New algorithm solves complex problems more easily and more accurately on a personal computer while requiring less processing power than a supercomputer
Credit: ill./©: Illia Horenko
The exponential growth in computer processing power seen over the past 60 years may soon come to a halt. Complex systems such as those used in weather forecast, for example, require high computing capacities, but the costs for running supercomputers to process large quantities of data can become a limiting factor. Researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) in Germany and Università della Svizzera italiana (USI) in Lugano in Switzerland have recently unveiled an algorithm that can solve complex problems with remarkable facility – even on a personal computer.
Exponential growth in IT will reach its limit
In the past, we have seen a constant rate of acceleration in information processing power as predicted by Moore’s Law, but it now looks as if this exponential rate of growth is limited. New developments rely on artificial intelligence and machine learning, but the related processes are largely not well-known and understood. “Many machine learning methods, such as the very popular deep learning, are very successful, but work like a black box, which means that we don’t know exactly what is going on. We wanted to understand how artificial intelligence works and gain a better understanding of the connections involved,” said Professor Susanne Gerber, a specialist in bioinformatics at Mainz University. Together with Professor Illia Horenko, a computer expert at Università della Svizzera italiana and a Mercator Fellow of Freie Universität Berlin, she has developed a technique for carrying out incredibly complex calculations at low cost and with high reliability. Gerber and Horenko, along with their co-authors, have summarized their concept in an article entitled “Low-cost scalable discretization, prediction, and feature selection for complex systems” recently published in Science Advances. “This method enables us to carry out tasks on a standard PC that previously would have required a supercomputer,” emphasized Horenko. In addition to weather forecasts, the research see numerous possible applications such as in solving classification problems in bioinformatics, image analysis, and medical diagnostics.
Breaking down complex systems into individual components
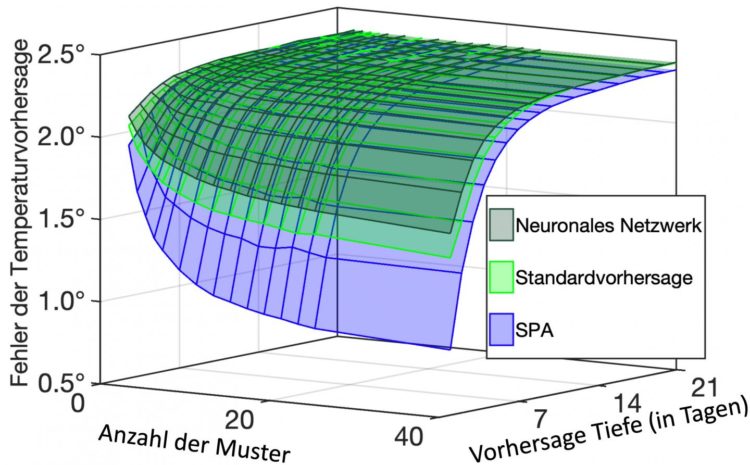
The paper presented is the result of many years of work on the development of this new approach. According to Gerber and Horenko, the process is based on the Lego principle, according to which complex systems are broken down into discrete states or patterns. With only a few patterns or components, i.e., three or four dozen, large volumes of data can be analyzed and their future behavior can be predicted. “For example, using the SPA algorithm we could make a data-based forecast of surface temperatures in Europe for the day ahead and have a prediction error of only 0.75 degrees Celsius,” said Gerber. It all works on an ordinary PC and has an error rate that is 40 percent better than the computer systems usually used by weather services, whilst also being much cheaper.
SPA or Scalable Probabilistic Approximation is a mathematically-based concept. The method could be useful in various situations that require large volumes of data to be processed automatically, such as in biology, for example, when a large number of cells need to be classified and grouped. “What is particularly useful about the result is that we can then get an understanding of what characteristics were used to sort the cells,” added Gerber. Another potential area of application is neuroscience. Automated analysis of EEG signals could form the basis for assessments of cerebral status. It could even be used in breast cancer diagnosis, as mammography images could be analyzed to predict the results of a possible biopsy.
“The SPA algorithm can be applied in a number of fields, from the Lorenz model to the molecular dynamics of amino acids in water,” concluded Horenko. “The process is easier and cheaper and the results are also better compared to those produced by the current state-of-the-art supercomputers.”
###
The collaboration between the groups in Mainz and Lugano was carried out under the aegis of the newly-created Research Center Emergent Algorithmic Intelligence, which was established in April 2019 at JGU and is funded by the Carl Zeiss Foundation.
Media Contact
Junior Professor Dr. Susanne Gerber
[email protected]
49-613-139-27331
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.