A new way to reduce heat penetration through building walls. Application of a phase change material and bubble injections to building walls.
Credit: Korea Institue of Science and Technology(KIST)
With the summer heat becoming increasingly unbearable and prolonged over the years due to climate change, the cooling load in the summertime has also been on the rise. Insulation is currently the primary solution for blocking heat from entering a building, but by applying an additional material that can delay heat penetration, it can suppress the indoor temperature from rising and in turn lower the cooling load of the building.
A research team in Korea has developed a new material for buildings walls that can help reduce the penetration of heat from the outside. The team directed by Dr. Sarng Woo Karng from the National Research Agenda Division of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) revealed that they have successfully lowered heat penetration through building walls by applying a phase change material (PCM).
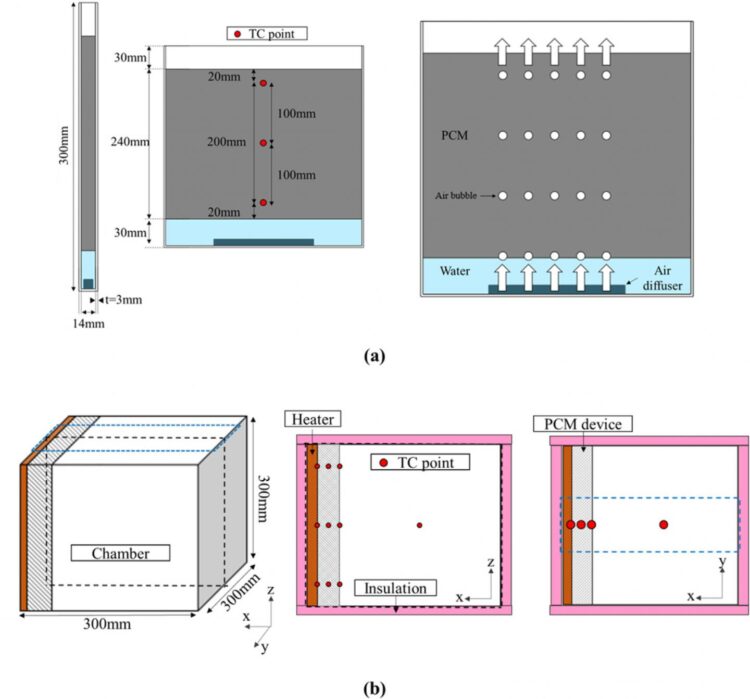
PCMs refer to materials that absorbs or releases heat from/to the surrounding area but does not change temperature during phase change. One of the most common types is paraffin oil, which is used to make candles. A solid PCM absorbs heat as it transitions into liquid phase, so by using a case to hold it when it is in liquid phase without causing any leakage, it is possible to apply them to a building wall to block heat from entering inside.
The problem is, however, PCMs do not melt evenly from the outside toward the inside during phase transition from solid to liquid. To be more specific, PCMs turn into liquid starting from the outermost layer, and the parts that are hot move upward, while the parts that are still relatively cool move downward. Thus, while the upper part may have completely melted, the lower part will have not, and as a result, heat will penetrate into the building through the area where the PCM is in liquid phase. Ultimately, the PCM becomes ineffective in controlling the indoor temperature and is rendered useless.
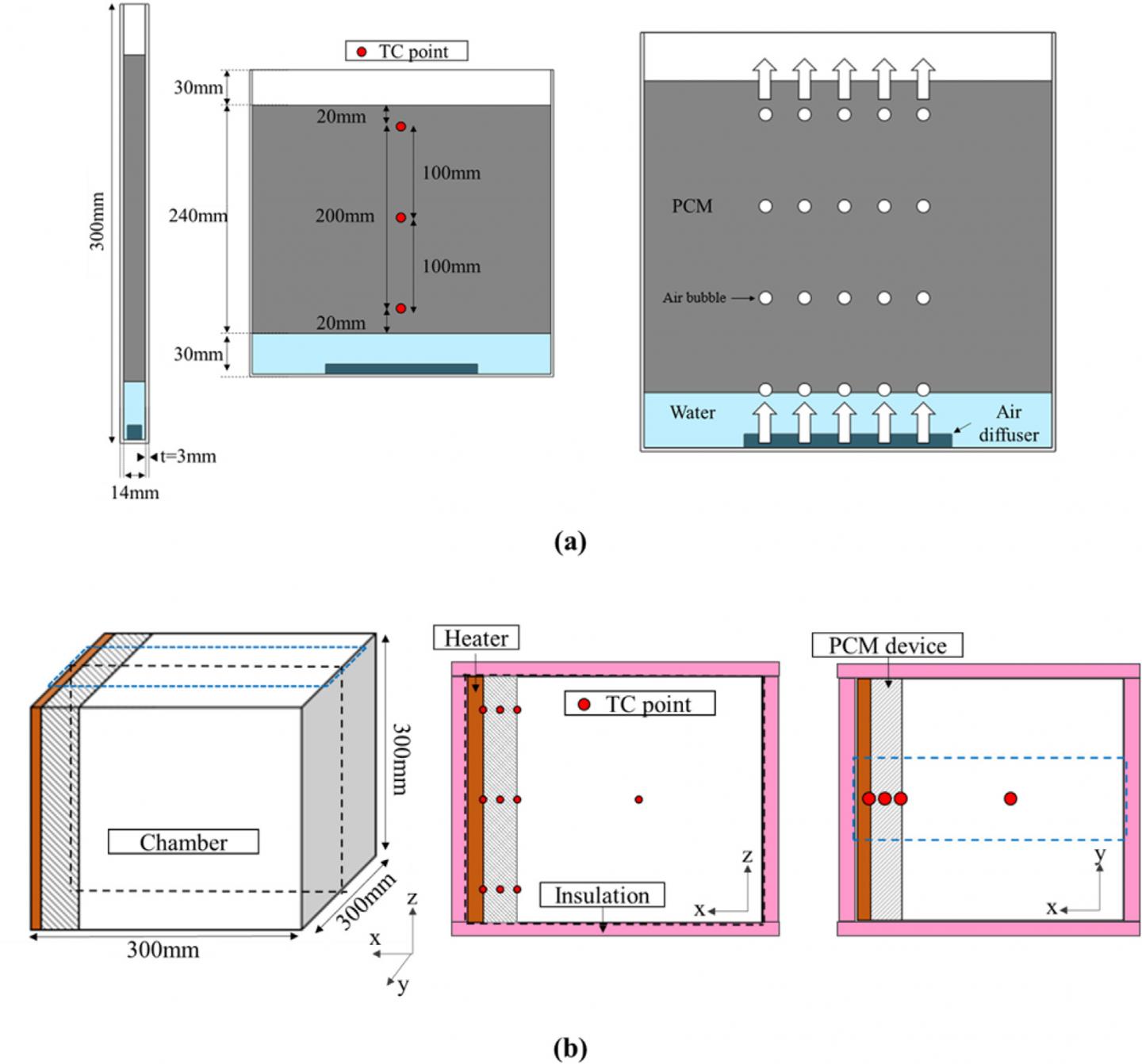
Dr. Karng’s team addressed the non-uniform phase change with bubble injections. By injecting bubbles into bottom part of the PCM during phase transition enabled uniform circulation of the PCM in liquid phase. As a result, the PCM melted from the area closest to the envelope in a uniform manner, and heat penetration was inhibited across the building wall until the entire PCM melted.
Dr. Karng said, “We expect that the insulating wall using the PCM bubble generator used in this study will contribute to reducing the amount of energy used to heat or cool a building. Insulation techniques using PCMs helps reduce heat penetration, in combination with the building insulating material, and it can also be used as the outer walls of zero-energy buildings.”
###
This study was carried out with a grant from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), as part of the Institutional R&D Program of KIST. It was published in the latest edition of Energy Conversion and Management (Top 1.87% in the field of JCR), a leading international journal in the energy sector.
Media Contact
Do-Hyun Kim
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.