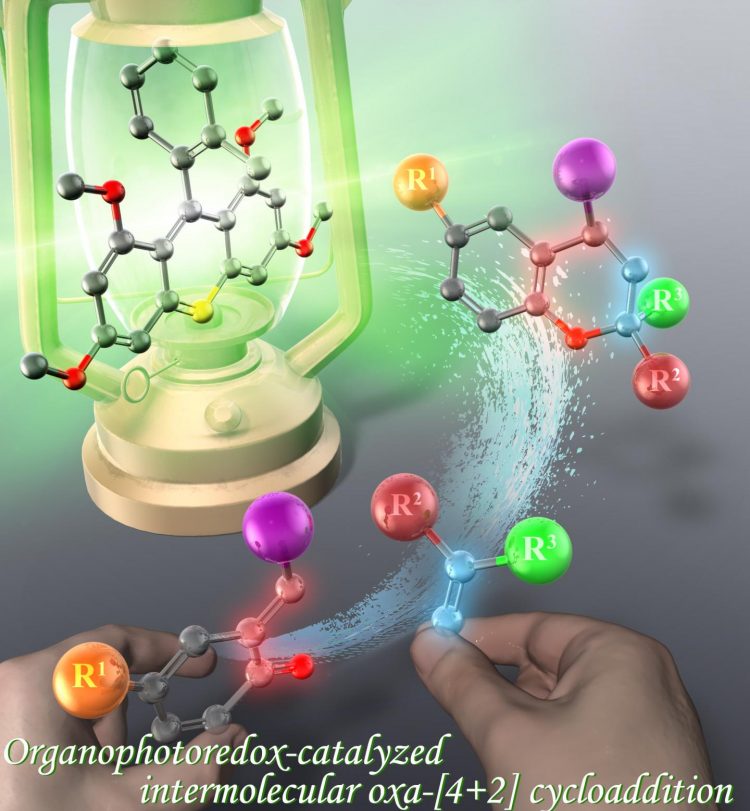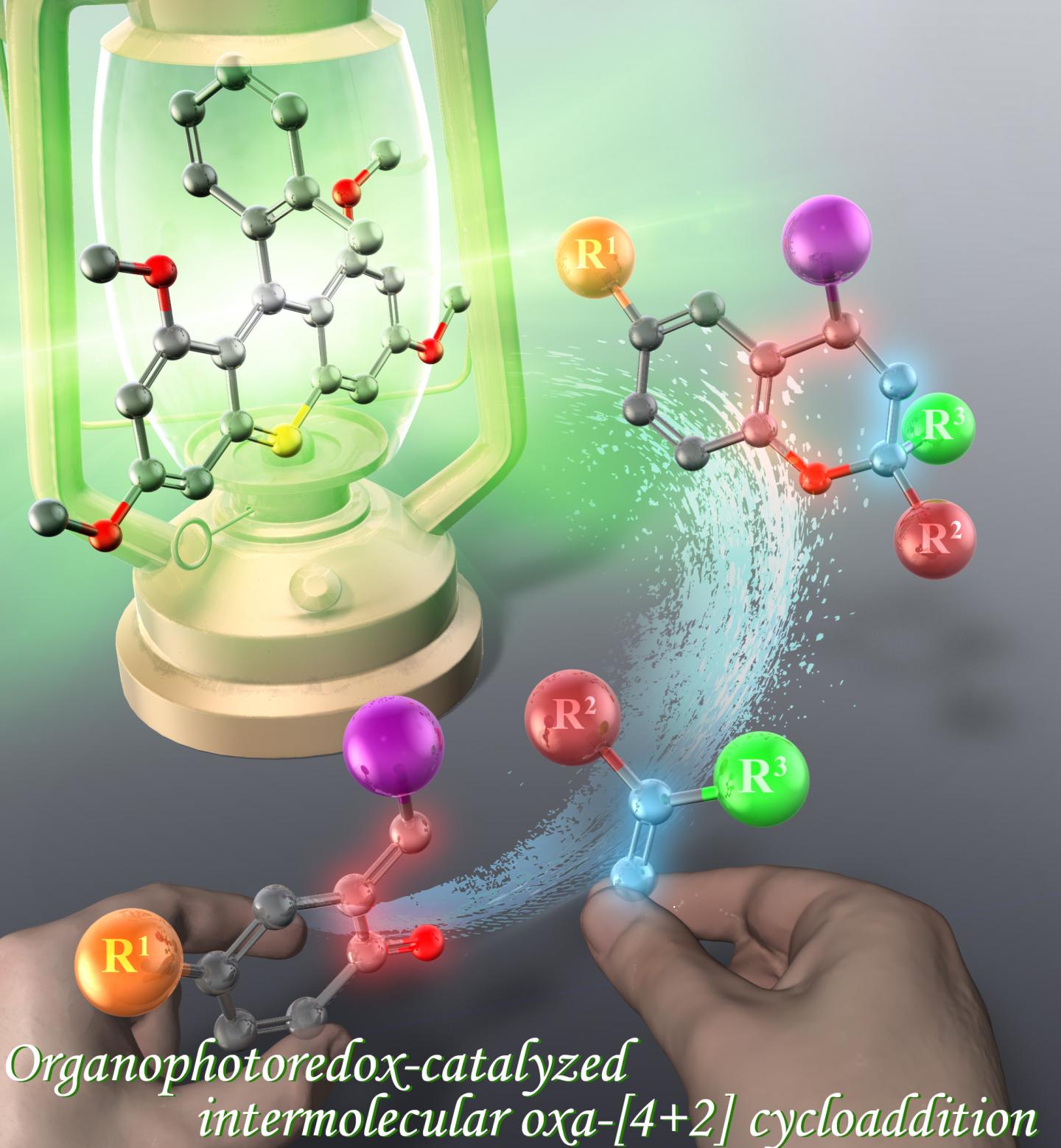
Credit: Yokohama National University
Every biological reaction is a chemical reaction. The exchange of carbon dioxide for oxygen in our lungs and blood cells, for example, is caused by molecules releasing chemicals and reforming with new ones. The uncontrolled replication of cancerous cells is the result of broken chemical compounds miscommunicating. The appeal of developing improved drugs to promote helpful reactions or prevent harmful ones has driven organic chemists to better understand how to synthetically create these molecules and reactions in the laboratory.
A team from Yokohama National University in Japan has taken a step toward making this wish a reality with their latest study, published on July 19 in the Journal of Organic Chemistry.
The researchers developed oxygen heterocycles, which are ring structures consisting of atoms from two or more elements. These compounds make up all of the nucleic acids in a person’s genetic code. Another version of heterocycles, containing nitrogen, are in more than half of the pharmaceuticals produced in the United States. Oxygen heterocycles in particular contain at least one oxygen atom. They have a variety of uses, including in medications to treat cancer and heart failure.
“We focused on oxygen heterocycles, which have attracted significant interest due to the relevance of their structural units in medicinal chemistry and materials science,” said Yujiro Hoshino, the study’s corresponding author and a research fellow in the Graduate School of Environment and Information Sciences at Yokohama National University.
Professor Kiyoshi Honda, another corresponding author of the study from the Graduate School of Environment and Information Sciences added that their “goal was to develop cost-effective and milder synthetic routes to create oxygen heterocycles.”
Traditionally, oxygen heterocycles are made by applying high temperatures to two molecules. The process consumes time and energy, and doesn’t produce a significant number of heterocycles. Honda and Hoshino’s team focused on a method involving the design of photo-sensitive carbon-based salts. They added the salts to two types of compounds, which form a ring once they react, and irradiated the combination with green light.
“This reaction was particularly attractive because it can hold a high number of atoms and provides efficient access to various synthetically useful oxygen-containing heterocycles,” Hoshino said. “This reaction can also be carried out in mild experimental conditions – room temperature and visible light.”
The process produced a high yield of oxygen heterocycles. According to Hoshino, the successful reaction was due to a structure on the salts called an electron-donating group. Electrons are excited by green light, and the salts extract an electron from the compound to react with the other compound components.
Next, the researchers plan to turn to different colored light to drive different reactions. They’re specifically interested in establishing a red-light reaction, which is more difficult, according to Hoshino. Red light is a longer wavelength and lower frequency than green light, meaning it’s closer infrared light than visible light on the spectrum chart. Red-light reactions could drive a higher production of heterocycles, but it requires more accuracy and efficiency.
“Our next goal is to expand the scope of reaction,” Hoshino said. “We envision the expansion of the use of various visible-light-driven reactions in the future, and we plan to continue contributing to it.”
###
Kenta Tanaka, Daichi Omata, Yosuke Asada and Kiyoshi Honda, all of the Graduate School of Environment and Information Sciences at Yokohama National University, also contributed.
Yokohama National University (YNU or Yokokoku) is a Japanese national university founded in 1949. YNU provides students with a practical education utilizing the wide expertise of its faculty and facilitates engagement with the global community. YNU’s strength in the academic research of practical application sciences leads to high-impact publications and contributes to international scientific research and the global society. For more information, please see: https:/
Media Contact
Akiko Tsumura
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.