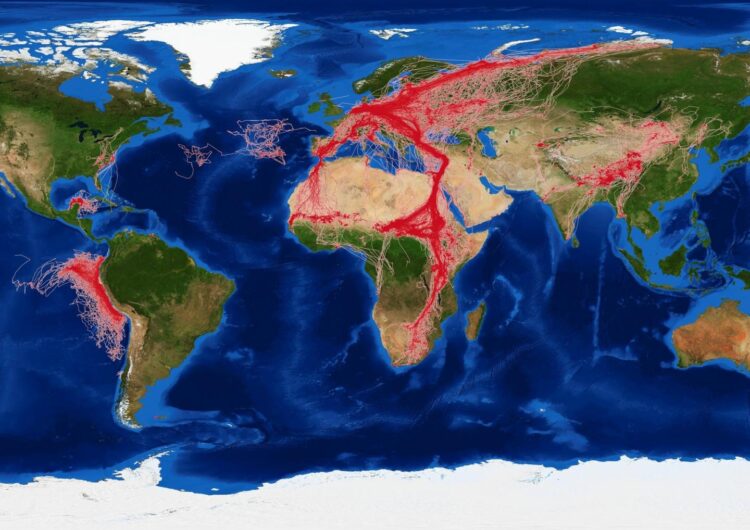
An international team of scientists is investigating how animals are responding to reduced levels of human activity during the Covid-19 pandemic.
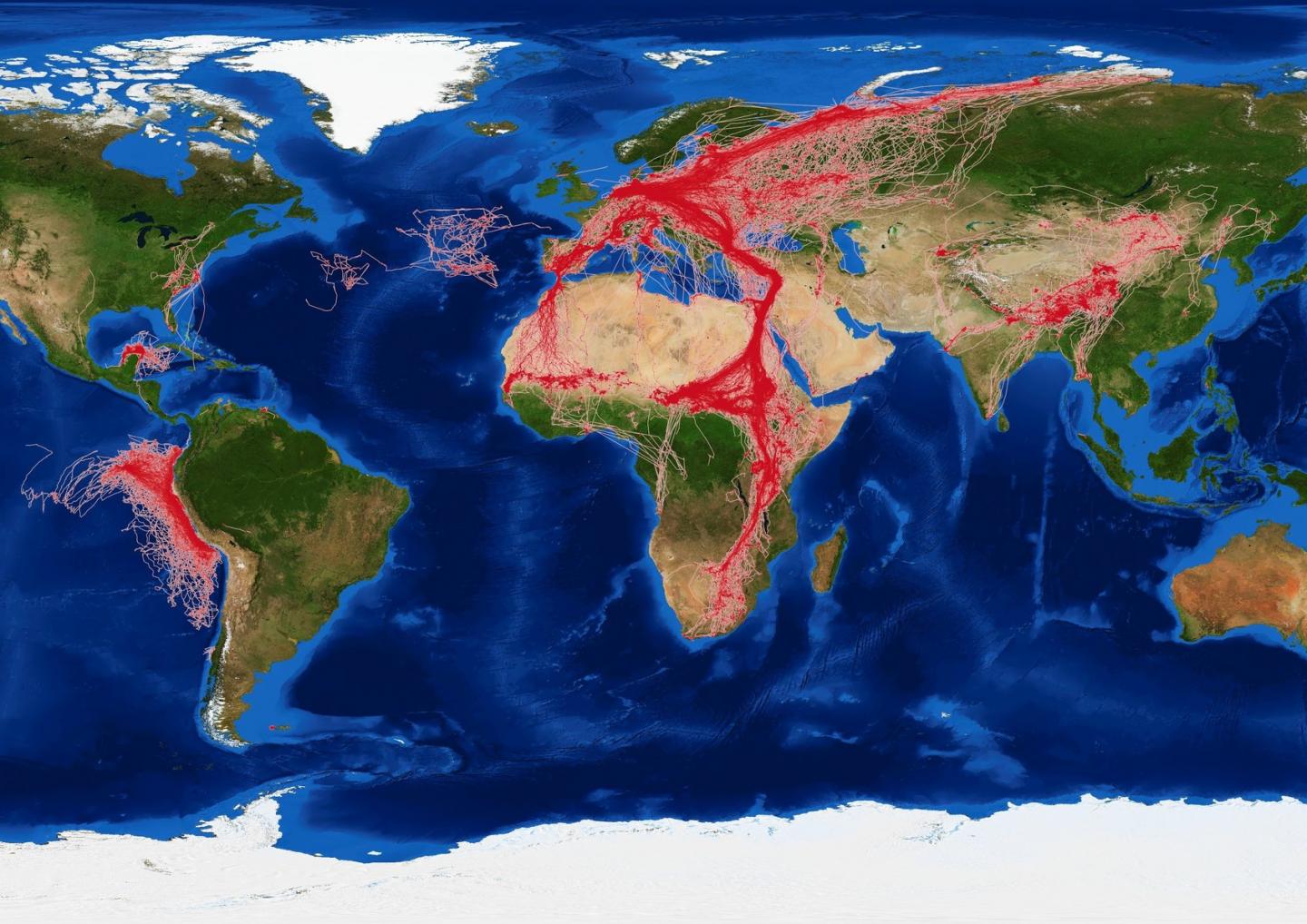
Credit: MPIAB/ MaxCine
In an article published in Nature Ecology & Evolution today (22 June), the leaders of a new global initiative explain how research during this devastating health crisis can inspire innovative strategies for sharing space on this increasingly crowded planet, with benefits for both wildlife and humans.
Many countries around the world went into lockdown to control the spread of Covid-19. Brought about by the most tragic circumstances, this period of unusually reduced human mobility, which the article’s authors coined “anthropause”, can provide invaluable insights into human-wildlife interactions.
There have been countless posts on social media over the past few months reporting unusual wildlife encounters. Anecdotal observations, especially from metropolitan areas, suggest that nature has responded to lockdown. There not only seem to be more animals than usual, but there are also some surprising visitors: pumas have been spotted prowling the streets of downtown Santiago, Chile, and dolphins recently showed up in untypically calm waters in the harbour of Trieste, Italy.
For other species, the pandemic may have created new challenges. For example, some urban-dwelling animals, like gulls, rats or monkeys, may struggle to make ends meet without access to human food. In more remote areas, reduced human presence may potentially put endangered species, such as rhinos or raptors, at increased risk of poaching or persecution.
The authors emphasise that society’s priority must be to tackle the immense human tragedy and hardship caused by Covid-19. But, they argue that we cannot afford to miss the opportunity to chart, for the first time on a truly global scale, the extent to which modern human mobility affects wildlife.
To address this challenge, researchers recently formed the “COVID-19 Bio-Logging Initiative”. This international consortium will investigate animals’ movements, behaviour and stress levels, before, during and after Covid-19 lockdown, using data collected with nifty animal-attached electronic devices called “bio-loggers”.
The article’s lead author, Professor Christian Rutz, a biologist at the University of St Andrews, UK, and President of the International Bio-Logging Society, explains: “All over the world, field biologists have fitted animals with miniature tracking devices. These bio-loggers provide a goldmine of information on animal movement and behaviour, which we can now tap to improve our understanding of human-wildlife interactions, with benefits for all.”
The team will integrate results from a wide variety of animals, including fish, birds and mammals, in an attempt to build a global picture of lockdown effects.
Dr Francesca Cagnacci, Senior Researcher at the Edmund Mach Foundation in Trento, Italy, and Principal Investigator of the Euromammals research network, says: “The international research community responded quickly to our recent call for collaboration, offering over 200 datasets for analysis. We are very grateful for this support.”
So, what do the scientists hope to learn? Dr Matthias-Claudio Loretto, a Marie Sk?odowska-Curie Fellow at the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior in Radolfzell, Germany, explains that it will be possible to address previously intractable questions: “We will be able to investigate if the movements of animals in modern landscapes are predominantly affected by built structures, or by the presence of humans. That is a big deal.”
These insights will in turn inspire innovative proposals for improving human-wildlife coexistence, according to Professor Martin Wikelski, Director of the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior in Radolfzell, Germany. “Nobody is asking for humans to stay in permanent lockdown. But we may discover that relatively minor changes to our lifestyles and transport networks can potentially have significant benefits for both ecosystems and humans.”
Coordinated global wildlife research during this period of crisis will provide unforeseen opportunities for humans to forge a mutually beneficial coexistence with other species, and to rediscover how important a healthy environment is for our own well-being.
###
Original publication
Christian Rutz, Matthias-Claudio Loretto, Amanda Bates, Sarah C. Davidson, Carlos M. Duarte, Walter Jetz, Mark Johnson, Akiko Kato, Roland Kays, Thomas Mueller, Richard B. Primack, Yan Ropert-Coudert, Marlee Tucker, Martin Wikelski and Francesca Cagnacci
COVID-19 lockdown allows researchers to quantify the effects of human activity on wildlife.
Nature Ecology & Evolution; 22 June, 2020
Media Contact
Dr. Carla Avolio
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.