Credit: IMP
Since the discovery of the double helix form of DNA and the hypothesis of DNA mutation induced by proton transfer more than 50 years ago, it has been recognized that proton transfer is crucial to many chemical and biological processes.
As these processes are known to be relevant to biophysics and radiation therapy, a question arises whether a massive ion could be transferred in biochemical processes and lead to fragmentation. Specifically, in a complex bio-environment, does heavy ion transfer play a role?
Published in Nature Communications on June 12, a study reporting a new channel involving heavy N+ ion transfer observed in a charged Van der Waals cluster helps address the above questions.
The study was conducted by a team of researchers from the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), the Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, and Centre de recherche sur les Ions, les MAtériaux et la Photonique (CIMAP) in France.
“Small van der Waals systems can be employed as experimentally feasible model systems,” said Prof. ZHU Xiaolong of IMP, one of the first authors. Van der Waals (vdW) clusters are weakly bound atomic/molecular systems. “They are common in nature and important for understanding microenvironmental chemical phenomena in biosystems.”
Interatomic Coulombic decay is a typical process that demonstrates the energy and charge transfer over a large distance between atomic components in a cluster and results in fragmentation, proving that forbidden channels for isolated atoms/molecules may be opened due to the presence of neighboring atoms. Here, the energy and charge transfers are mediated by virtual photon or Coulomb interaction.
In hydrogen-bond clusters, the proton transfer process plays an important role as well. It involves mass and charge migration over large distances within the cluster and results in fragmentation of the latter. Nevertheless, in previous research, this kind of transfer process was limited to hydrogen-bond clusters.
In the current work, the scientists used the neutral vdW cluster N2 Ar as a target in collisions with 1 MeV Ne8+ ions to produce the doubly charged cluster (N2Ar)2+.
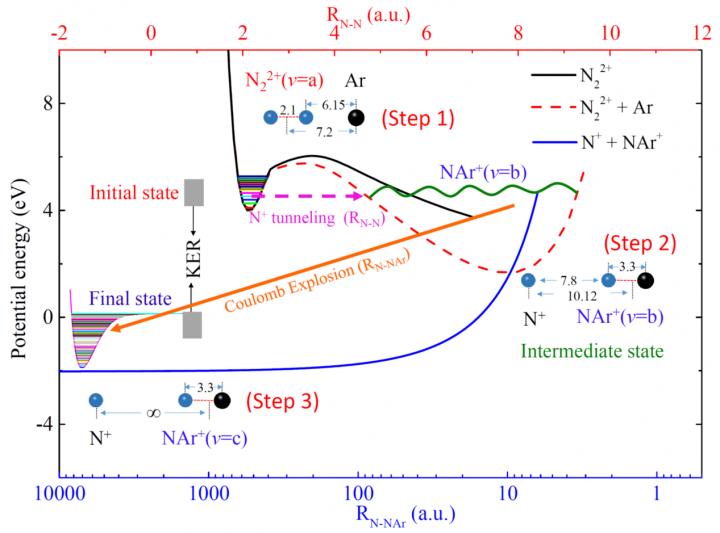
Surprisingly, an exotic heavy N+ ion transfer channel (N2 Ar)2+ → N+ + NAr+ was observed. It is the first time that such a heavy-ion transfer process in a vdW cluster has ever been reported and the consequent formation of NAr+ is a novel scenario.
According to the study, this channel originates from the dissociation of the parent doubly charged cluster N22+ Ar generated by the “N2-site” two-electron loss process.
Theoretical calculations show that the polarization interactions between Ar and N22+ lead first to an isomerization process ofN22+ Ar from its initial T-shape to a linear shape (N-N-Ar).
In addition, the neighboring neutral Ar atom decreases the N22+ barrier height and width, resulting in significantly shorter lifetimes for the metastable electronic state.
Consequently, the breakup of the covalent N+-N+ bond, the tunneling out of the N+ ion from the N22+ potential well, as well as the formation of the N-Ar+ bound system take place almost simultaneously. Then the Coulomb explosion starts between N+ and NAr+ ion pairs.
“This new mechanism might be general for molecular dimer ions in the presence of a neighboring atom, and be of potential importance in understanding the microdynamics of biological systems,” said Prof. MA Xinwen from IMP, one of the corresponding authors of this paper. “For example, it may help us understand the micromechanism of cancer therapy by heavy ion irradiation.”
###
Media Contact
LIU Fang
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




