Credit: Adapted from ACS Central Science 2020, DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.0c01056
As the COVID-19 pandemic rages on, researchers are working overtime to develop vaccines and therapies to thwart SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the disease Many efforts focus on the coronavirus spike protein, which binds the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) on human cells to allow viral entry. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have uncovered an active role for glycans — sugar molecules that can decorate proteins — in this process, suggesting targets for vaccines and therapies.
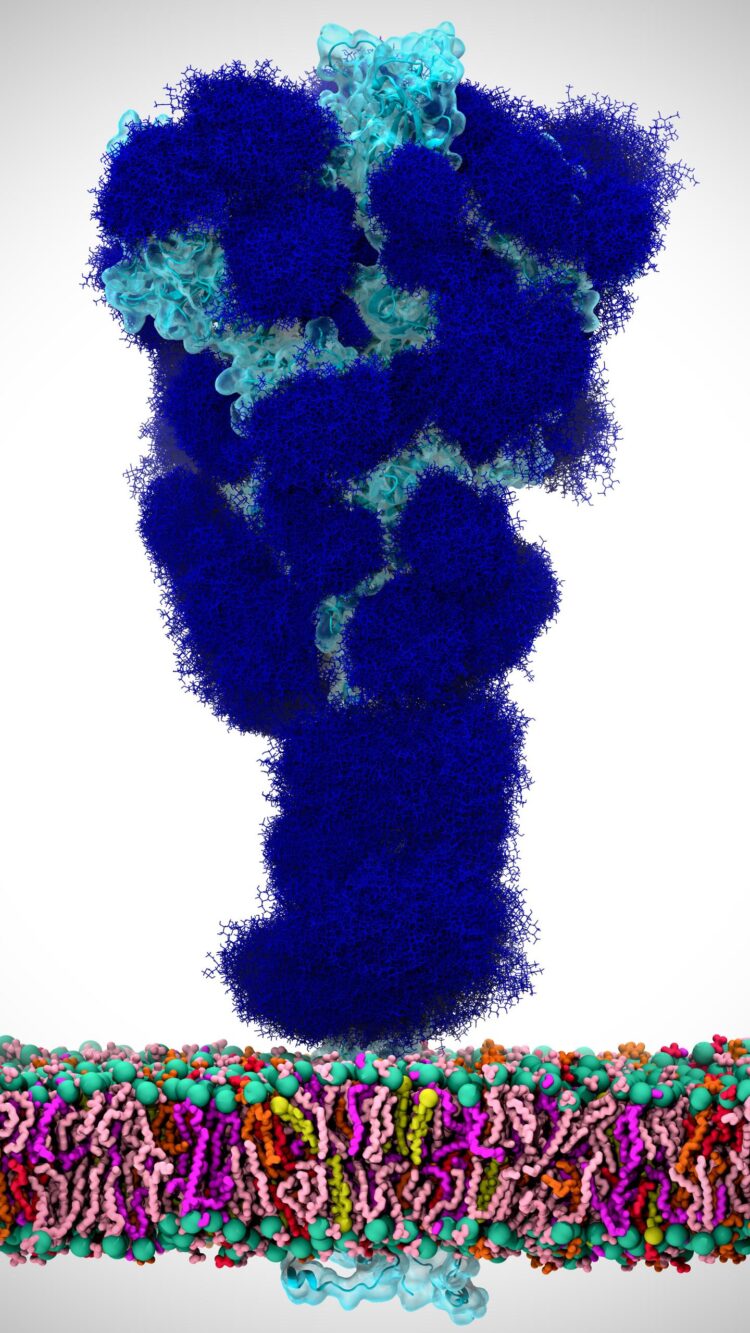
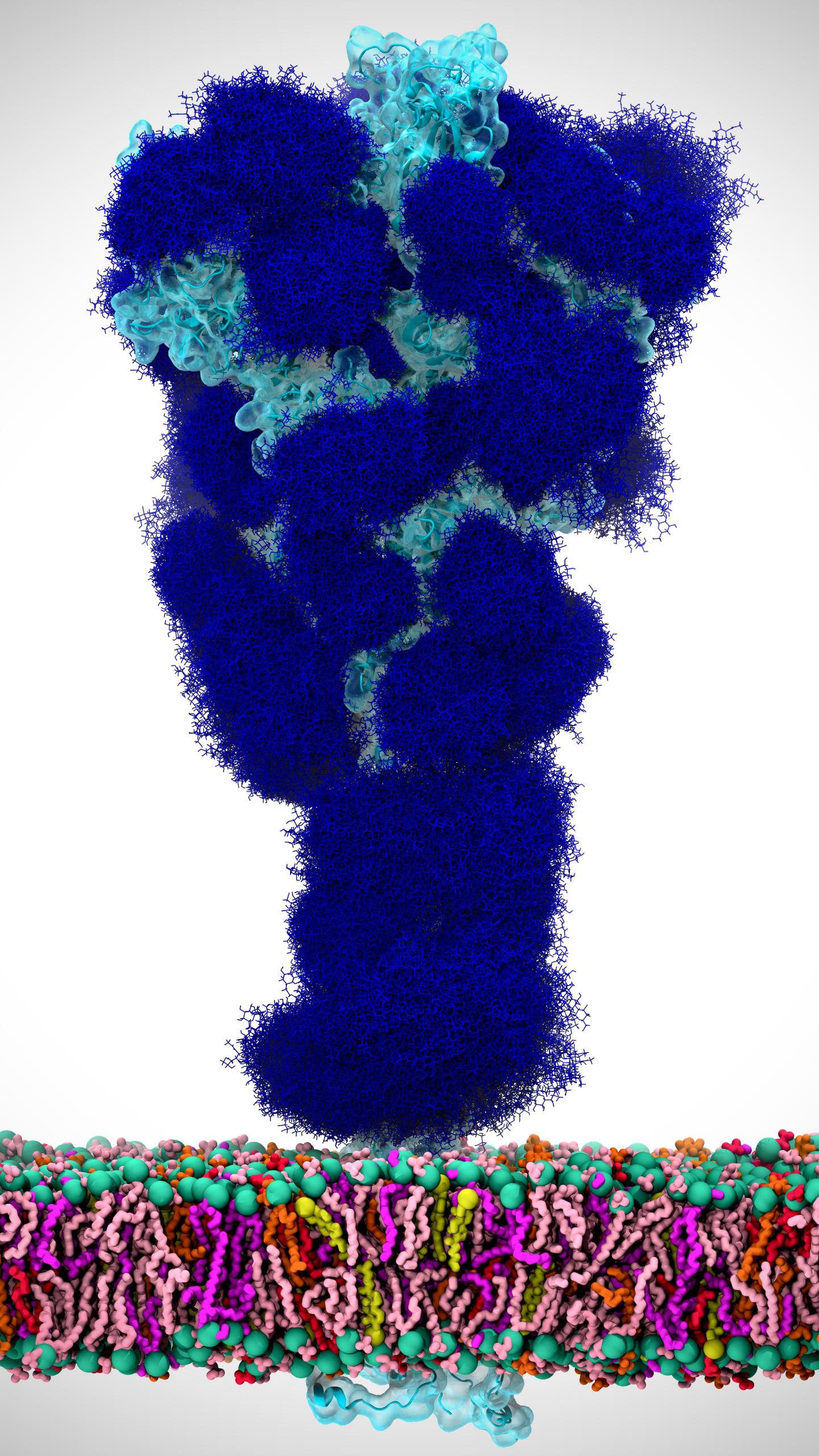
Before the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein can interact with ACE2 on a human cell, it changes shape to expose its receptor binding domain (RBD), the part of the protein that interacts with ACE2. Like many viral proteins, the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein has a thick coat of glycans on its surface. These glycans, which are attached at specific sites, help shield the viral proteins from the host immune system. Rommie Amaro and colleagues at University of California San Diego, Maynooth University (Ireland) and the University of Texas at Austin wondered whether certain glycans in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein might also be active players in the process leading to infection.
To find out, the researchers used structural and glycomic data to build molecular dynamics simulations of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein embedded in the viral membrane. The computer models, which presented a detailed snapshot of every atom in the spike glycoprotein, revealed that N-glycans linked to the spike protein at certain sites (N165 and N234) helped stabilize the shape change that exposes the RBD, which could help promote infection. The simulations also identified regions of the spike protein that weren’t coated by glycans and thus could be vulnerable to antibodies, especially after the shape change. In laboratory experiments using biolayer interferometry, the team showed that mutating the spike protein so that it no longer had glycans at N165 and N234 reduced binding to ACE2. These results lay the foundation for new strategies to fight the pandemic threat, the researchers say.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, the Research Corporation for Science Advancement, UC San Diego Moores Cancer Center, the Irish Research Council, and the Visible Molecular Cell Consortium.
The paper’s abstract will be available on September 23 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and its people. The Society is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a specialist in scientific information solutions (including SciFinder® and STN®), its CAS division powers global research, discovery and innovation. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]