Credit: ©Science China Press
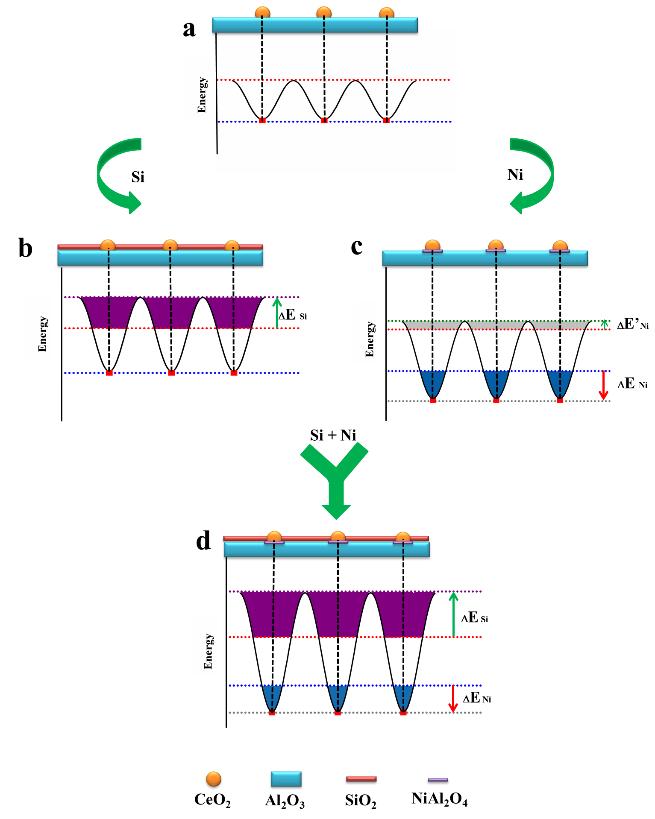
Nano-catalysts usually have higher catalytic activity than traditional bulk catalysts. And it is widely acknowledged that the smaller the particle size of the active component is, the higher the activity would be. However, the active component with small size tends to agglomerate or further grow into large particles. Many reaction processes, such as hydrocarbon cracking and combustion, methane dry/wet reforming and automobile exhaust gas purification, have to be operated at very high temperatures, it will lead to the decreasing of activity and product selectivity due to sintering at high temperatures, ultimately limits the practical application of nano-catalysts. Many researchers believe that the sintering of nanoparticles involves two processes: one is the ripening process, single atom or molecular species move from one particle to another; the other is the migration process, whole particles grow into large particles after migration and aggregation. Because the ripening process can hardly be avoided at high temperature, the current strategy to improve the stability of nano-catalysts is to inhibit the migration of nanoparticles on the basis of “confinement effect” or to construct a “migration barrier”.
Recently, Pt/CeO2/NiAl2O4/Al2O3@SiO2 model catalyst, based on the “composite energy trap” model, was developed by the State Key Laboratory of Rare Earth Resource Utilization of Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, which can effectively inhibit the migration and agglomeration of loaded nanoparticles. The model catalyst still remains high activity after aging at 1000 ?. The results of DFT indicate that the higher stability of the model catalyst should be attributed to the existence of two kinds of “confinement effect” in its structure, the “composite energy well” model is also suitable for the research and development of other supported catalysts. The first authors of this paper are Jingwei Li and Kai Li, and the correspondent authors are associate professor Yibo Zhang and professor Xiangguang Yang.
###
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0204301), National Nature Science Foundation of China (21872133 and 21273221) and Youth Innovation Promotion Association of Chinese Academy of Science (2018263)
See the article: Li J, Li K, Sun L, Zhang Z, Wu Z, Zhang Y, Yang X. Sinter-resistant and high-efficient Pt/CeO2/NiAl2O4/Al2O3@SiO2 model catalyst with “composite energy trap”. Sci. China Chem., 63, 519-525(2020), DOI: 10.1007/s11426-019-9678-5.
https:/
Media Contact
Xiangguang Yang
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




