Credit: SUTD
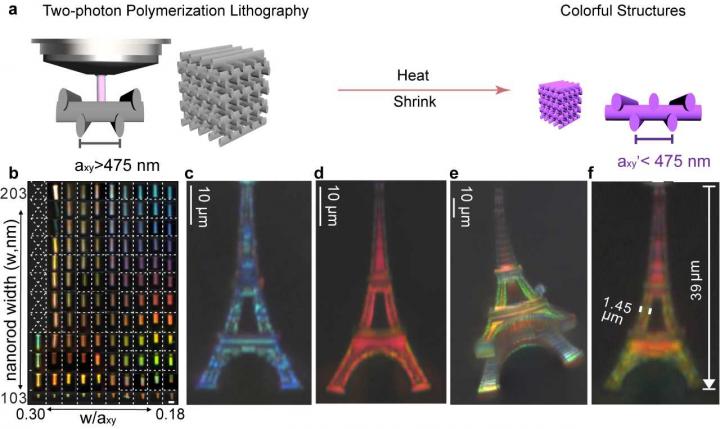
In a report recently published in Nature Communications, a research group led by Associate Professor Joel Yang from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) printed probably the smallest colorful 3D model of the Eiffel Tower. Impressively, no pigments or inks were used. Instead, the 3D-printed model of the Eiffel Tower, measuring less than half the width of a human hair at 39 micrometers, exhibits multiple colors due to the manner in which light interacts with the nanostructures that hold up the model. The 3D models are made of a finely printed mesh of transparent polymer, forming photonic crystals. These mostly hollow designs remarkably shrink down in size by about 5 times when heated to produce a wide range of colors.
Prof Yang said: “There is great excitement in the research community to further develop sustainable sources of colors that aren’t extracted from animals or plants. What if the products that we make could derive its color by nano-texturing of the material that it itself is made of? Certain butterflies and beetles have evolved to do this, perhaps we could learn to do this too.” Compared with pigments and dyes relying on chemical composition, structural colors are high-resolution, permanent, and eco-friendly.
In nature, the coloration of some butterflies, Pachyrhynchus weevils, and many chameleons are notable examples of natural organisms employing photonic crystals to produce colorful patterns. Photonic crystal structures reflect vivid colors with hues dependent on their lattice constants. To reflect vivid colors, the lattice constants of a photonic crystal must be sufficiently small. For example, the lattice constant is only ~280 nm on butterfly wings giving a blue hue of color. Due to the limitation on current 3D printing resolution, it is a challenge to print arbitrary colors and shapes in all three dimensions at this microscopic length scale.
To achieve the required dimension of lattice constants comparable to the butterfly scales, researchers from Prof Yang’s group employed a “coloring-by-shrinking” method which introduces an additive heating step to shrink the photonic crystals printed using a commercial two-photon polymerization lithography system, i.e. the Nanoscribe GmbH Photonic Professional GT. Prof Yang added: “The challenge is in shrinking structures at these nanoscopic dimensions without having them coalesce into a blob. By patterning larger structures, and shrinking them later, we produced structures that could not have been printed directly with standard methods.” Indeed, the repeating lines of the woodpile structures were shrunk down to 280 nm, almost 2x smaller than the machine specifications. As a bonus side-effect of shrinking, the refractive index of the cross-linked polymer increased in the heating process, which further benefits the generation of colors.
The full-color Eiffel Tower demonstrated the ability to print arbitrary and complex 3D color objects at the microscale level using the “coloring-by-shrinking” method. With the freedom of designing 3D photonic crystals that are shrunk to fit specific colors, this technology would be broadly applicable to achieve compact optical components and integrated 3D photonic circuity operating in the visible region.
###
Media Contact
Melissa Koh
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




