Credit: Robyn Roberts et al.
When a plant senses an invading pathogen, it activates a molecular signaling cascade that switch on its defense mechanisms. One such mechanism involves sacrificing host cells to the pathogen. This is a tightly controlled process that involves the work of plant proteins to ensure that the sacrificial cells are only killed if the pathogen is attacking. This process, called the cell death response, ensures that only a few host cells die.
Tomatoes employ this method when they are invaded by a bacterial pathogen known as Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato, which causes speck disease. Scientists understand how the tomato recognizes this pathogen and know many of the plant proteins that are involved in the signaling cascade, but until recently they did not know what linked these two processes, a mystery that has been around for decades.
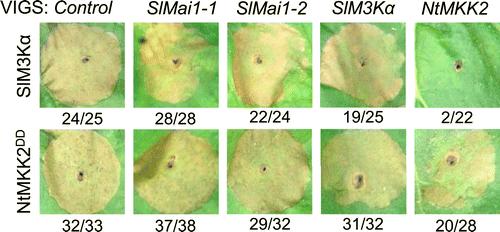
In a recent paper published in Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, scientists introduce a protein, called Mai1, that plays a role in this missing link. They found that when they muted the expression of Mai1, the plants could no longer defend themselves against pathogens through the cell death response. As a result, these plants were more susceptible to bacterial infection.
They also found that Mai1 directly interacts with a protein at the top of the signaling cascade and upregulates its activity, suggesting that Mai1 plays a key role in activating the cascade.
“Our research suggests that Mai1 has a central role in immunity that likely can not be substituted by other proteins,” according to first author Robyn Roberts. “Not only does this work give us better insight into how plants defend themselves on the molecular level, but this work reveals a key protein that is broadly involved in immunity. It is possible that Mai1 could serve as a target for crop improvement in the future.”
This research also showed that the muting of Mai1 stunted the plants, leaving them with brittle leaves and heightened sensitivity to mild stress, including pesticide application. This further shows the importance of Mai1, suggesting that the protein might also be involved in both immunity and plant growth and development.
###
For additional details, read “Mai1 Protein Acts Between Host Recognition of Pathogen Effectors and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling” published in the November issue of Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions.
Media Contact
Ashley Bergman Carlin
[email protected]
651-994-3832
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




