Credit: Osaka University
Most analytical methods in biology require invasive procedures to analyze samples, which leads to irreversible changes or even their destruction. Furthermore, the sensitivity of such approaches often stems from the averaging of signals generated by a large number of cells, making it impossible to study the underlying heterogeneity of responses.
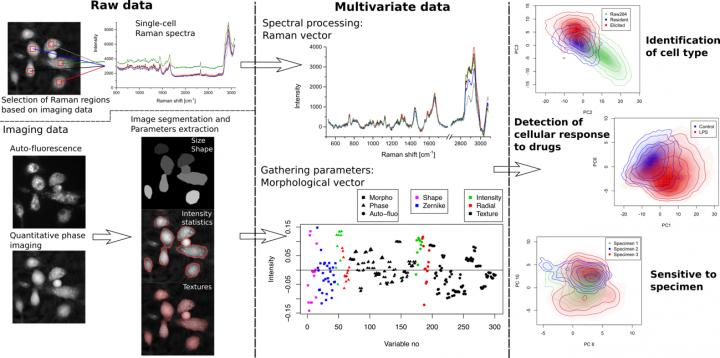
In the medical field, X-ray and MRI imaging are highly useful since they allow diagnosis through non-invasive imaging. Similarly, label-free techniques are becoming increasingly popular in microscopy thanks to their non-invasiveness. Quantitative phase1 microscopy, along with Raman spectroscopy2, are label-free techniques used in this study to extract biomarkers based on cellular morphology and intracellular content. These approaches have been previously used to characterize specimens and identify cells from different origins; however, the measurement of finer features than the cell type with these techniques has proven to be challenging.
Assistant Professor Nicolas Pavillon and Associate Professor Nicholas I. Smith of the Immunology Frontier Research Center (IFReC) at Osaka University developed a label-free multimodal imaging platform that enables the study of cell cultures non-invasively without the need of any contrast agent. The pair of researchers showed how the label-free signals can be employed to create models that can detect the activation state of macrophage cells and distinguish between different cell types even in the case of highly heterogeneous populations of primary cells. “We devised specific statistical tools that allow for the identification of the best methods for detecting responses at the single-cell level, and show how these models can also identify different specimens, even within identical experimental conditions, allowing for the detection of outlier behaviors,” says Associate Professor Smith.
The findings of this study show that a non-invasive optical approach, which enables the study of live samples without requiring contrast agents, can also achieve high sensitivity at the single-cell level. “In particular,” says Assistant Professor Pavillon, “our results show that this method can identify different cell sub-types and their molecular changes during the immune response, as well as outlier behaviors between specimens.”
###
The article, “Immune cell type, cell activation, and single cell heterogeneity revealed by label-free optical methods” was published in Scientific Reports at DOI: https:/
Terminology:
1. Quantitative phase microscopy
An optical imaging method that enables dynamic measurement of live cell cultures, providing quantitative information about the local optical density of cells, related to the refractive index.
2. Raman spectroscopy
An optical method that measures the vibrational modes of molecules, enabling their identification through spectral features. Applied to living cells, it is an indirect non-invasive method to assess their molecular content.
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and now has expanded to one of Japan’s leading comprehensive universities. The University has now embarked on open research revolution from a position as Japan’s most innovative university and among the most innovative institutions in the world according to Reuters 2015 Top 100 Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017. The university’s ability to innovate from the stage of fundamental research through the creation of useful technology with economic impact stems from its broad disciplinary spectrum.
Website: https:/
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
81-661-055-886
Original Source
http://biophotonics.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




