Credit: ©Science China Press
According to the statistics from World Health Organization (WHO), cardiovascular disease has become the leading cause of death worldwide, inducing almost 1/3 of death each year. Owing to its importance and promise in cardiovascular disease treatment, vascular regeneration has attracted global attentions in both academic and clinic. Within the vascular regeneration process, endothelium remodeling, which refers to the formation of a confluent vascular endothelial cell monolayer on the lumen, plays a vital role. However, rapid endothelialization confronts grand challenge using existing synthetic biomaterials or engineering methods as vascular endothelium remodeling is a complicated and dynamic process. Successful endothelium remodeling has become the key to the success of vascular remodeling.
Throughout the endothelialization process of native blood vessels, vascular endothelial cells and progenitor cells is first recruited/migrated to the regeneration sites, followed by the adhesion and spreading of vascular endothelial cells to form a confluent vascular endothelial cell monolayer. In human body, such process is implemented through extracellular matrix (ECM)-mediated stepwise modulation of vascular endothelial cell functions at different stages. Nevertheless, existing synthetic biomaterials usually exhibit static properties, which cannot offer dynamic and particularly on-demand inducements for manipulating specific vascular endothelial cell functions at different stages of endothelium remodeling.
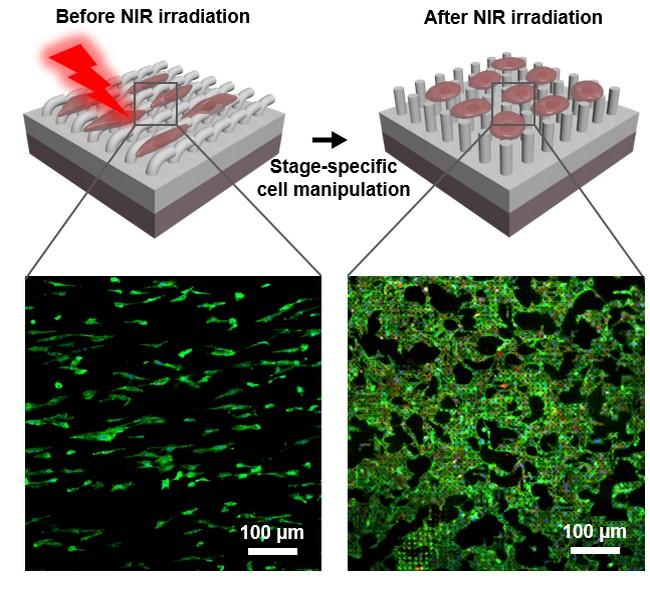
To realize the on-demand manipulation of vascular endothelial cell functions for meeting the requirements of endothelium remodeling, in a research article recently published in the Beijing-based National Science Review, scientists at Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China demonstrate a remote-controlled “smart” platform that effectively directs programmed vascular endothelium remodeling in a temporally controllable manner. In this work, Co-authors Dr. Qilong Zhao (first author), Ms. Juan Wang (co-first author) and Dr. Xuemin Du (corresponding author) develop a bilayer platform with programable surface topographies using a shape-memory polymer and a photothermal agent, gold nanorods. The bilayer platform possesses originally stable anisotropic microgroove array topography at the physiological environment, which can significantly direct cell polarization and thereby enhance the collective migration of vascular endothelial cells. Upon 10-s near infrared (NIR) irradiation, the heat generated on the bottom layer can induce the change in the surface topographies of the platform from original anisotropic microgroove array to permanent isotropic micropillar array. Correspondingly, the focal adhesion and spreading of vascular endothelial cells can be subsequently promoted at the later stage of endothelialization by the platform with altering topographies. The platform with remote-controlled “smart” properties successfully promote different functions of vascular endothelial cell in turn, which mimics the dynamic ECM-mediated effects throughout the endothelialization process for the first time using synthetic biomaterials.
“Traditionally, biomaterials and tissue engineering scaffolds offer suitable platforms to support cell attachment and ingrowth. Nowadays, we aim to develop biomaterials with dynamic properties to actively modulate different cell functions in specific spatiotemporal manners, just like the native ECM in our bodies.” Dr. Xuemin Du said, “We believe the biomaterials with dynamic properties will significantly contribute to the progresses of wound healing and complex tissue/organ regeneration”.
###
This research received funding from the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Guangdong Province, and Shenzhen.
See the article:
Qilong Zhao, Juan Wang, Yunlong Wang, Huanqing Cui and Xuemin Du
A Stage-specific cell manipulation platform for on-demand inducing endothelialization
Natl Sci Rev, doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwz188
https:/
The National Science Review is the first comprehensive scholarly journal released in English in China that is aimed at linking the country’s rapidly advancing community of scientists with the global frontiers of science and technology. The journal also aims to shine a worldwide spotlight on scientific research advances across China.
Media Contact
Xuemin Du
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




