Credit: © Tamtögl
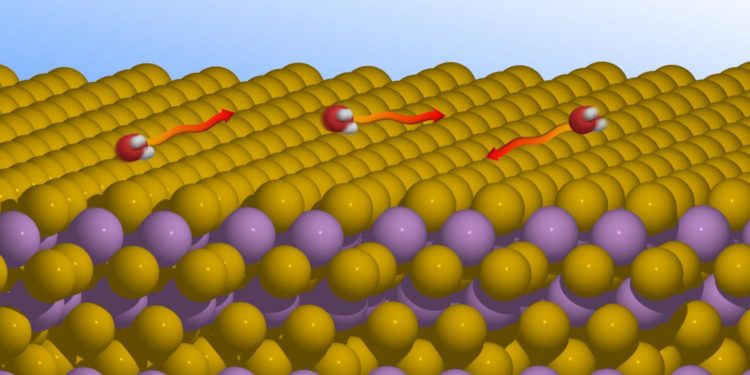
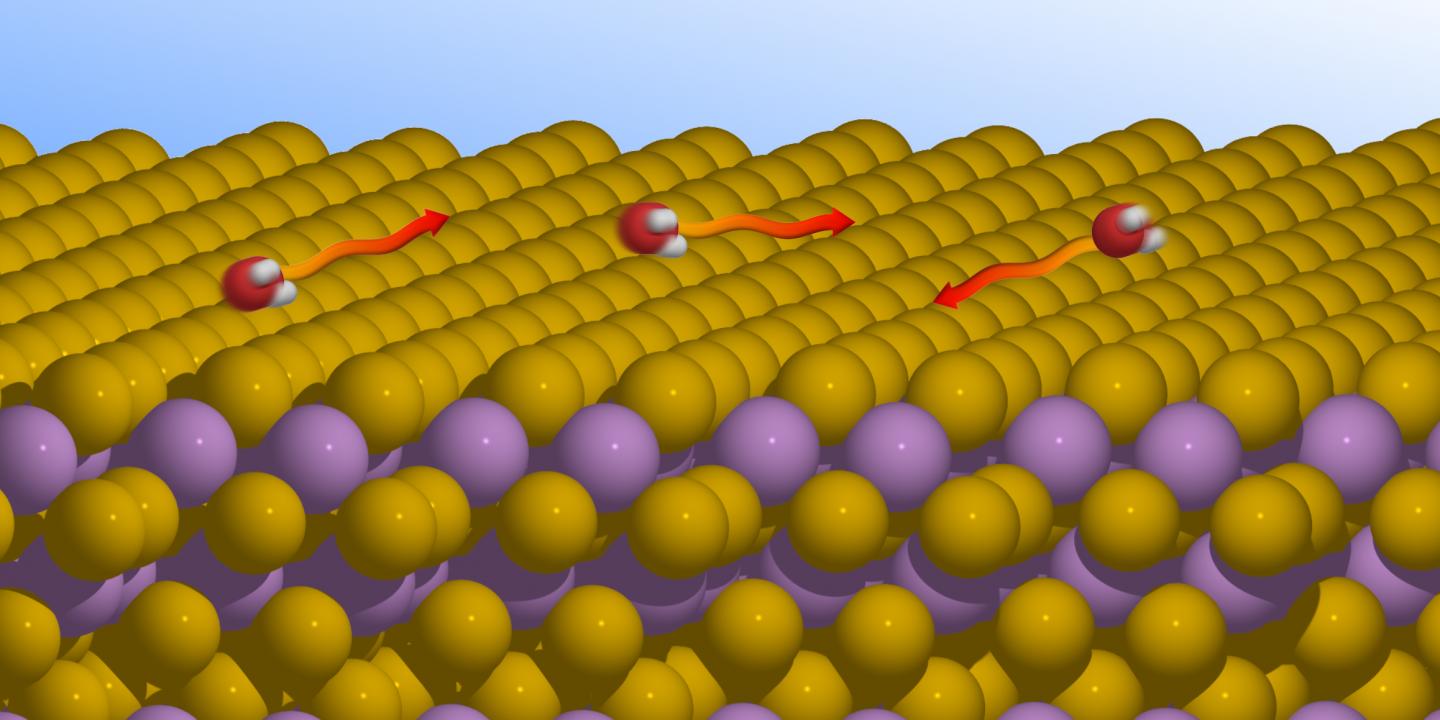
Water is a mysterious substance. Understanding how it behaves at the atomic level is still a challenge for experimental physicists, as light hydrogen and oxygen atoms are difficult to observe using conventional experimental methods. This is especially true for any researcher looking to study the microscopic movements of individual water molecules that run off a surface in a matter of picoseconds. As they report in their paper, entitled ‘Nanoscopic diffusion of water on a topological insulator’, researchers from the Exotic Surfaces working group at TU Graz’s Institute of Experimental Physics joined forces with counterparts from the Cavendish Laboratory at the University of Cambridge , the University of Surrey and Aarhus University. Together, they made significant advances, performing research into the behaviour of water on a material that is currently attracting particular interest: a topological insulator called bismuth telluride. This compound could be used to build quantum computers. Water vapour would be one of the environmental factors to which applications based on bismuth telluride might be exposed during operation.
In the course of their research, the team used a combination of a new experimental method called helium spin-echo spectroscopy and theoretical calculations. Helium spin-echo spectroscopy uses very low-energy helium atoms that allow isolated water molecules to be observed without influencing their motion in the process. The researchers discovered that water molecules behave completely differently on bismuth telluride compared with those on conventional metals. On such metals, attractive interactions between water molecules can be observed, leading to accumulations in the form of films. But the opposite is the case with topological insulators: the water molecules repel one another and remain isolated on the surface.
Bismuth telluride appears to be impervious to water, which is an advantage for applications exposed to typical environmental conditions. Plans are in place for further experiments on similarly structured surfaces, which are intended to clarify whether the movement of water molecules is attributable to specific features of the surface in question.
###
This area of research is part of TU Graz’s Advanced Materials Science Field of Expertise, one of the university’s five strategic research focuses.
Media Contact
Anton Tamtögl
[email protected]
43-316-873-8143
Related Journal Article
http://dx.