Credit: Tae-Woo Lee
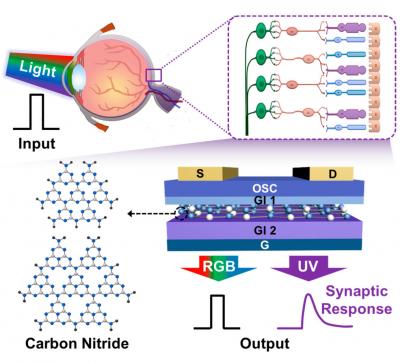
Researchers at Seoul National University and Inha University in South Korea developed photo-sensitive artificial nerves that emulated functions of a retina by using 2-dimensional carbon nitride (C3N4) nanodot materials. Further, through the photo-sensitive artificial nerves which selectively detected ultraviolet (UV) light and processed the information, smart window platform was demonstrated for in-situ modulation of exposure to UV rays depending on the degree of UV exposure and risk.
Neuromorphic electronics which emulate the biological nervous systems are promising candidates to overcome the challenges of von-Neurmann computing architecture such as energy efficiency, high-density integration, and data processing rate in the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT). Particularly, photo-sensitive neuromorphic electronics are regarded as core technology for application of next-generation smart sensors, because they can efficiently replicate the functions of biological synapses (interconnection between two neurons, key roles in learning and memorizing) and detect various types of external light information. However, previous investigations were only focused on the integration of light sensing and synaptic functions in a single device, so actual applications have not been explored.
The work reported in January 27 in Advanced Materials describes retina-inspired photo-sensitive neuromorphic devices by using ultraviolet (UV)-responsive 2-dimensional carbon nitride (C3N4) nanodot layers to selectively detect and process UV exposure information. UV light (wavelength from 10 to 400 nm) is harmful to human health, but the human retina cannot detect UV. Thus, by emulating the retina, photo-sensitive neuromorphic electronics that can selectively detect and process UV stimuli would expand the human visual sense beyond visible light and be applicable to healthcare devices. The research group synthesized C3N4 nanodots dominantly absorbing UV light, and this was introduced as a UV-responsive floating-gate layer in transistor geometry. The presented devices consumed only 18.06 fJ/synaptic event, which is comparable to the energy consumption of biological synapses. Furthermore, the research team at Seoul National University demonstrated in-situ modulation of exposure to UV light by integrating the devices with UV transmittance modulators. These smart systems would be further developed to combine detection and dose-calculation to determine how and when to decrease UV transmittance for preventive health care.
Professor Tae-Woo Lee, a professor at Seoul National University said “This smart system platform will be widely applicable to advanced electronic skin that is able to automatically adapt to the changing light-dose environment, smart windows that can selectively control transmittance of strong UV lights, smart glasses that detect and block harmful UV rays, smart sensors, artificial retina for soft humanoid robots, and neural prostheses compatible with biological optic nerves.” Lee said, “The development of human-like robots, neural prostheses that replicate and expand the human sense, and preventive health care devices can benefit from our work.”
###
This work was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, South Korea; by Seoul National University (SNU).
Media Contact
Tae-Woo Lee
[email protected]




