Researchers open a new avenue to quantum computing with a breakthrough experiment: a large-scale quantum processor made entirely of light
Credit: Shota Yokoyama 2019
An international team of scientists from Australia, Japan and the United States has produced a prototype of a large-scale quantum processor made of laser light.
Based on a design ten years in the making, the processor has built-in scalability that allows the number of quantum components – made out of light – to scale to extreme numbers. The research was published in Science today.
Quantum computers promise fast solutions to hard problems, but to do this they require a large number of quantum components and must be relatively error free. Current quantum processors are still small and prone to errors. This new design provides an alternative solution, using light, to reach the scale required to eventually outperform classical computers on important problems.
“While today’s quantum processors are impressive, it isn’t clear if the current designs can be scaled up to extremely large sizes,” notes Dr Nicolas Menicucci, Chief Investigator at the Centre for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology (CQC2T) at RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia.
“Our approach starts with extreme scalability – built in from the very beginning – because the processor, called a cluster state, is made out of light.”
Using light as a quantum processor
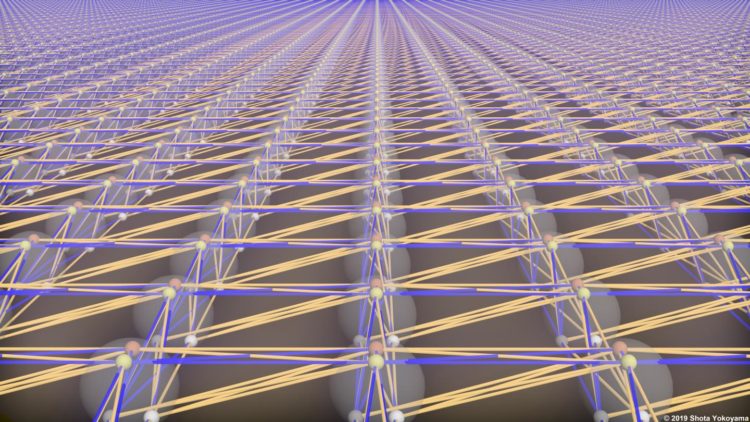
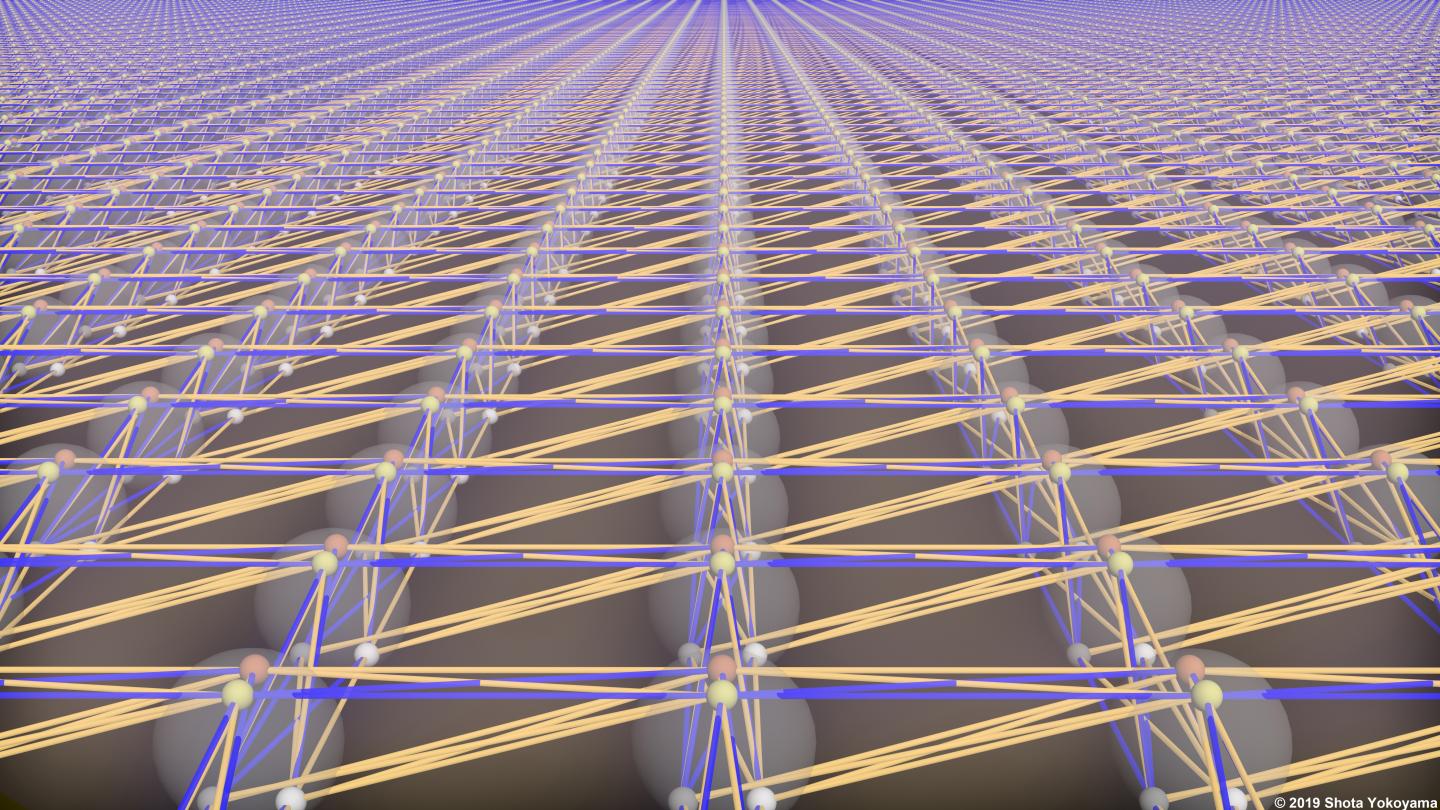
A cluster state is a large collection of entangled quantum components that performs quantum computations when measured in a particular way.
“To be useful for real-world problems, a cluster state must be both large enough and have the right entanglement structure. In the two decades since they were proposed, all previous demonstrations of cluster states have failed on one or both of these counts,” says Dr Menicucci. “Ours is the first ever to succeed at both.”
To make the cluster state, specially designed crystals convert ordinary laser light into a type of quantum light called squeezed light, which is then weaved into a cluster state by a network of mirrors, beamsplitters and optical fibres.
The team’s design allows for a relatively small experiment to generate an immense two-dimensional cluster state with scalability built in. Although the levels of squeezing – a measure of quality – are currently too low for solving practical problems, the design is compatible with approaches to achieve state-of-the-art squeezing levels.
The team says their achievement opens up new possibilities for quantum computing with light.
“In this work, for the first time in any system, we have made a large-scale cluster state whose structure enables universal quantum computation.” Says Dr Hidehiro Yonezawa, Chief Investigator, CQC2T at UNSW Canberra. “Our experiment demonstrates that this design is feasible – and scalable.”
###
The experiment was an international effort, with the design developed through collaboration by Dr Menicucci at RMIT, Dr Rafael Alexander from the University of New Mexico and UNSW Canberra researchers Dr Hidehiro Yonezawa and Dr Shota Yokoyama. A team of experimentalists at the University of Tokyo, led by Professor Akira Furusawa, performed the ground-breaking experiment.
Media Contact
Nicolas Menicucci
[email protected]
61-422-679-084
Related Journal Article
http://dx.