Credit: Source: Nature Biotechnology
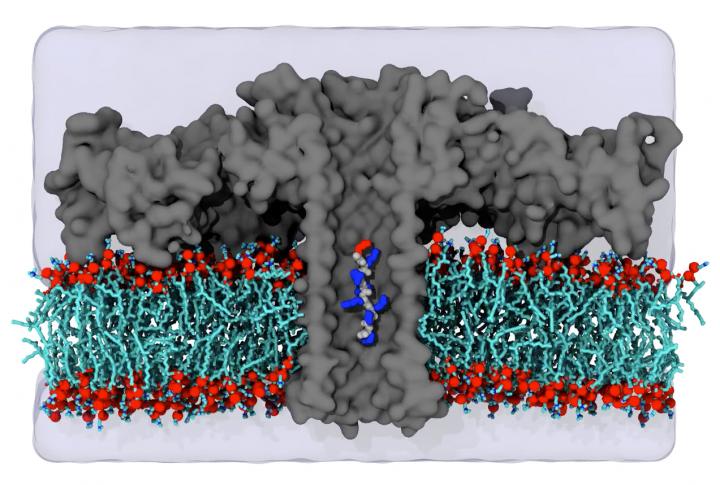
A large part of the work inside cells is done by proteins acting as enzymes, transporters, channels, motors, supporting pillars and signaling devices. Proteins are three-dimensionally folded chains of diverse amino acids in a genetically encoded sequence. Whereas scientists have already succeeded in obtaining sequence information from single DNA strands, a further major challenge in bioanalytics is the direct determination of the amino acid sequence from individual proteins. A team of researchers from the University of Cergy-Pontoise, France, the University of Freiburg and the University of Illinois in the US has now been able to differentiate, for the first time, between individual amino acids in short peptides, i.e. protein fragments, using a tiny pore the size of a nanometer. The scientists have thus laid the foundation for direct sequencing of individual proteins. They recently presented their results in the current issue of the journal Nature Biotechnology.
Because previous techniques, such as mass spectrometry, are not sensitive enough, for instance to accurately determine the protein composition of a single cell, the pore forming protein aerolysin was incorporated into an artificial cell membrane and electrodes were used to pass an ion current through the pore, explains Prof. Dr. Jan C. Behrends from the Institute of Physiology at the Medical Faculty of the University of Freiburg. Several years ago, researchers at the Universities of Freiburg and Cergy had already shown that blockades of this current caused by a molecule entering the pore enabled the very sensitive measurement of its size. On this basis, the team was able to show that the sensitivity of the so-called aerolysin pore is so high that short proteins, i.e. peptides, that only differ in a single amino acid can be distinguished from each other.
Using a particularly high-resolution electrophysiological measurement method developed at the University of Freiburg, the team was even able to differentiate between the amino acids leucine and isoleucine with more than 90 percent reliability. These two amino acids have the same composition, and therefore mass, and differ only in the spatial arrangement of the molecular groups. The differentiation of such so-called structural isomers by means of the aerolysin pore proves that the current signal is not exclusively dependent on the molecular mass, as was previously assumed, thereby showing that the new technology is superior, in principle, to mass spectrometry. The researchers in the US showed in simulations that this high resolution is based on a kind of molecular trap within the pore. This trap immobilizes the peptides for about one hundredth of a second, which is what makes accurate measurement possible. This enabled the recently published study to reliably differentiate eleven of the 20 amino acids involved in the construction of proteins, using the nanopore current signal without additional chemical alterations.
###
The Freiburg investigations were funded by the International Research Training Group Soft Matter Science at the EUCOR Universities of Freiburg, Strasbourg/France, Mulhouse/France and Basel/Switzerland.
Original publication:
Ouldali, H., Sarthak, K., Ensslen, T., Piguet, F., Manivet, P., Pelta, J., Behrends, J.C., Aksimentiev, A., Oukhaled, A. (2019): Electrical recognition of the twenty proteinogenic amino acids using an aerolysin nanopore. In: Nature Biotechnology. DOI: 10.1038/s41587-019-0345-2
Contact:
Institute of Physiology
University of Freiburg
Media Contact
Dr. Jan C. Behrends
[email protected]
49-761-203-5146
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




