Credit: Dr. Michal Klivický et al., Bentham Science Publishers
The content of active ingredients in pharmaceuticals is mostly assessed by reversed-phase HPLC. Nevertheless, the excipients in case of suppositories are usually not soluble in commonly used mobile phases solvents (methanol, acetonitrile). That is the reason why a labour intensive and tedious sample pre-treatment is necessary, in order to remove the matrix from the sample.
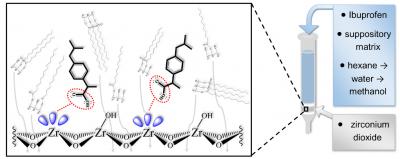
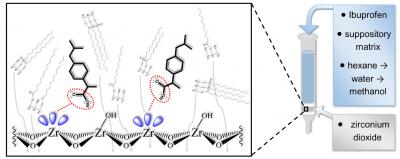
The presence of Lewis acid sites on the surface of metal oxides is responsible for strong interactions with Lewis bases due to ligand exchange. Although this phenomenon is not desirable in chromatography, these interactions might be employed in a sample pre-treatment based on solid phase extraction.
We newly tested this approach on ibuprofen, which is a favourable drug for the management of pain and fever. Due to the inability of infants to swallow tablets, ibuprofen is often administered in the form of suppositories and oral suspensions in paediatric clinics.
Using the zirconium dioxide as the extraction material, efficient trapping of ibuprofen from a hydrophobic suppository matrix was enabled. It demonstrated the pivotal role of interactions between the carboxylic moiety of ibuprofen and the Lewis acid sites on the zirconia surface. The excellent extraction of ibuprofen was also obtained from the hydrophilic environment, which was tested on an oral suspension. Titania as a second tested material was not capable of trapping ibuprofen from pharmaceuticals efficiently due to its weaker ligand exchange properties.
We have described the first successful utilization of the ligand exchange process on zirconia in the extraction of ibuprofen from hydrophobic as well as hydrophilic media using two different dosages forms. The procedure can be applied in cases where excipients or a drug are not soluble in commonly used HPLC solvents and/or if co-eluting peaks from matrix are an issue. The recoveries of ibuprofen were 95 % and 94 % from suppositories and the oral suspension, respectively.
###
For more information about the article, please visit http://benthamscience.com/journals/current-analytical-chemistry/article/135981/
Reference: Klivický, M.; et al (2016). Solid-Phase Extraction of Ibuprofen from Pharmaceuticals via Ligand Exchange Using Zirconium Dioxide. Curr Anal Chem., DOI: 10.2174/1573411012666151022194146
Media Contact
Faizan ul Haq
[email protected]
@BenthamScienceP
http://benthamscience.com/
via scienmag.com