Credit: Author
In a report published in NANO, a group of researchers from the Republic of Korea have discovered a method to promote cancer cell growth using silica-coated gold nanorods. The cell growth by near infrared (NIR) exposure of Si-AuNRs nano heat islands revealed a higher growth rate of 36.13% than the normal incubator condition.
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have been brought to the forefront of cancer research in recent years. They possess a number of favourable properties such as ease of synthesis and surface modification, strongly enhanced and tunable optical properties as well as excellent biocompatibility for clinic setting. Gold nanorods (AuNRs) are considered suitable materials for diverse biomedical applications in controlling cell behaviors.
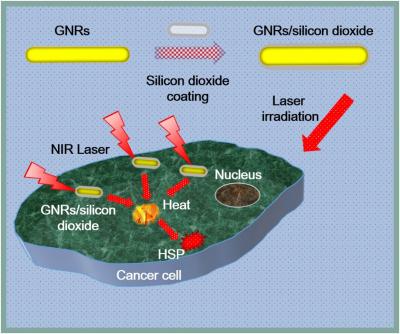
The nano island system with well dispersed silica coated Au nanorods (Si-AuNRs) was used to demonstrate the enhanced cell growth of normal and cancer cells from the induced expressions of the heat shock proteins. Heat shock proteins could hinder the formation of unwanted intermolecular bond when combined with unconjugated protein.
The researchers believe that the growth of cancer cells in near infrared region using Si-AuNRs induced the activities of heat shock proteins, which could help the protein folding in cell growth and survival in comparison to the cells grown in the incubator only. Unlike external heating sources, such as infrared radiation, steamed heats, or water bath, the internalized nanomaterials for mediating heats were effective with minimal side effects.
“The cell growth with NIR exposure to Si-AuNRs nano heat islands could be an alternative way to grow cells in comparison to the conventional system, such as an incubator. Such cells can be used in diverse cellular applications in future”, said lead investigator of study Dong Kee Yi.
###
This research was supported by the Korean National Research Foundation (NRF-2018R1A2B6007786).
Corresponding author for this work is Dong Kee Yi ([email protected]).
For more insight into the research described, readers are invited to access the paper on NANO.
IMAGE
Caption: The nano island system with well dispersed silica coated Au nanorods (Si-AuNRs) was used to demonstrate the enhanced the cell growth of normal and cancer cells from the induced expressions of the heat shock proteins (HSP). The over expressions of HSP could help in protein folding in cell proliferations and growths of both the normal and cancer cells. The cell growth enhancing technology could be expanded in diverse applications in cell culture systems.
NANO is an international peer-reviewed monthly journal for nanoscience and nanotechnology that presents forefront fundamental research and new emerging topics. It features timely scientific reports of new results and technical breakthroughs and publishes interesting review articles about recent hot issues.
About World Scientific Publishing Co.
World Scientific Publishing is a leading independent publisher of books and journals for the scholarly, research, professional and educational communities. The company publishes about 600 books annually and about 140 journals in various fields. World Scientific collaborates with prestigious organizations like the Nobel Foundation and US National Academies Press to bring high quality academic and professional content to researchers and academics worldwide. To find out more about World Scientific, please visit http://www.
For more information, contact Tay Yu Shan at [email protected].
Media Contact
Tay Yu Shan
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




