Credit: by Tengfei Hao, Qizhuang Cen, Shanhong Guan, Wei Li, Yitang Dai, Ninghua Zhu, and Ming Li
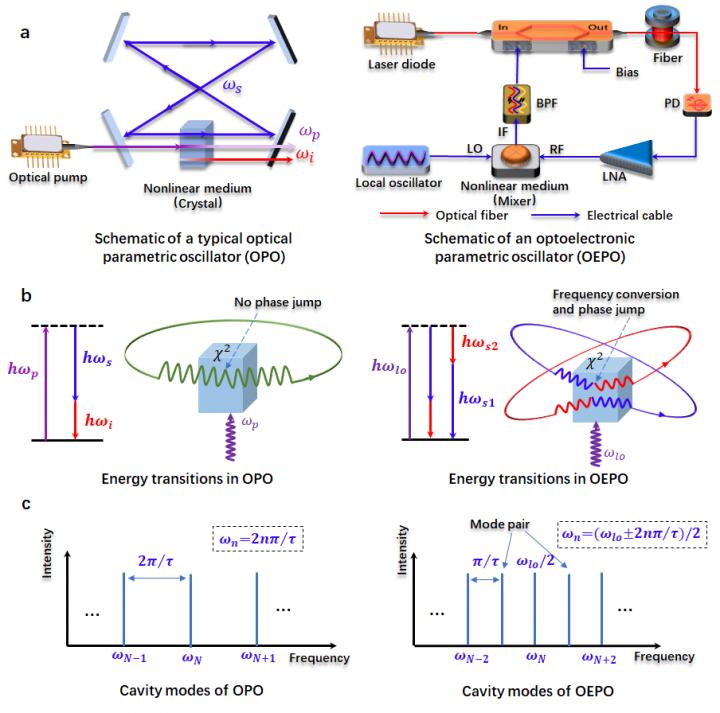
Parametric oscillators are a driven harmonic oscillator that based on nonlinear process in a resonant cavity, which are widely used in various areas of physics. In the past, parametric oscillators have been designed in pure optical and pure electrical domain, i.e., an optical parametric oscillator (OPO) and a varactor diode, respectively. Particularly, the OPO has been widely investigated in recent years since it greatly extends the operating frequency of laser by utilizing the second-order or third-order nonlinearity, noted that the operating frequency range of the ordinary laser is limited to the simulated atomic energy level. On the other hand, the oscillation in both the OPO and electrical parametric oscillator is a delay-controlled operation, which means that a steady oscillation is confined by the cavity delay since the signal must repeat itself after each round-trip. This operation leads difficulty in frequency tuning, and the frequency tuning is discrete with a minimum tuning step determined by the cavity delay.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, a team of scientists, led by Professor Ming Li from State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China, and co-workers have developed a new parametric oscillator in the optoelectronic domain, i.e., an optoelectronic parametric oscillator (OEPO) based on second-order nonlinearity in an optoelectronic cavity. Thanks to the unique energy transition process in the optoelectronic cavity, the oscillation in the OEPO is a phase-controlled operation, leading to a steady single mode oscillation or multi-mode oscillation that is not bound by the cavity delay. Furthermore, the multi-mode oscillation in the OEPO is stable and easy to realize thanks to the phase control of parametric frequency conversion process, while stable multi-mode oscillation is difficult to achieve in conventional oscillators such as an optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) or OPO due to the mode hopping and mode competition effect. The proposed OEPO has great potential in applications such as, microwave signal generation, oscillator-based computation, and radio-frequency phase-stable transfer.
A pair of oscillation modes is converted into each other in the nonlinear medium by a local oscillator in the proposed OEPO. The sum phase of each mode pair is locked by the local oscillator, which ensures stable multimode oscillation that is difficult to realize in conventional oscillators. Moreover, owing to the unique energy transition process in the optoelectronic cavity, frequency of the single-mode oscillation can be independent of the cavity delay. Continuous frequency tuning is achieved without the need for modification of the cavity delay. These scientists summarize the difference between the OEPO and traditional oscillators:
“In conventional oscillators, cavity modes are integer multiples of the fundamental one and are restricted by the cavity delay. The phase evolution of the cavity modes is linear or quasi-linear. In our proposed OEPO, the parametric frequency conversion provides a phase jump for the cavity modes. The phase evolution is not linear owing to this phase jump. We can call such oscillation phase-controlled operation, while the conventional oscillation is delay-controlled operation. As a result, the cavity modes of OEPO are not restricted by the cavity delay.”
“Owing to the unique phase-controlled oscillation in the proposed OEPO, stable and tuneable multimode oscillation is easy to realize. The OEPO can therefore be applied in scenarios requiring stable, wideband and complex microwave waveforms. By increasing the cavity length of the OEPO, the mode spacing of the optoelectronic cavity can be as small as several kHz, which would allow many densely distributed modes to oscillate in the cavity simultaneously. Oscillator-based computation can benefit from such a large mode number. Furthermore, when the OEPO operates in single-mode, the parametric frequency conversion actually works as a phase conjugate operation. Therefore, the OEPO can be used for phase-stable RF transfer since the phase error resulting from cavity turbulence can be auto-aligned.” the scientists forecast.
###
Media Contact
Ming Li
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




