A newly discovered property of cadmium could lead to the most accurate clock ever
Credit: (c) 2019 Katori et al.
Researchers experimentally determined a property of cadmium called the magic wavelength which is considered essential for the development of the most accurate clocks ever envisaged. The researchers hope this may permit simple and robust atomic clocks so accurate they could be used to improve our understanding of current theories and even test for new physics.
What time do you make it? How about now? Time is constantly changing but it is not changing constantly. It sounds confusing, but since Einstein’s time we’ve known that time progresses at different rates depending on where you are. This is mainly due to the effect of gravity, the stronger gravity is in your vicinity the slower time progresses relative to where gravity is weaker. To us this difference is imperceptible, but highly accurate atomic clocks can measure it.
These imperceptible differences in the rate of the passage of time are far from trivial however. Accurate measurements of time can actually help researchers measure other corresponding quantities which relate to how time flows at a specific location. For example given the way increased gravitational strength alters the passage of time, the density of material below your feet could be accurately measured with a sufficiently accurate clock. And this kind of information could be useful to those who study volcanoes, plate tectonics and earthquakes.
However, to measure time at the accuracies required for such purposes is an immensely complex challenge. State of the art atomic clocks based on the vibration of atoms such as caesium, for example, operate with an uncertainty – the opposite of accuracy – in the region of 1×10-16 or to 16 decimal places. This is extremely accurate for the measurement of distance and is thus used in current global positioning system (GPS) technology. But researchers strive for even greater accuracy, and one kind of clock may be able to offer uncertainties as low as 1×10-19 or to 19 decimal places. The optical lattice clock promises to offer such accuracy.
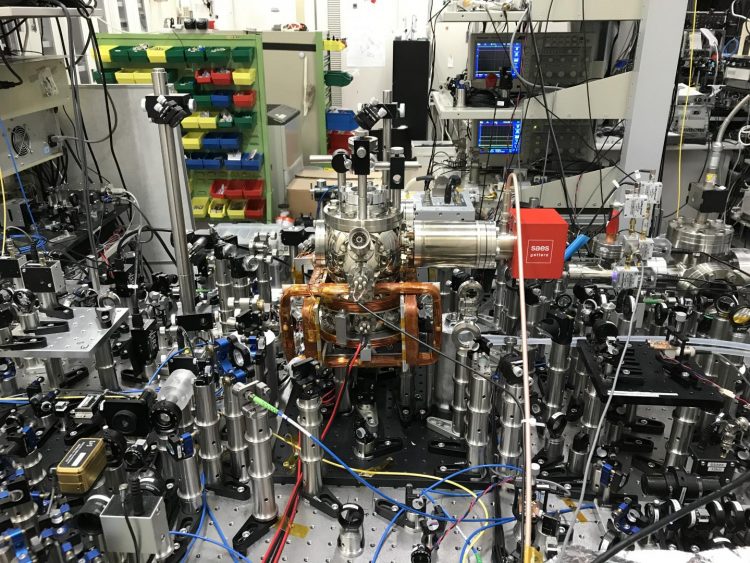
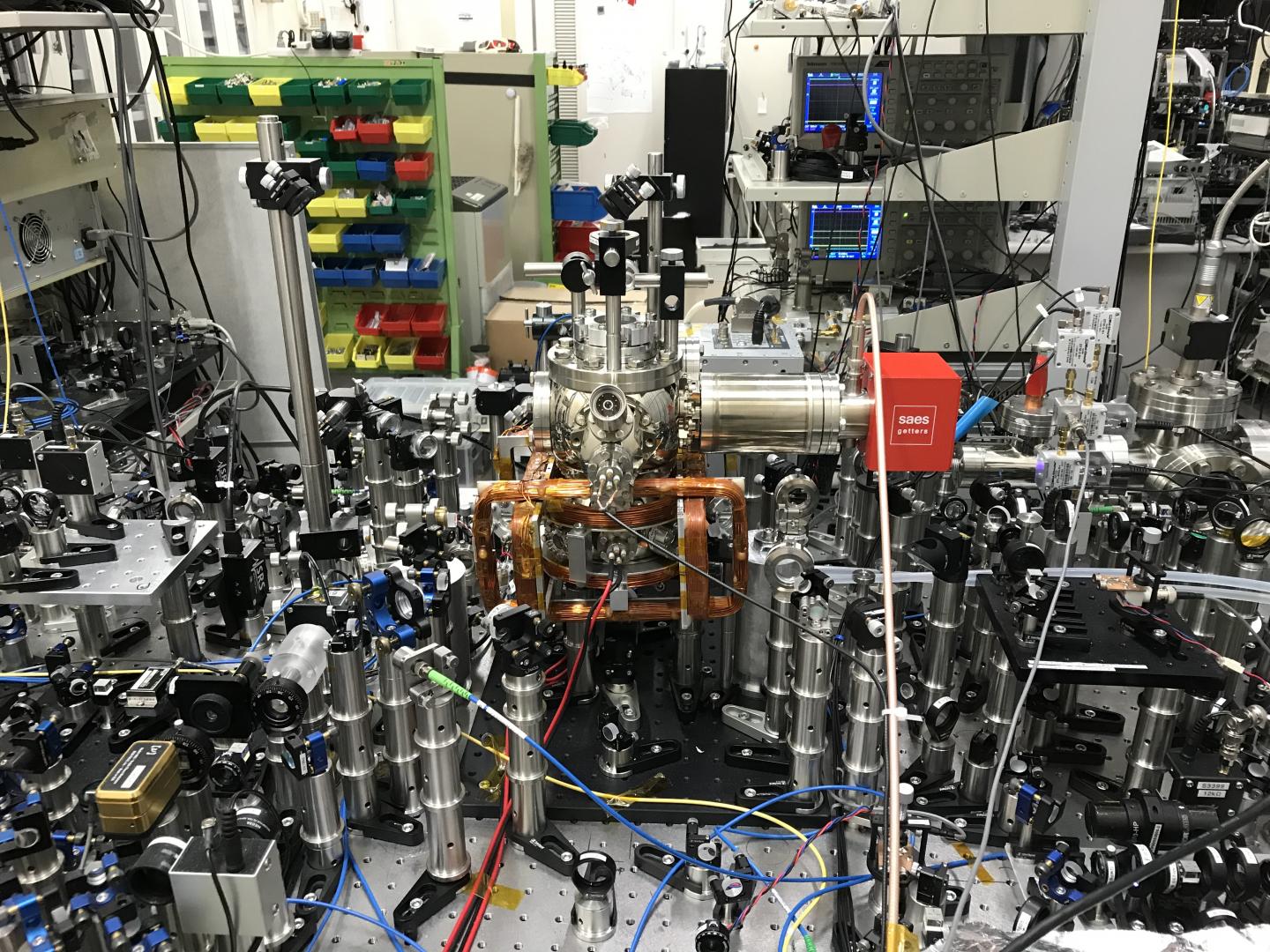
First proposed by Professor Hidetoshi Katori from the Department of Applied Physics in 2001, the idea is to trap a large number of atoms in a lattice of lasers. With many atoms trapped their vibrations can be measured simultaneously, which greatly improves the accuracy of the measurement of time. Isotopes of Cadmium are ideal as they have some properties which help to reduce noise in this kind of quantum system. But in order to create a clock based on this principle there are several hurdles to overcome, and researchers have just jumped one.
“We experimentally determined the so-called ‘magic wavelength’ for cadmium which is one of the essential parameters to operate the optical lattice clock,” said research scientist Atsushi Yamaguchi from RIKEN. “In a lattice clock the optical lattice created by interference patterns of laser light, the wavelength of which is related to the atoms the lattice needs to hold. The optimal or ‘magic’ wavelength to construct a lattice around Cadmium isotopes is around 419.88 nanometers, which is almost exactly the value of 420.10 nanometers we originally predicted.”
One important feature of Cadmium isotopes which makes them ideal for lattice clocks is that they are more robust to changes to their environment than many other atoms and isotopes. An application researchers aim for is the ability to make measurements in different locations with the same device, meaning it must be relatively portable, so it helps to be robust. With the theory in place, researchers now wish to evaluate the performance of such a clock.
“Careful and detailed evaluation is required so scientists in different fields can make use of this high precision instrument,” explained Katori. “Such a device will afford us the chance to study and maybe one day challenge established ideas in cosmology such as general relativity and perhaps even the fundamental constants of nature.”
###
Journal article
A. Yamaguchi, M. S. Safronova, K. Gibble, and H. Katori. Narrow-line Cooling and Determination of Magic Wavelength of Cd. Physical Review Letters. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.123.113201
https:/
This work is supported by JST ERATO Grant No. JPMJER1002 10102832 (Japan), by JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Specially Promoted Research Grant No. JP16H06284, by JST-Mirai Program Grant Number JPMJMI18A1, Japan, by the National Science Foundation (KG), and by the USA Office of Naval Research, Grant No. N00014-17-1-2252 (MSS).
Related links
Department of Applied Physics
http://www.
Graduate School of Engineering
https:/
Quantum Metrology Laboratory, RIKEN
http://www.
Space-Time Engineering Research Team, RIKEN
http://www.
Research Contact
Professor Hidetoshi Katori
Department of Applied Physics, Graduate School of Engineering,
The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8656, JAPAN
Tel: +81-03-5841-1790 (PR office) – Email: [email protected]
Press Contact
Mr. Rohan Mehra
Division for Strategic Public Relations, The University of Tokyo
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8654, JAPAN
Tel: +81-3-5841-0876 – Email: [email protected]
About the University of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo is Japan’s leading university and one of the world’s top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world’s top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 4,000 international students. Find out more at https:/
Media Contact
Rohan Mehra
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.