Credit: Institute of Microbial Chemistry
Under JST’s Strategic Basic Research Programs, Noda Nobuo (Laboratory Head) and Yamasaki Akinori, Postdoctoral Fellow (currently Assistant Professor, Tokyo Institute of Technology), at the Institute of Microbial Chemistry in collaboration with other researchers, have discovered that autophagy is effective for selectively degrading protein in a state of liquid droplet(1) that is formed through liquid-liquid phase separation(2) but does poorly with the degradation of protein in aggregation or solid state.
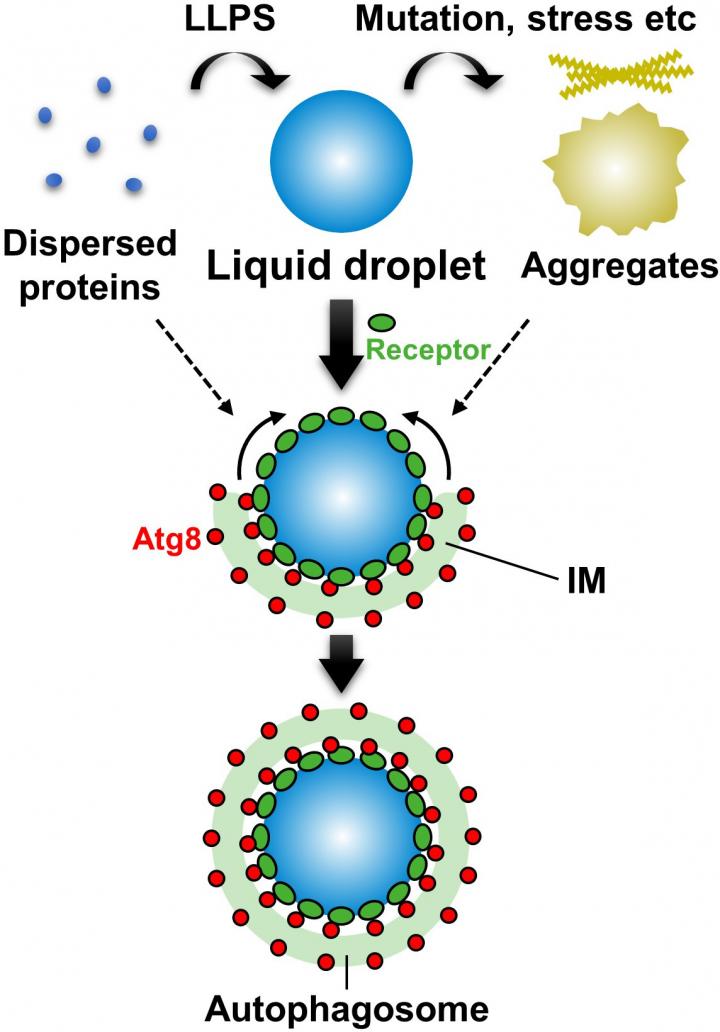
Autophagy is one of the mechanisms through which cellular protein is degraded. There exists a selective type of autophagy named selective autophagy(3) that targets and degrades specific proteins and organelles. It has been assumed that selective autophagy prevents the onset of diseases, but the state of proteins in which they could be efficiently degraded had been unclear.
This research group used the selective autophagy of Ape1 protein in yeast as the model system and succeeded in reconstituting the Ape1 isolation process with a lipid membrane in a test tube. It revealed that Ape1 protein is effectively isolated by the lipid membrane through the functioning of the Atg8 and receptor proteins when Ape1 forms droplets but is not isolated by the lipid membrane when Ape1 forms aggregates.
The discovery that selective autophagy is effective in degrading protein droplets but does poorly in degrading protein aggregates indicates that the activation of autophagy alone is insufficient in the prevention of and therapeutic medication development for neurodegenerative diseases and other diseases that are believed to be caused by the accumulation of abnormal proteins and that it is important to develop drugs that change aggregations into droplets. This will hopefully lead to the discovery of drugs that target “liquid-liquid phase separation,” which is the mechanism for creating droplets.
It was also proved for the first time that the isolation step for the targeted protein in selective autophagy can be conducted with just the Atg8 and receptor proteins. Autophagy also selectively degrades mitochondria and other organelles as well as pathogenic bacteria. Atg8 and receptor proteins could be responsible for selective isolation in a similar mechanism in these cases as well. The application of the test-tube reconstitution system developed here would promote research on the selective autophagy mechanisms for a wide variety of targets.
(1) Liquid droplet
A condensate of macromolecules with fluidity created when protein and/or nucleic acids undergo liquid-liquid phase separation. The droplets are also known as “membraneless organelles” and perform various functions within the cell. A droplet spontaneously assumes a spherical form. It also has high internal fluidity, and it actively exchanges molecules with its surroundings.
(2) Liquid-liquid phase separation
This is the phenomenon of a uniform liquid phase separating into multiple liquid phases. It is observed in daily life as the separation of water and oil, which occurs within cells with proteins and nucleic acids.
(3) Selective autophagy?
Autophagic pathway that degrades specific targets when it is required by the cell, unlike ordinary autophagy, which is triggered by starvation and degrades intracellular components indiscriminately. In selective autophagy, there are receptor proteins that recognize the wide variety of targets for degradation. It is believed that they all selectively load their targets into autophagosomes by connecting to both the degradation targets and the Atg8 proteins on the autophagosomes.
###
Media Contact
Nobuo Noda
[email protected]
81-334-414-173
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




