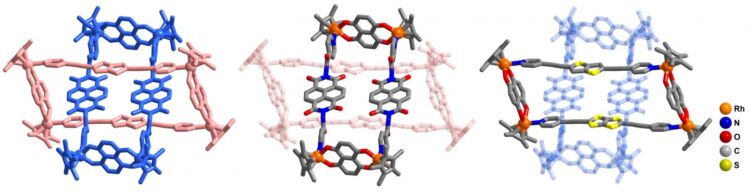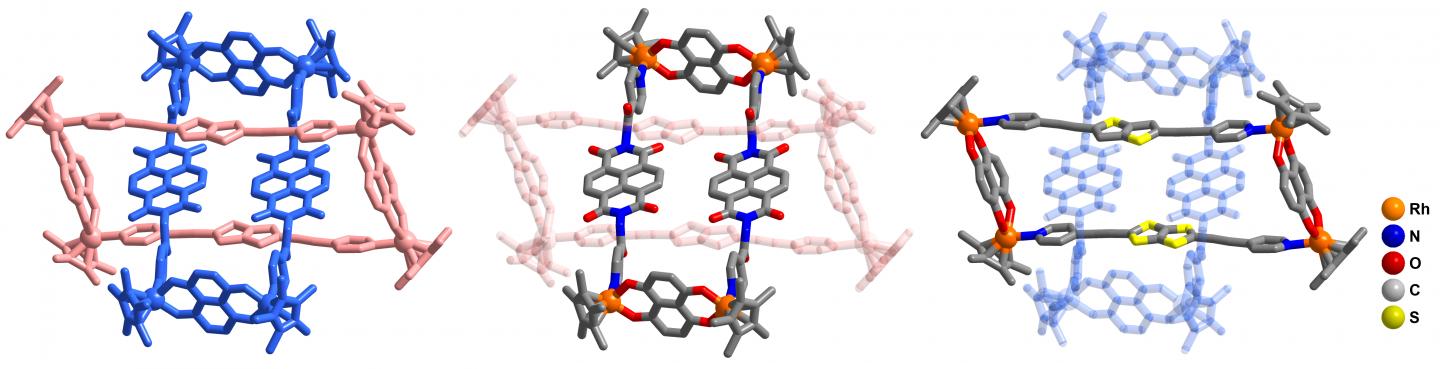
Credit: ©Science China Press
Interlocked molecular species have received considerable attention recently, not only because of their intriguing structures and topological importance, but also because of their important applications as molecular machines and nanoscale devices. Benefiting from the reversible coordination bond, some complicated interlocked structure could be realized by high-yield, one-step processes, for example, [2]catenanes and Solomon knot. Molecular Borromean rings (BRs) are [3]catenanes topoisomers in which none of the component rings are linked, but also cannot be separated without breaking one of the rings (Fig. 1). Linear [3]catenanes is another fascinating interlocked three-ring motif (Fig. 1). Several effective methods for the construction of organic linear [3]catenanes have been presented. However, the feasible strategies for the synthesis of organometallic linear metalla[3]catenanes based on coordination-driven self-assembly are still very rare. Beyond linear [3]catenanes, ring-in-ring complex are also a very rare structural motif, which can be considered as substructures of BRs and key intermediates for the preparation of BRs (Fig. 1).
Recently, Ye Lu, Dong Liu, Yue-Jian Lin, Zhen-Hua Li and Guo-Xin Jin from Fudan University (Shanghai, China) made exciting progress and developed self-assembly of metalla[3]catenanes, Borromean rings and ring-in-ring complex using a simple π-donor unit.
Due to the large electron cloud of the sulfur atom, S-containing heterocyclic compounds usually present stronger stacking interactions than polycyclic aromatic compounds under similar conditions. In order to enhance the stacking interactions, bithiophenyl groups were used as building blocks to replace the widely used phenylene or polycyclic aromatic groups. Meantime, electrostatic interactions between electron-rich (π-donor, D) and electron-deficient (π-acceptor, A) aromatic groups are important driving forces in host-guest chemistry. Metallarectangles or cages based on coordination self-assembly commonly bear several positive charges. Due to Coulombic repulsion, this type of metallarectangles or cages is more suitable for combination with electroneutral or electron-rich guests than with electron-poor cations, and overcoming the Coulombic repulsion between a cationic guest and a cationic host is still a challenge. Bithiophenyl groups are strong D units, thus their introduction into metallarectangles could lead to strong interactions between D units and A units, which is a promising strategy to overcome the Coulombic repulsion and potentially allow introduction of a positively-charged cation inside a positively-charged cationic metallarectangle. Following this logic, if an electron-deficient cation could be introduced into a cationic metallarectangle by taking advantage of strong D-A interactions, it could also be possible to thread a cationic metallarectangle based on A units inside a metallarectangle based on D units, to obtain a heterogeneous D-A ring-in-ring complex.
In this work, a series of Cp*Rh-based (Cp* = pentamethylcyclopentadienyl) homogeneous metalls[2]catenanes, as well as linear metalla[3]catenanes and BRs structure were realized through the use of building blocks based on bithiophenyl groups, a simple π-donor unit (Fig. 2). Bithiophenyl groups play a crucial role in the formation of the homogeneous interlocked structures, namely enhancing the strength of the inter-ring interactions. By taking advantage of strong electrostatic interactions between D and A units, the electron-deficient methylviologen cation was used as a guest molecule to realize reversible conversion between a [2]catenanes and a monomeric rectangle. Furthermore, a cationic metallarectangle based on A units was threaded inside a metallarectangle based on bithiophenyl groups, leading to a heterogeneous ring-in-ring complex (Fig. 3). This method for forming ring-in-ring complex was extended by use of a metallarectangle based on pyrenyl group.
These findings will help the understanding of coordination self-assembly and advance the field of organometallic assemblies.
###
See the article:
Self-assembly of metalla[3]catenanes, borromean rings and ring-in-ring complex using a simple π-donor unit
https:/
Media Contact
Guo-Xin Jin
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.