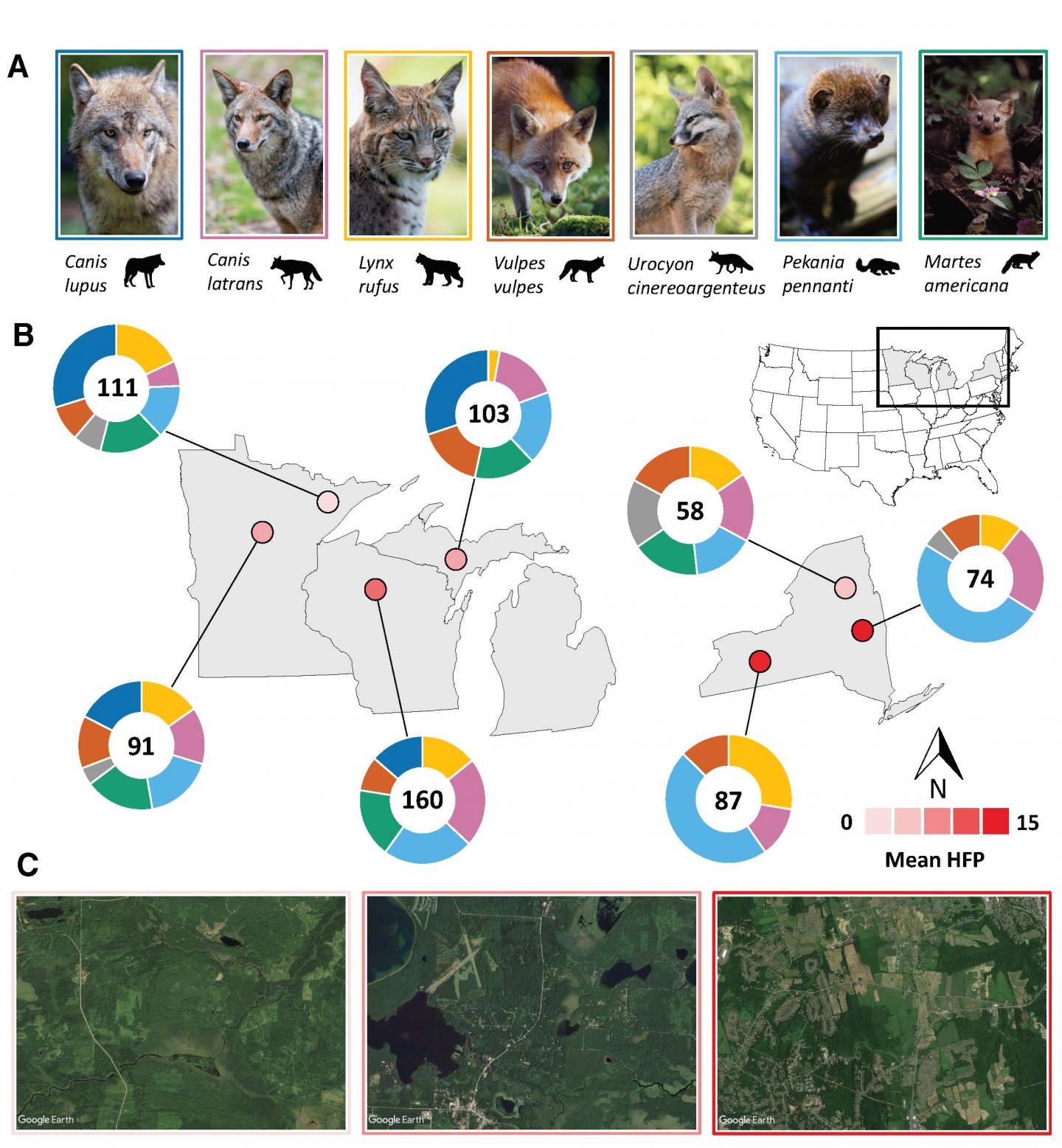
The researchers studied the diets of seven predator species across the Great Lakes region of the U.S. They gathered bone and fur samples for chemical analysis from areas as remote as national parks to major metropolitan regions like Albany, New York. They found that the closer carnivores lived to cities and farms, the more human food they ate.
While evolution has shaped these species to compete for different resources, their newfound reliance on a common food source could put them in conflict with one another. That conflict could be reordering the relationship between different carnivores and between predators and prey, with an unknown but likely detrimental impact on ecosystems that evolved under significant influence of strong predators.
Jon Pauli, a UW-Madison professor of forest and wildlife ecology, and his former graduate student Phil Manlick, published their findings this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The study is the most comprehensive look yet at how most of the region’s major carnivores — like gray wolves, coyotes, and bobcats — have changed their diets in response to people.
How much human food they ate varied considerably by location. On average, more than 25 percent of the carnivores’ diets came from human sources in the most human-altered habitats.
It also varied by species. For instance, committed carnivores like bobcats ate a relatively small amount of human food. “But what you see is that the sort of generalist species that you might expect — coyotes, foxes, fishers, martens — in human-dominated landscapes, they’re getting upwards of 50 percent of their diet from human foods,” says Manlick, the lead author of the study who is now a postdoctoral researcher at the University of New Mexico. “That’s a relatively shocking number, I think.”
Pauli and Manlick found that relying on human food sources increased how much carnivores overlapped one another in their competition for food. Compared to when these predators vie for distinct prey, this increased competition could lead to more conflicts between animals. Their reliance on human food could also make the carnivores vulnerable to human attacks near towns, or even change how and when they hunt traditional prey, with potentially harmful ecological consequences.
The researchers studied the diets of almost 700 carnivores, including red and gray foxes, fishers, and American martens. They gathered bone and fur samples from Minnesota, Wisconsin, New York and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan with the help of state and federal researchers and citizen-science trappers. The researchers compared the carnivores’ diets to the extent of human development in the region, which varied from essentially pristine wilderness to urban sprawl.
Thanks to quirks in how plants incorporate carbon as they grow, a sample of bone or fur is enough to get a snapshot of an animal’s diet. Different weights, or isotopes, of carbon are common in different plants — and in the animals who ultimately eat them.
“Isotopes are relatively intuitive: You are what you eat,” says Manlick. “If you look at humans, we look like corn.”
Human foods, heavy in corn and sugar, lend them distinctive carbon signatures. In contrast, the diets of prey species in the wild confer their own carbon signatures. The ratio of these two isotope fingerprints in a predator’s bone can tell scientists what proportion of their diet came from human sources, either directly or from their prey that ate human food first.
The geographic extent of the study and the large number of species the ecologists examined demonstrate that the trend of human food subsidies in carnivore diets is not limited to a single location or species. The ultimate outcome of such widespread disruptions remains unclear.
“When you change the landscape so dramatically in terms of one of the most important attributes of a species — their food — that has unknown consequences for the overall community structure,” says Pauli. “And so I think the onus is now on us as ecologists and conservation biologists to begin to understand these novel ecosystems and begin to predict who are the winners and who are the losers.”
###
This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation (grant DGE-1144752), the National Institute of Food and Agriculture (Hatch Projects 1006604 and 1003605), and the National Park Service.
–Eric Hamilton, (608) 263-1986, [email protected]
Media Contact
Jon Pauli
[email protected]