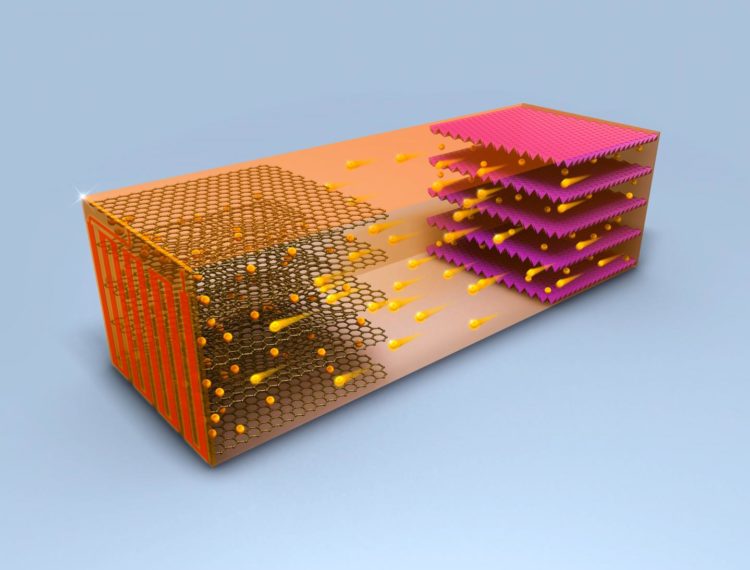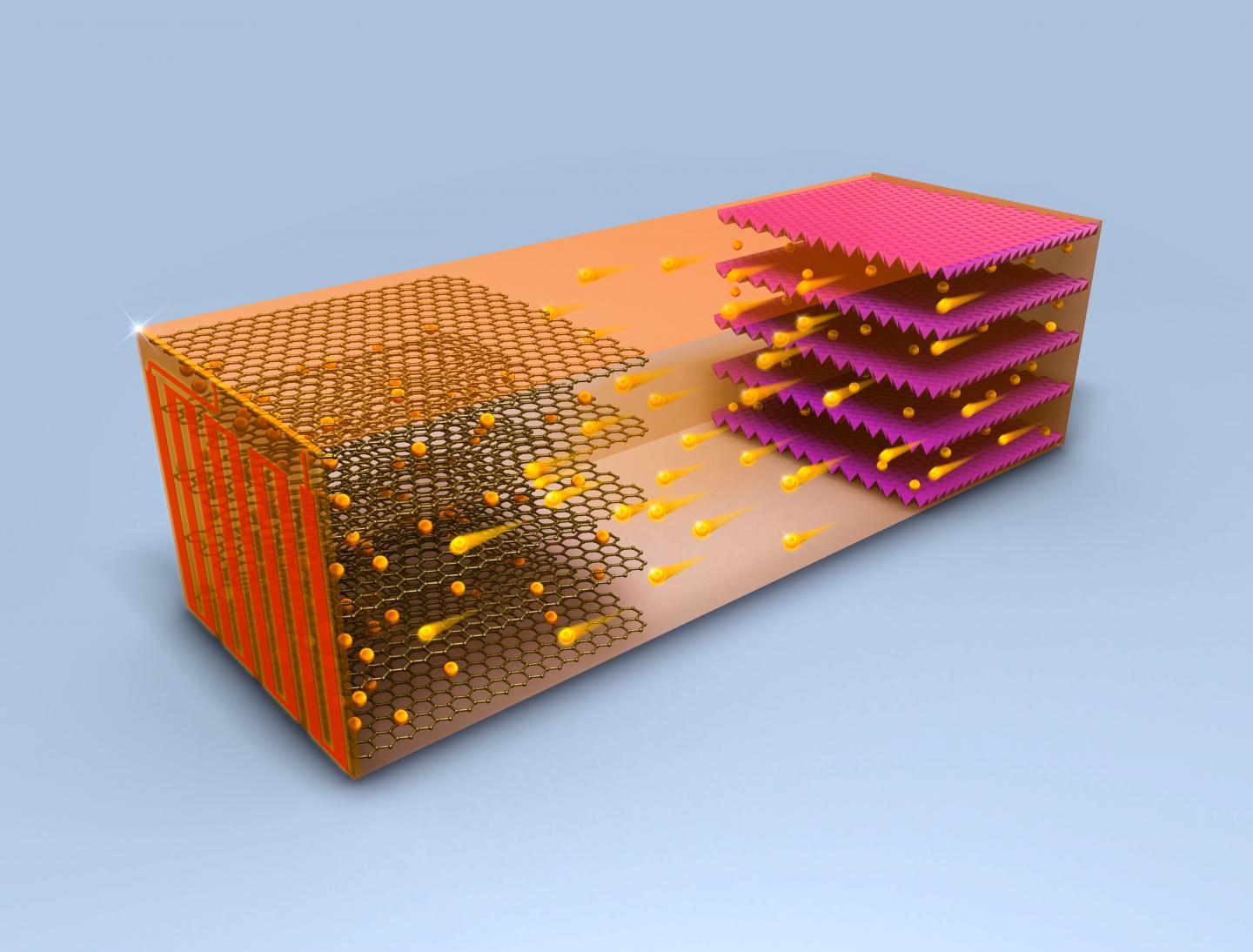
Credit: Chao-Yang Wang Lab, Penn State
Electric vehicle owners may soon be able to pull into a fueling station, plug their car in, go to the restroom, get a cup of coffee and in 10 minutes, drive out with a fully charged battery, according to a team of engineers.
“We demonstrated that we can charge an electrical vehicle in ten minutes for a 200 to 300 mile range,” said Chao-Yang Wang, William E. Diefenderfer Chair of mechanical engineering, professor of chemical engineering and professor of materials science and engineering, and director of the Electrochemical Engine Center at Penn State. “And we can do this maintaining 2,500 charging cycles, or the equivalent of half a million miles of travel.”
Lithium-ion batteries degrade when rapidly charged at ambient temperatures under 50 degrees Fahrenheit because, rather than the lithium ions smoothly being inserted into the carbon anodes, the lithium deposits in spikes on the anode surface. This lithium plating reduces cell capacity, but also can cause electrical spikes and unsafe battery conditions.
Batteries heated above the lithium plating threshold, whether by external or internal heating, will not exhibit lithium plating.
The researchers had previously developed their battery to charge at 50 degrees F in 15 minutes. Charging at higher temperatures would be more efficient, but long periods of high heat also degrade the batteries.
“Fast charging is the key to enabling wide spread introduction of electric vehicles,” said Wang.
Wang and his team realized that if the batteries could heat up to 140 degrees F for only 10 minutes and then rapidly cool to ambient temperatures, lithium spikes would not form and heat degradation of the battery would also not occur. They report their results in today’s (Oct 30) issue of Joule.
“Taking this battery to the extreme of 60 degrees Celsius (140 degrees F) is forbidden in the battery arena,” said Wang. “It is too high and considered a danger to the materials and would shorten battery life drastically.”
The rapid cooling of the battery would be accomplished using the cooling system designed into the car, explained Wang. The large difference from 140 degrees to about 75 degrees F will also help increase the speed of cooling.
“The 10-minute trend is for the future and is essential for adoption of electric vehicles because it solves the range anxiety problem,” said Wang.
Adding to the reduction of range anxiety — fear of running out of power with no way or time to recharge — will be, according to Reuters, the establishment of 2,800 charging stations across the U.S., funded by the more than $2 billion penalty paid by Volkswagen after admitting to diesel emissions cheating. These charging stations will be in 500 locations.
The self-heating battery uses a thin nickel foil with one end attached to the negative terminal and the other extending outside the cell to create a third terminal. A temperature sensor attached to a switch causes electrons to flow through the nickel foil to complete the circuit. This rapidly heats up the nickel foil through resistance heating and warms the inside of the battery.
###
Also working on this project from Penn State are Xiao-Guang Yang, assistant research professor; Teng Liu, graduate student; Yue Gao, post-doctoral scholar; Shanhai Ge, assistant researcher professor; Yongjun Leng, assistant research professor; and Donghai Wang, professor, all in the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
The U.S. Department of Energy supported this work.
Media Contact
A’ndrea Elyse Messer
[email protected]
814-865-5689