Utah State University and Butantan Institute scientists publish evolutionary findings in ‘iScience.’
Credit: Butantan Institute, Brazil
LOGAN, UTAH, USA – Utah State University biologist Edmund ‘Butch’ Brodie, Jr. and colleagues from São Paulo’s Butantan Institute report the first known evidence of oral venom glands in amphibians. Their research, supported by the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, appears in the July 3, 2020, issue of iScience.
“We think of amphibians – frogs, toads and the like — as basically harmless,” says Brodie, emeritus professor in USU’s Department of Biology. “We know a number of amphibians store nasty, poisonous secretions in their skin to deter predators. But to learn at least one can inflict injury from its mouth is extraordinary.”
Brodie and his colleagues discovered the oral glands in a family of caecilians, serpent-like creatures related to frogs and salamanders. Neither snakes nor worms, caecilians are found in tropical climates of Africa, Asian and the Americas. Some are aquatic and some, like the ringed caecilian (Siphonops annulatus) studied by Brodie’s team, live in burrows of their own making.
In 2018, the team reported the species secreted substances from skin glands at both ends of its snake-like body. Concentrated at the head and extending the length of the body, the creature emits a mucous-like lubricant that enables it to quickly dive underground to escape predators. At the tail, caecilians have glands armed with a toxin, which acts as a last line of chemical defense, blocking a hastily burrowed tunnel from hungry hunters.
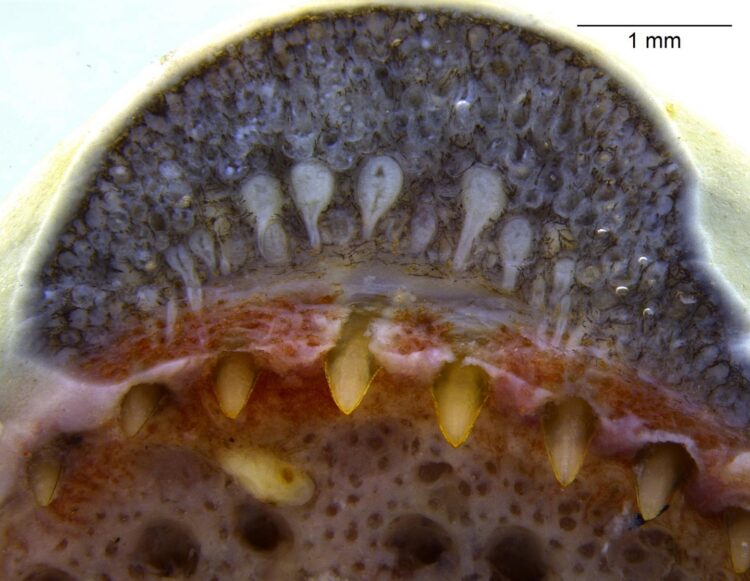
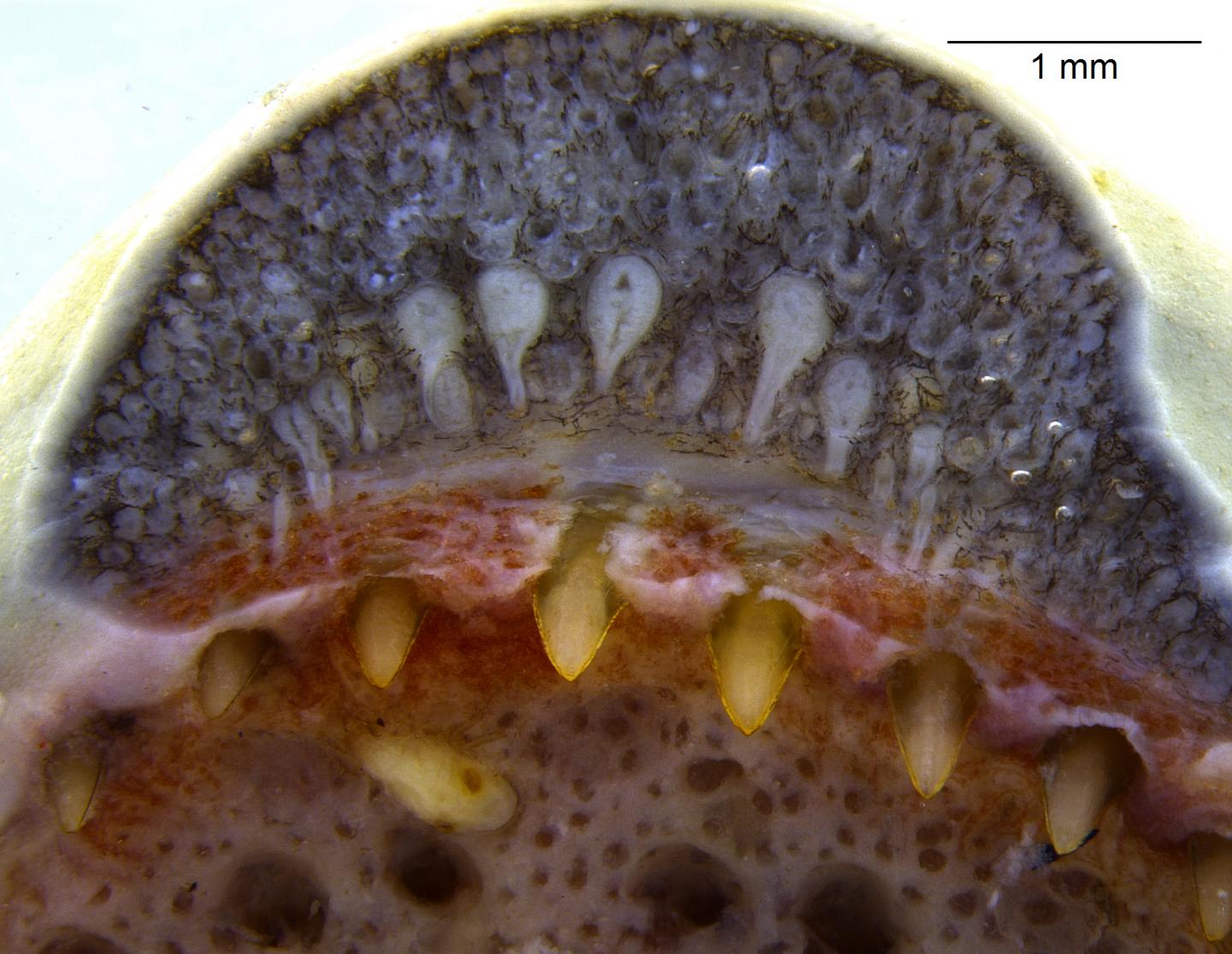
“What we didn’t know is these caecilians have tiny fluid-filled glands in the upper and lower jaw, with long ducts that open at the base of each of their spoon-shaped teeth,” Brodie says.
His research colleague Pedro Luiz Mailho-Fontana, who studied with Brodie as a visiting graduate student at USU’s Logan campus in 2015, noticed the never-before-described oral glands. Using embryonic analysis, Mailho-Fontana, first author of the paper, discovered the glands – called “dental glands” – originated from a different tissue than the slime and poison glands found in the caecilian’s skin.
“The poisonous skin glands form from the epidermis, but these oral glands develop from the dental tissue, and this is the same developmental origin we find in the venom glands of reptiles,” he says.
The researchers surmise caecilians, equipped with no limbs and only a mouth for hunting, activate their oral glands when they bite down on prey, including worms, termites, frogs and lizards.
The team doesn’t yet know the biochemical composition of the fluid held in the oral glands.
“If we can verify the secretions are toxic, these glands could indicate an early evolutionary design of oral venom organs,” Brodie says. “They may have evolved in caecilians earlier than in snakes.”
###
Media Contact
Edmund ‘Butch’ Brodie, Jr.
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.