A new test was publicized by Kazan Federal University in Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering
Credit: Kazan Federal University
Despite the large number of existing reagents, research is ongoing in the world to obtain universal catalysts that are distinguished by their efficiency, low cost and neutral impact on the environment. After conducting laboratory studies, KFU scientists were able to create a new type of reagent based on nickel and cobalt carboxylates, which are highly effective catalysts for the refinement of heavy oil.
The use of catalysts injected into a reservoir intensifies the destruction of asphaltene-resinous compounds, those which most affect the viscosity of oil.
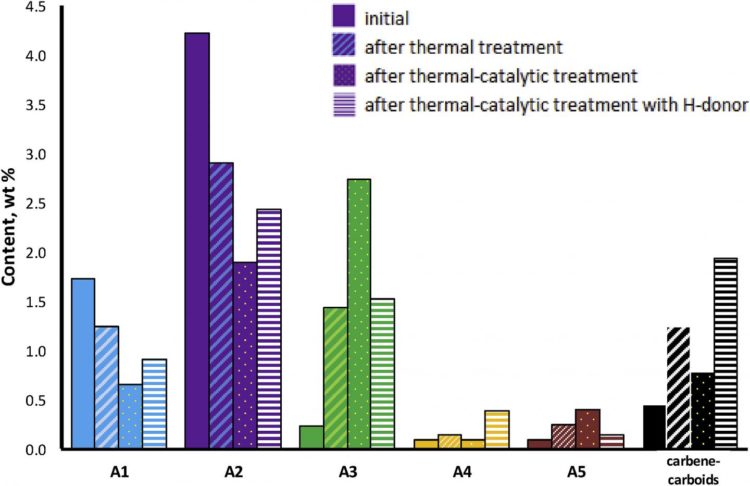
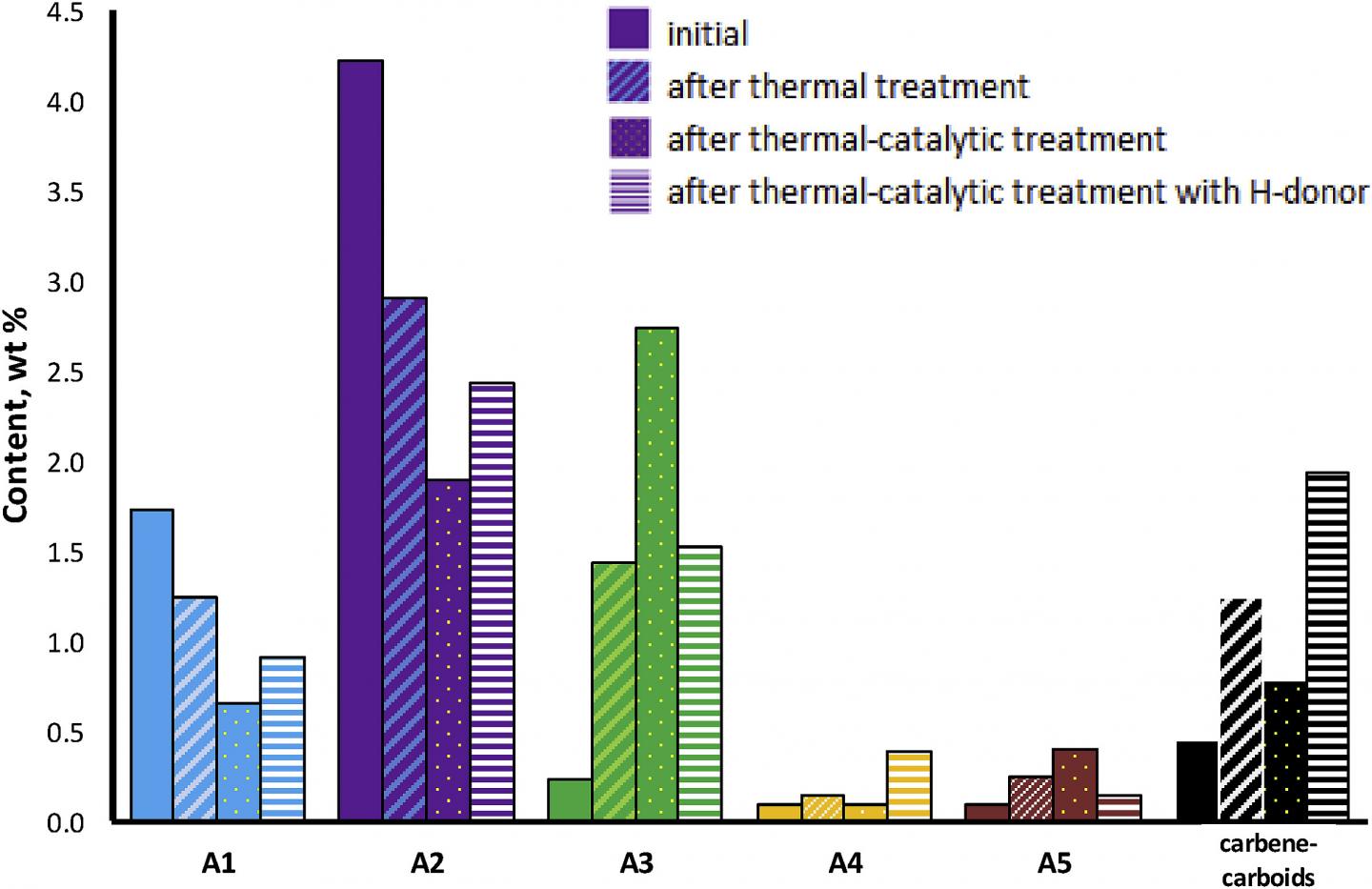
In the paper, chemical changes in the composition of asphaltene subfractions of heavy oil under the influence of oil-soluble Co-based catalyst were investigated. The results of SARA-analysis and MALDI-spectroscopy revealed a decrease in absolute content of asphaltenes and their molecular masses in the presence of catalyst. Moreover, the sulfur content was decreased under the catalyst influence and it was mostly observed in the subfraction with the highest molecular weight (A5). The main catalytic reaction was a destructive hydrogenation, directed to break the -C-S-C- bonds in the asphaltene molecules. The 13C NMR spectra revealed the decrease in average length of chain (MCL) after catalytic treatment by 15 times in A1 subfraction, which was accepted as a solvate layer and almost by 13 times in A2 subfraction. The C-O and C-S bonds break in the side chains of aromatic and alicyclic hydrocarbons. The content of primary (Cp) and the sum of secondary and quaternary (Csq) carbons was increased, while the content of tertiary (Ct) and aromatic carbons (Car) declined. The high-molecular poly-alicyclic and polyaromatic components had lost the straight and branched aliphatic hydrocarbons, and then were transformed into coke like substance – carbene-carboids.
“The aquathermolysis technology is used to work with catalysts. These reagents are our own production. To date, they have found their application in Cuba and on Ashalchi field in Tatarstan,” said Salikh Indad Sharif Salikh, Junior Research Associate at the In-Situ Combustion Lab.
The market, according to the researcher, has already appreciated this technology – the catalysts are being introduced into production by the largest Russian companies.
“Representatives from Iran, Iraq, Algeria and other countries work at our laboratory. And it is no coincidence that we have plans to promote our catalysts in other countries of the world. We are convinced that they can perform well on numerous overseas oilfields,” said Irek Mukhamatdinov, Senior Research Associate at the same laboratory.
###
The publication was made available online on 19th November 2019.
Media Contact
Yury Nurmeev
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.